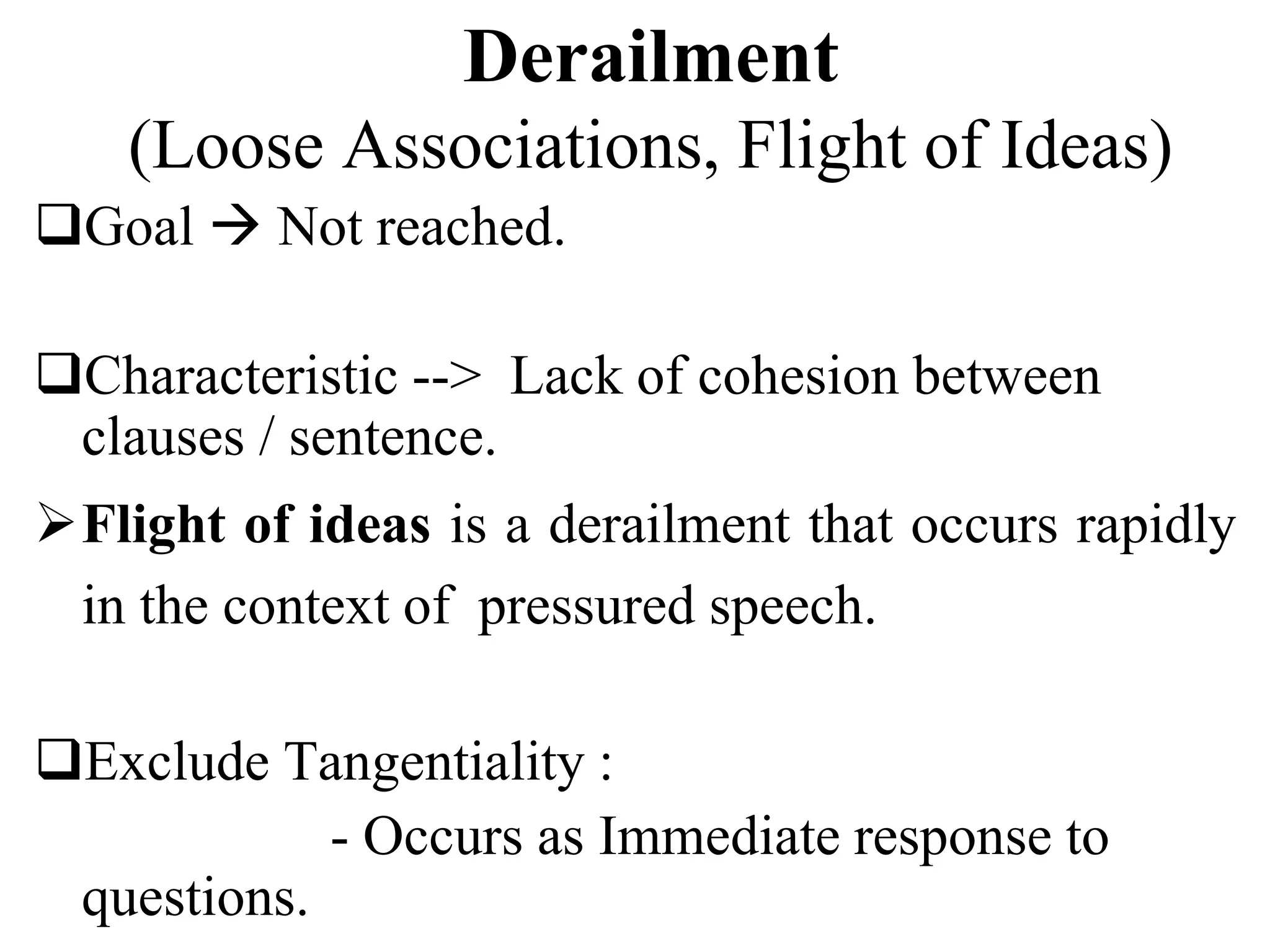
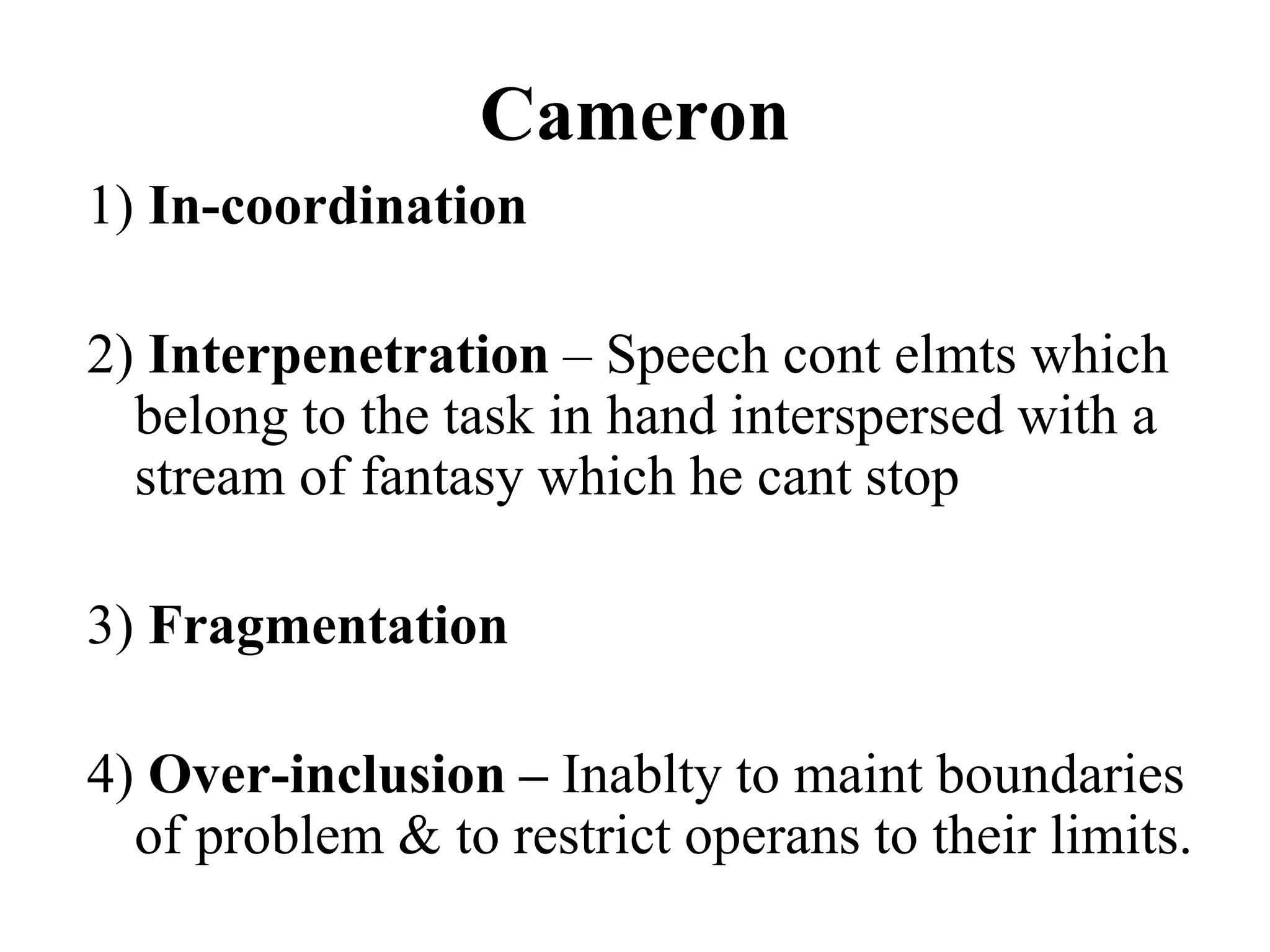
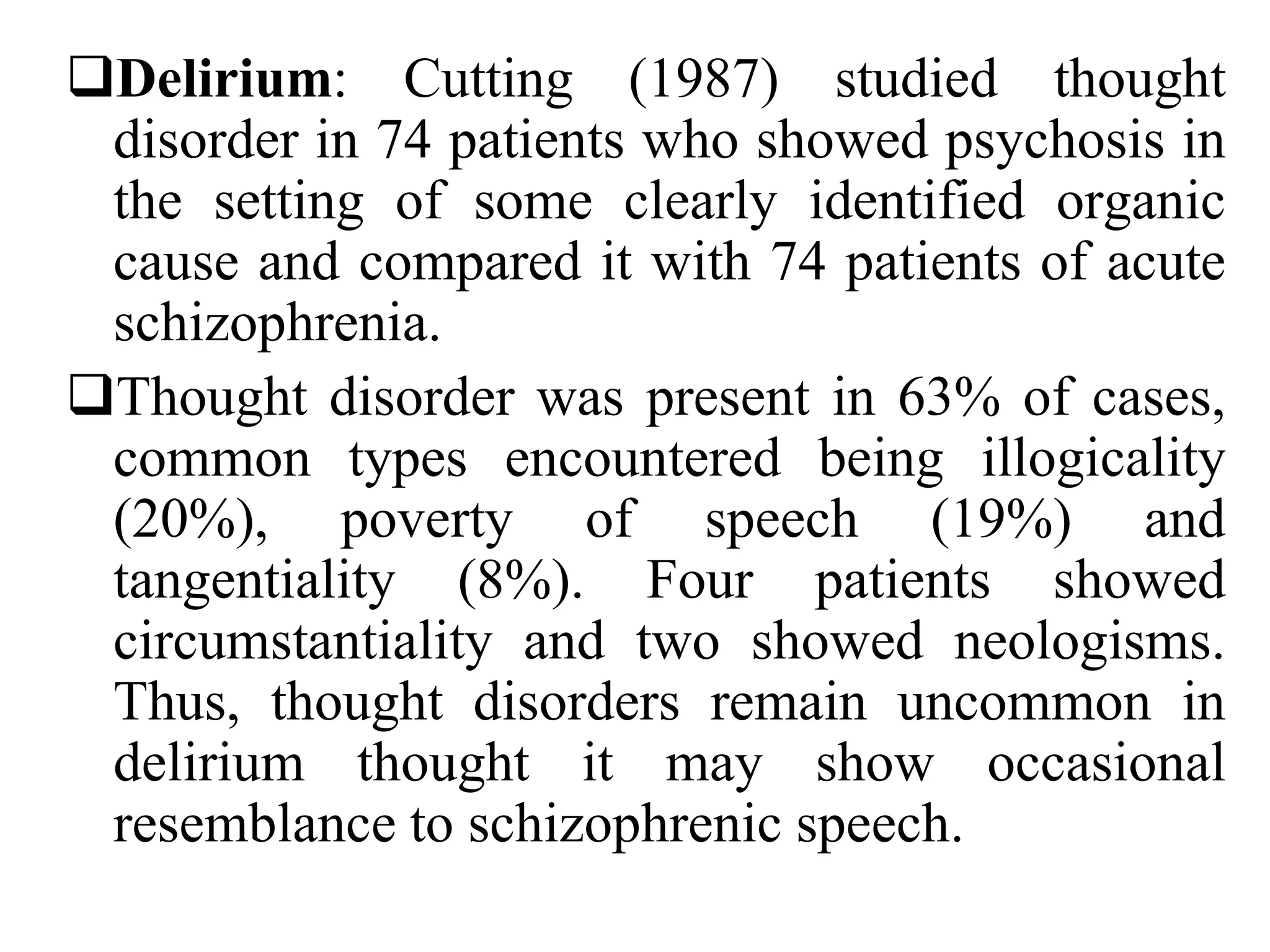
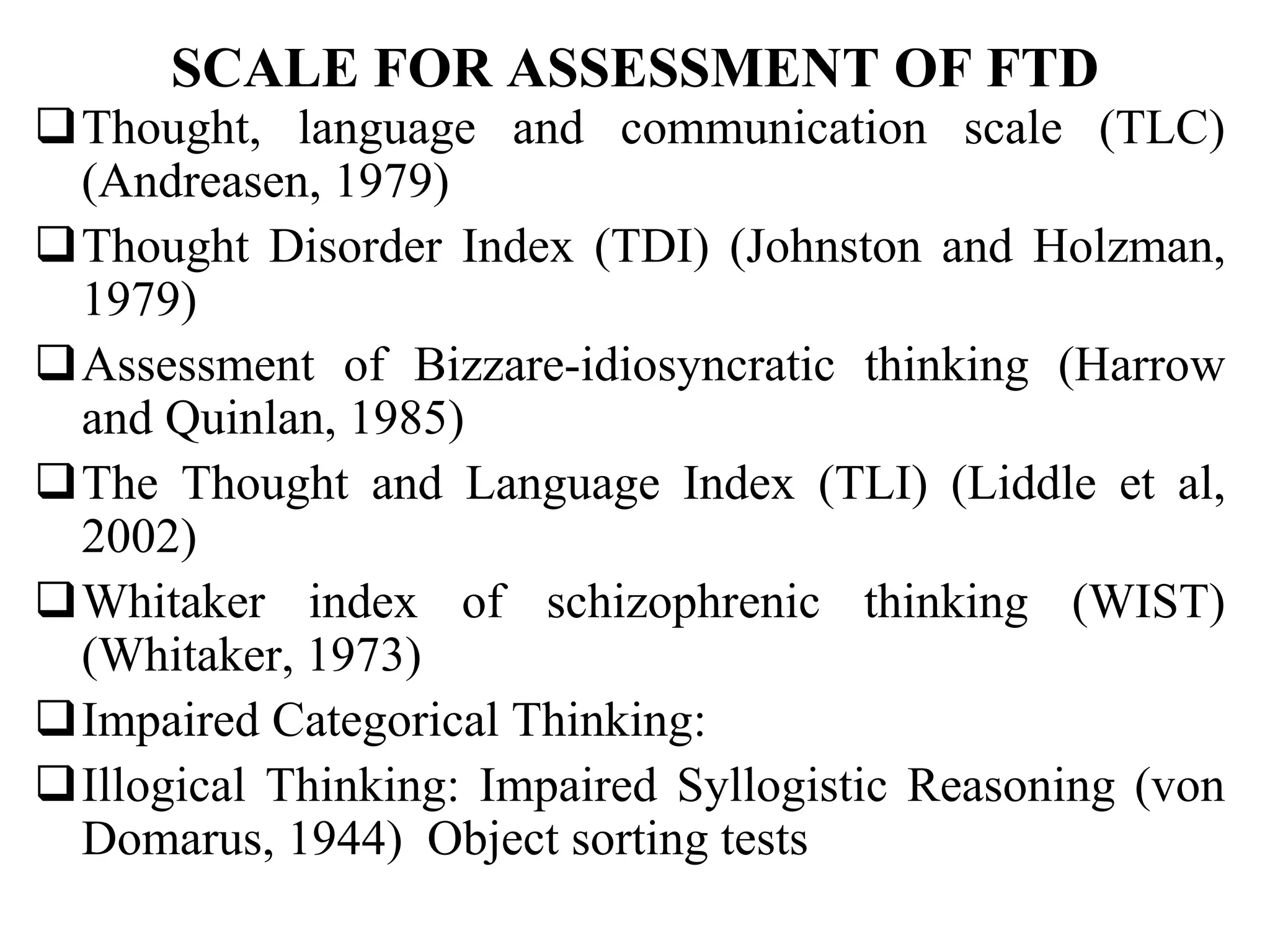
The document discusses formal thought disorders, particularly in relation to schizophrenia, detailing various symptoms and categories, such as positive and negative forms of thought disorder. It outlines communication disorders like poverty of speech and tangentiality, as well as the structural features of thought processes, drawing on historical perspectives and various researchers' contributions. The conclusion emphasizes the complexity of thought disorders across psychiatric conditions and the ongoing challenges in understanding their etiology and terminology.