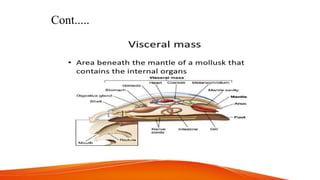
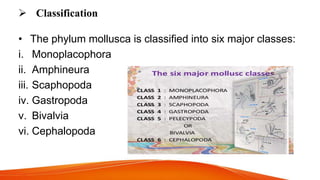
Phylum Mollusca is the second largest invertebrate phylum, comprising approximately 85,000 extant species, with members characterized by a soft body, bilateral symmetry, and typically a calcareous shell. The phylum is divided into six major classes, including Gastropoda and Cephalopoda, each exhibiting distinct body structures and adaptations. Molluscs possess a variety of traits such as a well-developed digestive system, open circulatory system (except cephalopods), and diverse reproductive strategies.