Mu phage
- 1. Life cycle integration, significance &transposition of integrons 06/02/2021 MU Phage 1 Presented by: M.Adeel Akram M.Sajjad Presented to: Sir Mohsin
- 2. Introduction • Integrons are genetic elements that contain the site specific recombination system able to integrate express and exchange specific DNA elements called gene cassettes. • These integrons are not considered as a mobile elements because they have lack function for the mobility. • Integrons are consists of promotors an attachment site(attI) and a gene(intI) for integrase that encode site specific recombination. • Integrase is viral enzyme that help in integration of bacterial and viral genome. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 2
- 3. Introduction • An attC sequence is present on the ends of the cassettes that’s enable it to the integrate at the attI site. • attC is 59 bp sequence that is recognized by the integrase enzyme. Transposition • Ability of the integrons to change its position on the chromosomes called its transposition. Significance • They are able to capture, integrate & express gene cassettes. • Help in the dissemination of the antibiotic resistance in bacteria (particularly in gram negative). 06/02/2021 MU Phage 3
- 4. Viruses of Bacteria (MU phage) Replicate by transposition 06/02/2021 MU Phage 4
- 5. Introduction to MU phage • Phage Mu is also known as 'bacteriophage Mu. • Since it infects the members of enterobacteria, it is also called enterobacteria phage Mu. • It belongs to the family Myoviridae and dsDNA viruses. • It is a temperate and transposable phage which causes transposition of genes at the time of its multiplication cycle. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 5
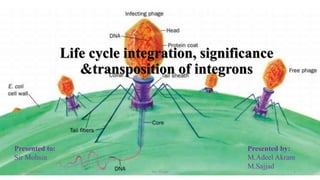
- 6. Structure of Mu Phage • As we know the basic structure of the bacteriophage, that is comprised of head, neck and tail. • The structure of Mu phage is also divided into three parts i.e. head neck and tail. Head • It is the terminal part of the Mu phage which carries the viral genome and surrounds by a protein layer refers as Capsid. • The head of Mu phage is having icosahedral symmetry. • The shape is like spheroid. • The diameter is 54 nm. • Capsid is the layer which surrounds the hexagonal head. The capsid of Mu phage is composed of about 152 smaller protein subunits, known as “Capsomeres”. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 6
- 7. Structure of Mu Phage Neck • It is the middle portion of the Mu phage, acts as the joining element which joins the two components i.e. Head and tail. Tail • It is long, thick and contractile because of the presence of cross bands. • The size of the tail is 183 X 16-20nm. • Sheath is the covering of the contractile tail, which is composed of stacked rings. At the time of contraction, the sheath becomes shorter and thicker. And the length of the sheath during contraction is up to 60-90nm. • Tails fibers are thin and thread-like structures which are attached to the large base plate. There are six long terminal fibres. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 7
- 8. Genetic map of Mu Phage • Mu phage consists of a ds-DNA which is linear, • The genome of Mu phage consists of 37,611 base pairs. • The guanine and cytosine content is 35%. • Genome consists of some unusual base pairs(hydroxy methyl uracil) and terminally redundant sequences. • Mu phage genome encodes 55 genes which perform different functions in its life cycle. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 8
- 9. Mu-Phage cycle • MU phage complete its life cycle in several stages Attachment • The virion fibers attach to the host cell surface lipopolysaccharides (LPS) thereby initiating infection. DNA ejaculation • Upon binding to the host cell surface, the baseplate changes its conformation and triggers sheath contraction, driving the rigid internal tail tube through the cell envelope leading to viral genome entry. Circulation • The N protein, which is present in the virion, is ejected with, and binds to the viral DNA in order to circularize it. The DNA ends are thus protected from host nucleases. Integration • There must be some early transcription giving rise to at least the Repc and Ner repressors and to the DDE recombinase A (MuA) which performs the integration. Flanking bacterial sequences are cut away from the viral genome prior to integration. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 9
- 10. Mu-Phage cycle Latency-replication switch • The ratio of Repc and Ner repressors determines if the phage enters latency or lytic cycle (replication). Repc represses the early promoter thereby establishing latency. • Ner represses Repc expression thereby promoting early genes expression leading to the onset of viral replication. Replicative transposition • When the repressor Repc is inactivated, both the DDE recombinase A (MuA) and the target DNA activator B (MuB) are expressed. • MuA is part of the transpososome complex which performs recombination between the viral genome ends and the host DNA. • This viral-host DNA structure is resolved by target-primed replication leading to two copies of the viral genome. This process is called replicative transposition. The selection of the transposition sites is performed by the MuB. • Successive rounds of replicative transposition can lead up to about 100 copies of the viral genome. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 10
- 11. Mu-Phage cycle Modification of viral DNA • Late transcription allows the expression of the adenine modification enzyme which modifies the adenines in the viral DNA in order to make it resistant to the host restriction enzymes. The new viral particles that will be formed will thus be protected. Assembly • Structural genes are also expressed in the late phase leading to the assembly of empty capsids, fibers and tails. DNA packaging/excision • The bacterial DNA is cut 50-150 bp on the left of the integrated Mu genome to initiate packaging and a second cut occurs once the phage head has been filled. • some bacterial DNA on the right side of the Mu genome is also taken and packaged with the viral genome. • Since each Mu genome is packaged from a different site in the bacterial genome, the host DNA on Mu ends is unique in every different phage head. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 11
- 12. Mu-Phage cycle 06/02/2021 MU Phage 12
- 13. Mu-Phage cycle Lysis • The newly synthesized virion are released by lysis. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 13
- 14. 06/02/2021 MU Phage 14