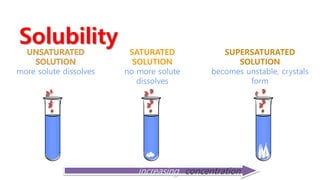
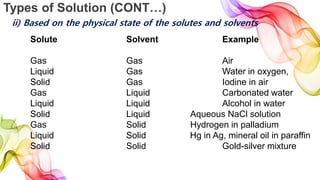
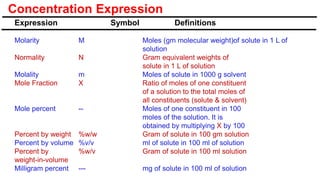
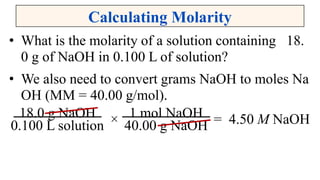
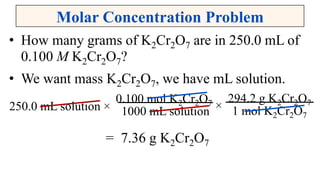
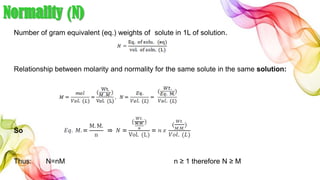
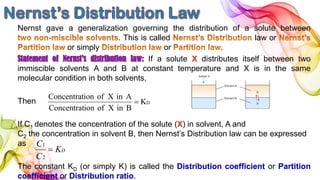
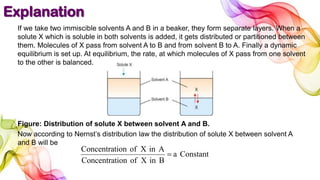
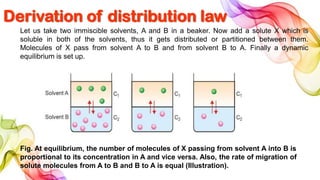
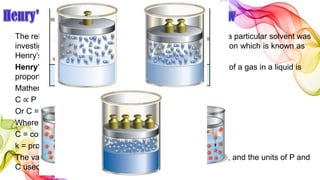
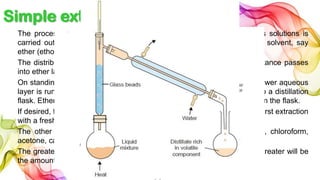
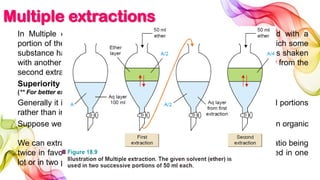
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of solute and solvent where solubility determines the extent of dissolution. Solutions can be classified based on solute concentration (saturated, unsaturated, supersaturated) and the physical state of solutes and solvents, with several measurement methods for concentration such as molarity and normality. Factors affecting solubility include temperature, pressure, molecular size, and the principle of 'like dissolves like,' alongside concepts such as dilution and Nernst's distribution law.