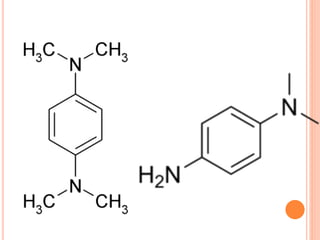
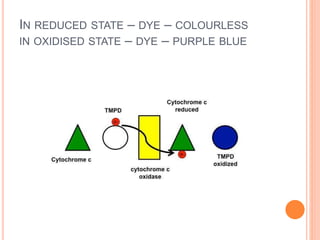
The document describes the oxidase test, which is used to identify bacteria. It works by detecting cytochrome c, an iron-containing protein in the respiratory chain, which causes an oxidase reagent to turn purple in oxidase-positive bacteria within 5-10 seconds. The document outlines several methods for performing the test, such as using filter paper or commercial strips soaked in reagents like tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine. It lists both oxidase-positive and -negative bacteria and notes the test is useful for bacterial classification. Modifications to the standard method are presented to more rapidly and accurately detect weakly oxidase-positive organisms.





















![ It was possible to quantitate the terminal oxidase(s)
reaction using bacterial resting-cell suspensions
and demonstrate the usefulness of this reaction for
taxonomic purposes. Resting-cell suspensions of
physiologically diverse bacteria were examined for
their capabilities of oxidizing N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-
p-phenylenediamine (TMPD) using a manometric
assay. For organisms having this capability, it was
possible to calculate the conventional TMPD
oxidase Q(O2) value (microliters of O2 consumed
per hour per milligram [dry weight]). All cultures
were grown heterotrophically at 30 C, under
identical nutritional conditions, and were harvested
at the late-logarithmic growth phase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oxidasetest-150427105521-conversion-gate01/85/Biochemical-reactions-Microbe-identification-26-320.jpg)





