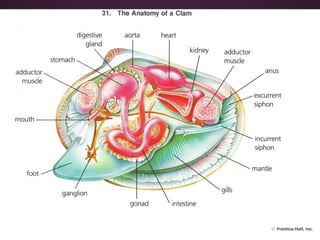
This document summarizes the phylum Mollusca. It describes their soft-bodied structure, shells, body zones, digestive and excretory systems. It also discusses their nervous systems, circulation, reproduction, locomotion, and the three main types - gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods. Key details are provided on anatomy and examples of common mollusks within each type. Their ecological importance as food and environmental indicators is also noted.