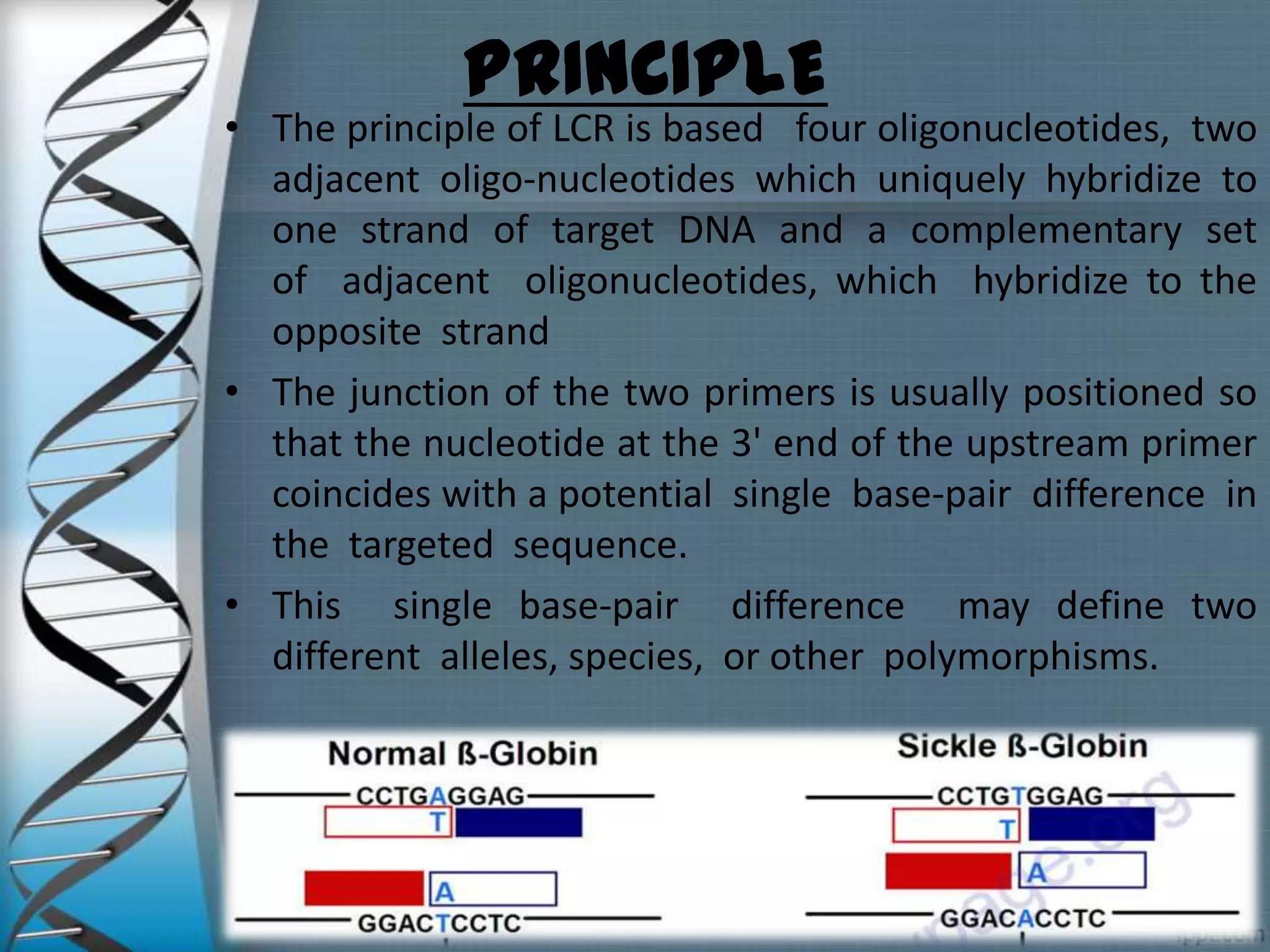
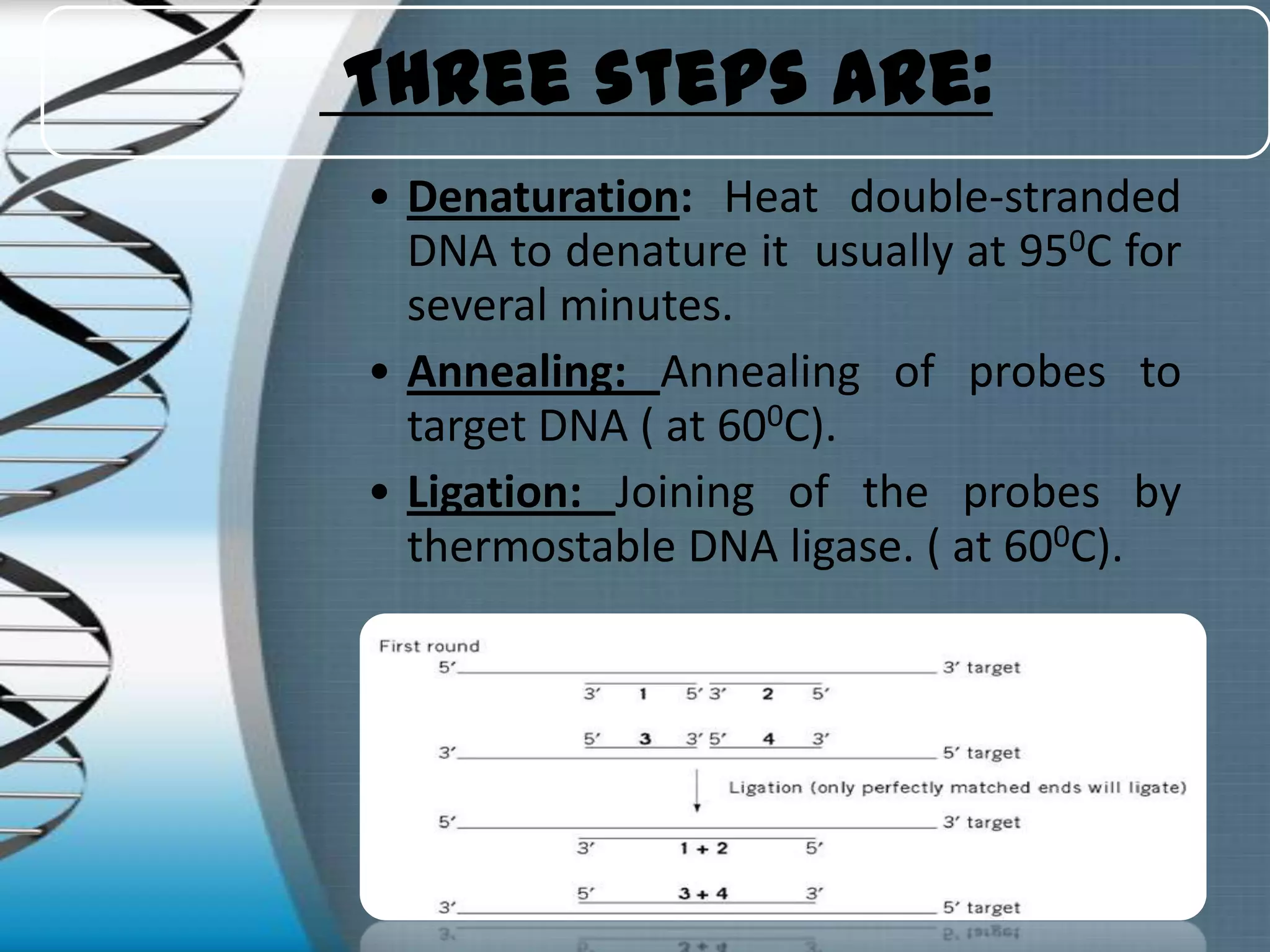
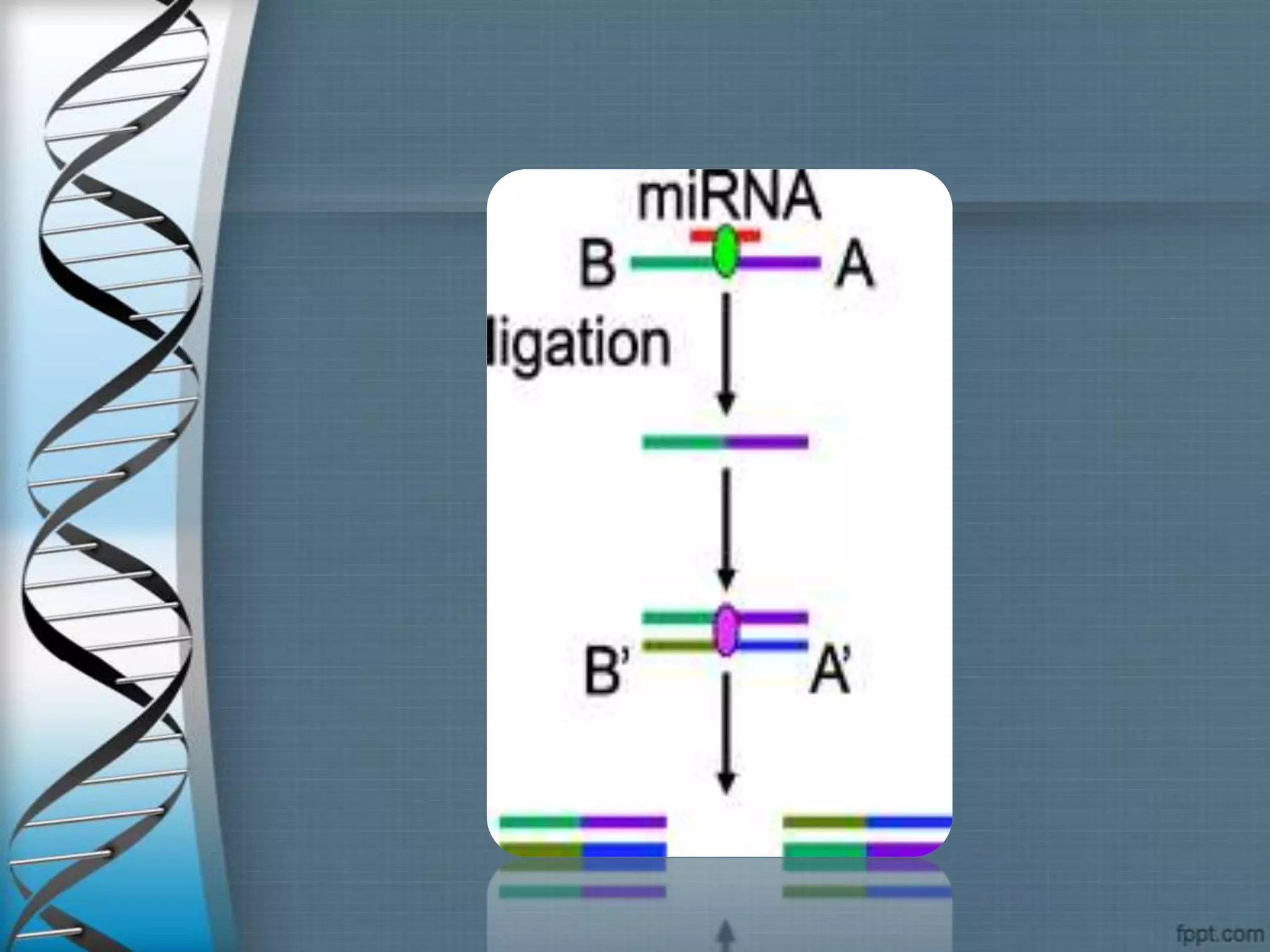
The document summarizes the ligase chain reaction (LCR) technique. LCR amplifies DNA sequences using four probes and ligase and polymerase enzymes instead of amplifying DNA through nucleotide polymerization like PCR. It can detect single nucleotide polymorphisms. The process involves denaturing the DNA, annealing probes to the target sequence, and ligating the probes if they match, repeating for exponential amplification. Products are detected through gel electrophoresis or non-radioactive methods. LCR has applications in infectious disease detection, genotyping and mutation analysis.