Embed presentation
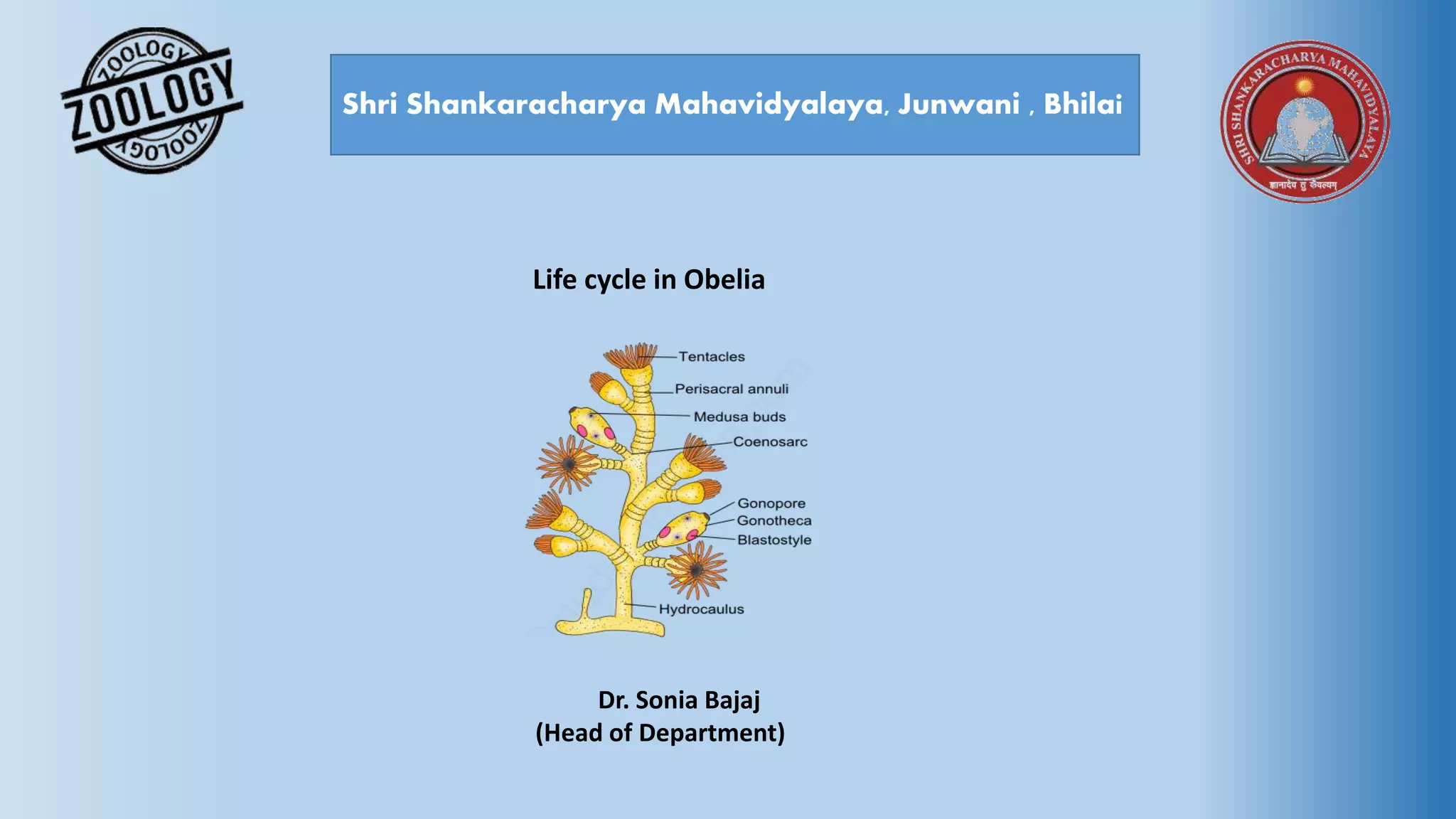
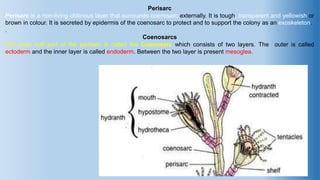
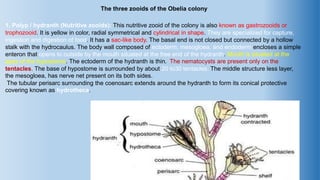
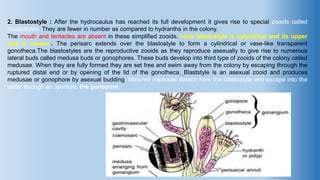
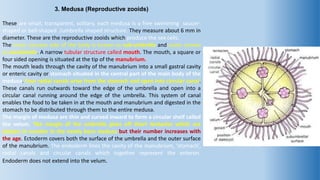
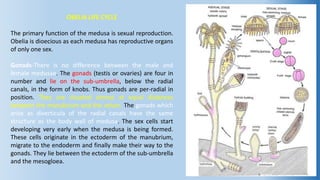
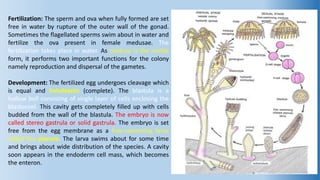
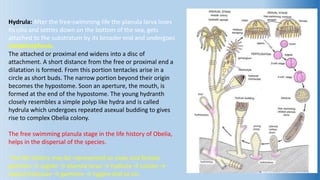

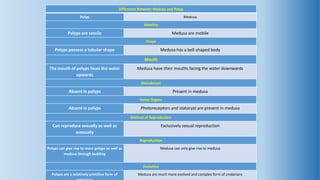

The document provides an in-depth overview of the life cycle, morphology, and reproductive strategies of Obelia, a marine colonial coelenterate. It explains the different forms of zooids including hydranth, blastostyle, and medusa, highlighting their roles in nutrition, reproduction, and structure. Additionally, it discusses alternation of generations between the polyp and medusa forms, and compares their characteristics such as mobility, shape, and reproduction methods.











