Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times






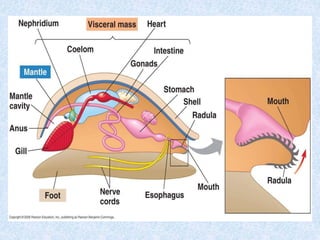
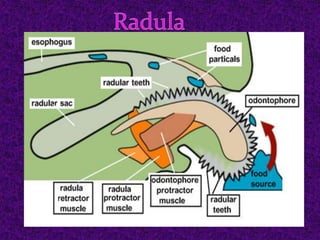

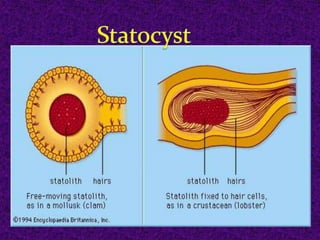


The document provides an introduction and overview of the general characteristics of molluscs. It states that molluscs are soft-bodied animals that inhabit all habitats except air, have existed since the early Cambrian period, and are the second largest phylum of animals. The general characteristics described include having a triploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical body divisible into head, mantle, foot, and visceral mass, with shells sometimes present either internally or externally. Digestion and respiration occur through various organs like the radula, gills, lungs, and the circulatory system utilizes haemocyanin.










