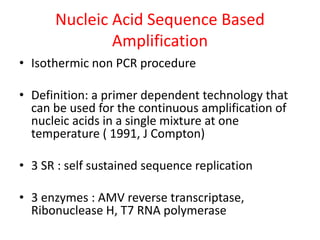
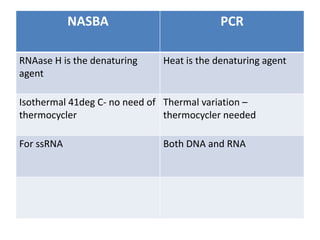
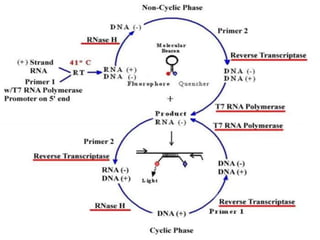
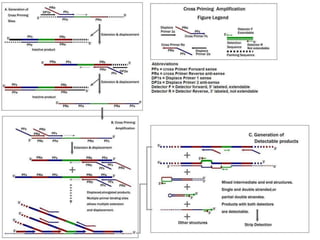
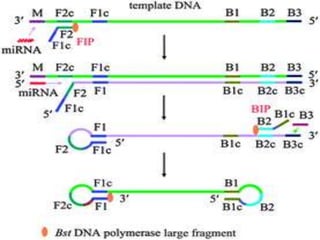
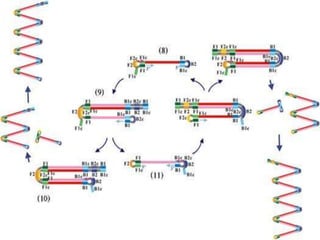
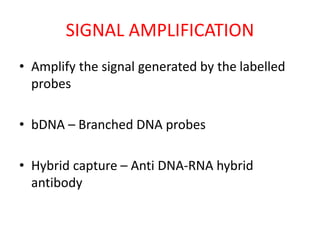
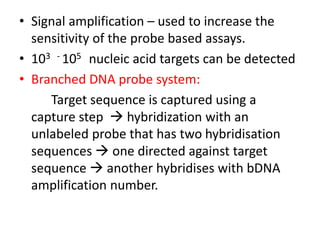
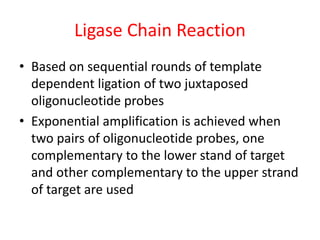
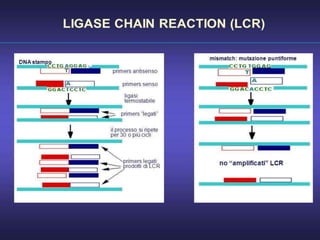
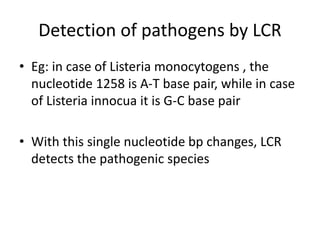
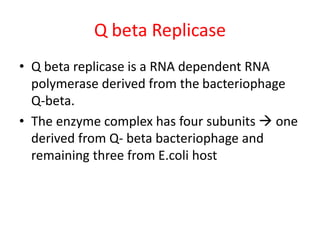
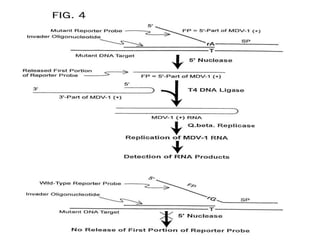
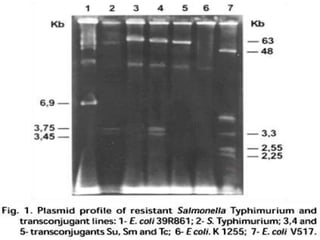
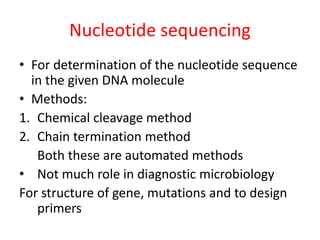
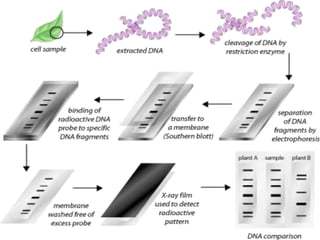
This document discusses various molecular techniques used for diagnosis of infectious diseases. It notes that molecular methods are most important for pathogens that are difficult to detect by conventional methods, like Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Chlamydia trachomatis. Several amplification techniques are described, including PCR, NASBA, TBA, SDA, and LAMP. These allow detection of pathogens in clinical samples and identification of antibiotic resistance. The document also discusses probe-based methods like hybrid capture, signal amplification techniques like branched DNA, and other methods like plasmid profiling, nucleotide sequencing, and RFLP for microbial classification and epidemiological analysis.