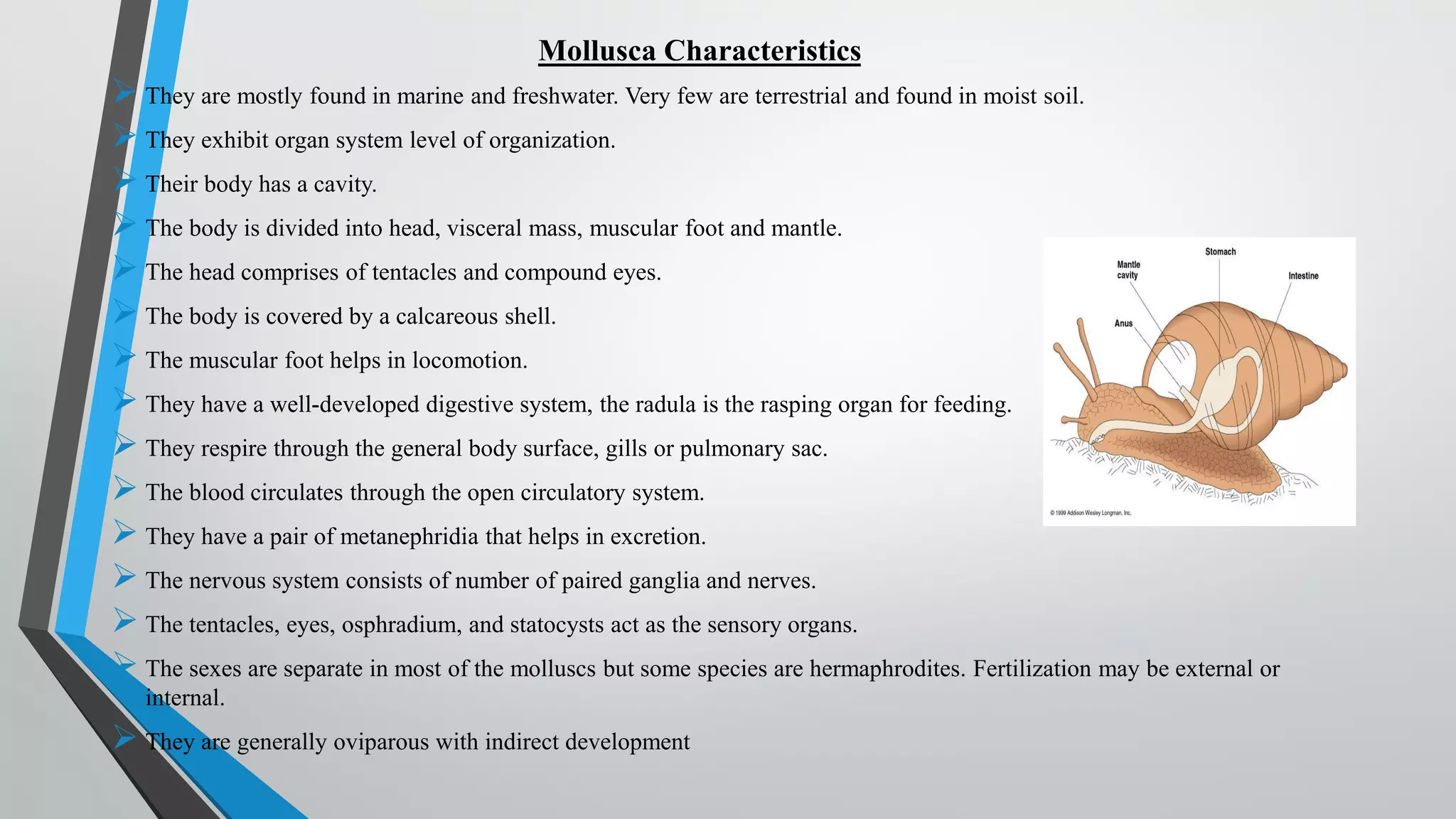
The document discusses the general characteristics and classification of the phylum Mollusca, highlighting their primarily aquatic habitats, organ system organization, and distinct bodily features such as tentacles and a muscular foot. It details various classes of mollusks, including Aplacophora, Monoplacophora, Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Scaphopoda, Pelecypoda, and Cephalopoda, along with their specific traits and examples. Mollusks exhibit diverse reproductive methods and systems, with most being oviparous and exhibiting indirect development.