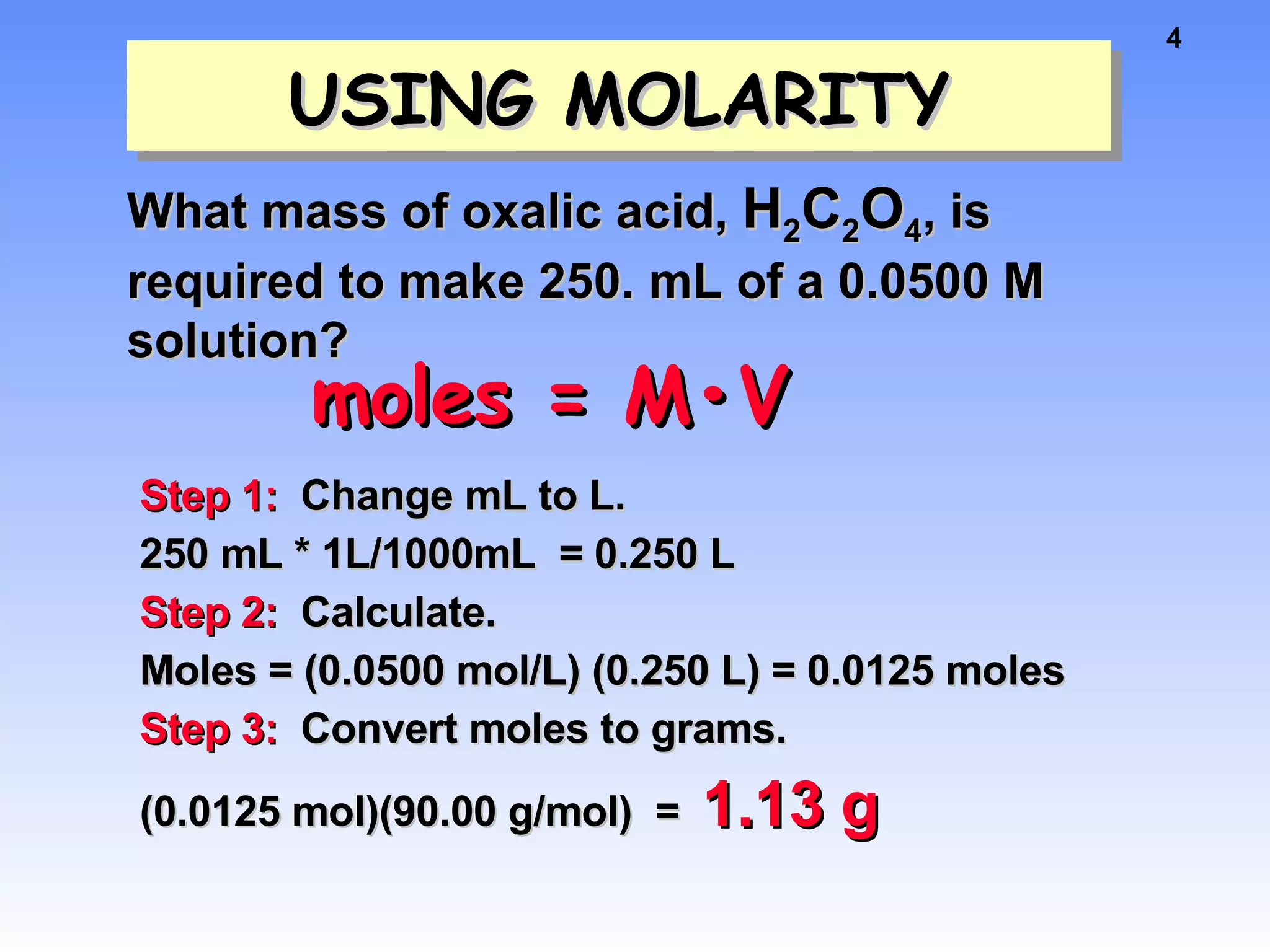
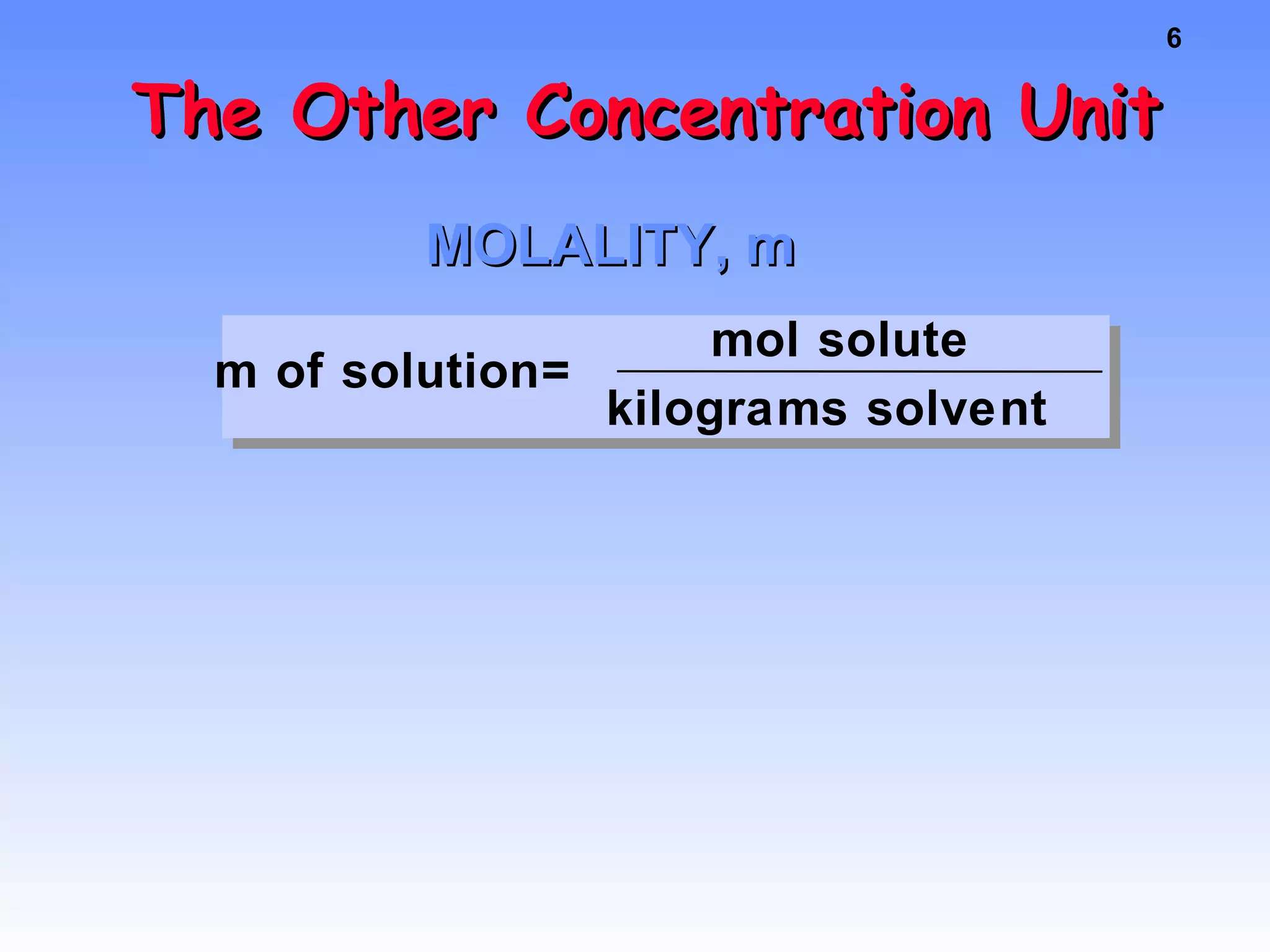
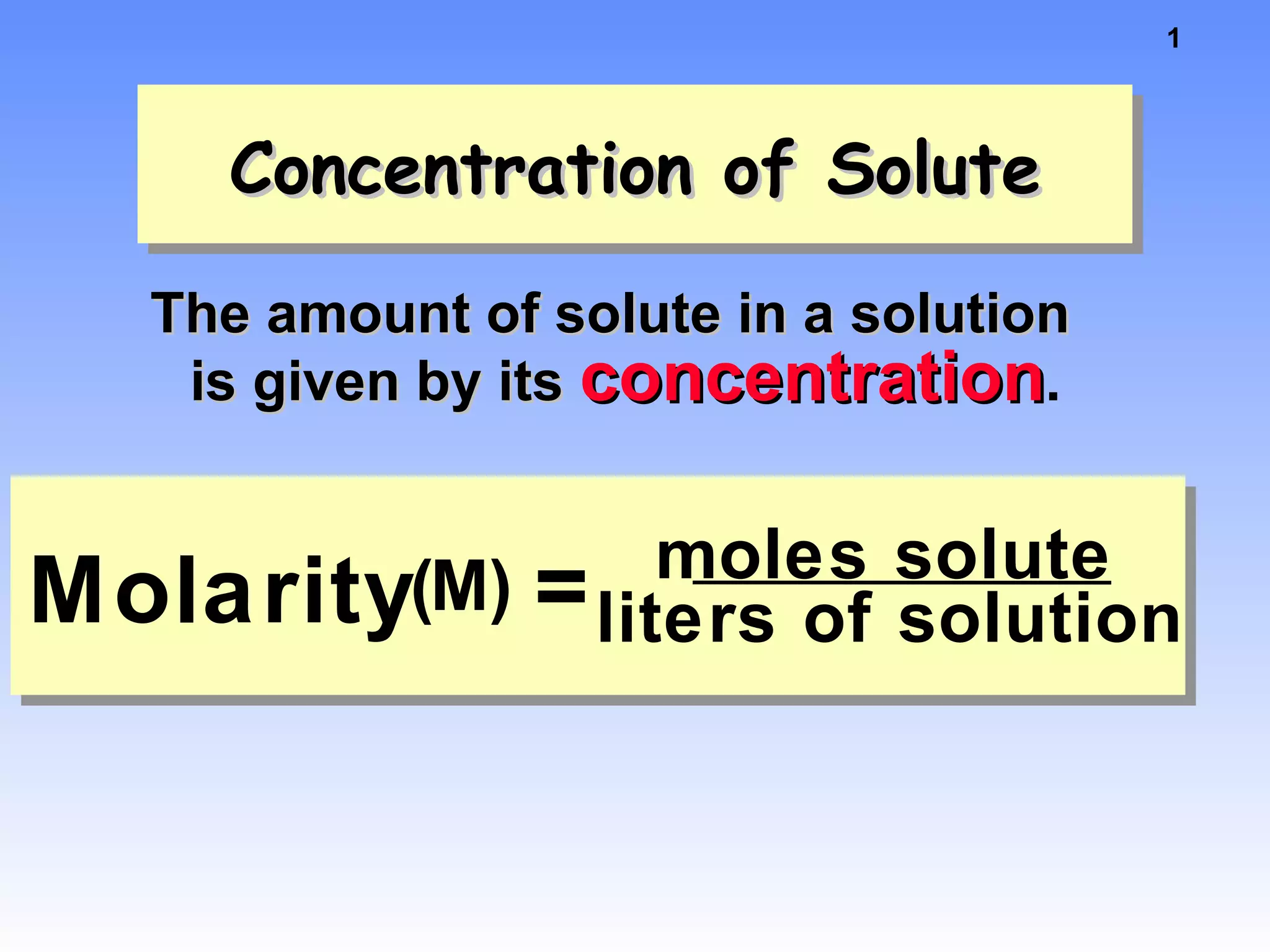
This document discusses concentration of solutions in chemistry. It defines molarity as moles of solute per liter of solution. It provides an example problem calculating the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 5 grams of nickel chloride hexahydrate in 250 mL of water. It also discusses molality, defined as moles of solute per kilogram of solvent, and provides an example problem calculating the molality of a sodium chloride solution. Finally, it discusses the process of diluting solutions through calculations that conserve the number of moles while changing the volume.

![PROBLEM: Dissolve 5.00 g of NiCl 2 •6 H 2 O in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. Calculate the Molarity. Step 1: Calculate moles of NiCl 2 •6H 2 O Step 2: Calculate Molarity [ NiCl 2 •6 H 2 O ] = 0.0841 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molaritymolalitydilutions-090506075922-phpapp01/75/Molarity-Molality-Dilutions-3-2048.jpg)