This document contains a chemistry jeopardy game covering topics from 5 units:
1. Measurements and calculations
2. States of matter and properties
3. Atomic structure
4. Radioactivity
5. Periodic trends
The questions test knowledge of concepts like significant figures, conversions, physical and chemical properties, atomic structure, radioactive decay, electron configurations, and trends in atomic radius and ionization energy across the periodic table.



















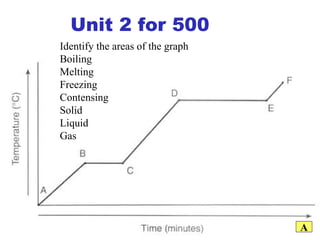
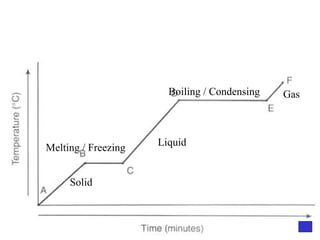







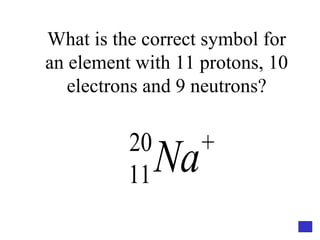















![Give the electron configuration for Bromine Full: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5 Noble Gas Shorthand: [Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semester1reviewjeopardy-100323212151-phpapp01/85/Semester-1-Review-Jeopardy-46-320.jpg)





