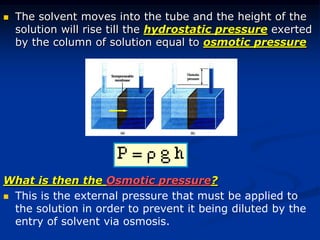
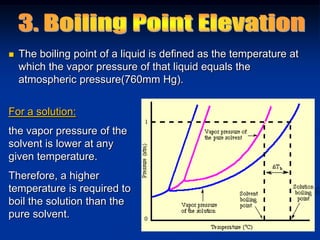
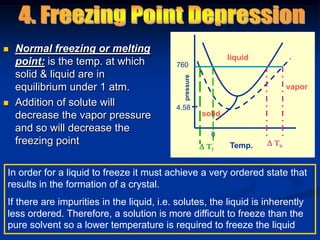
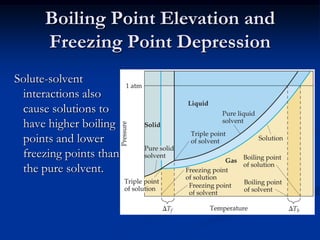
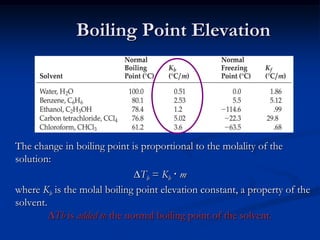
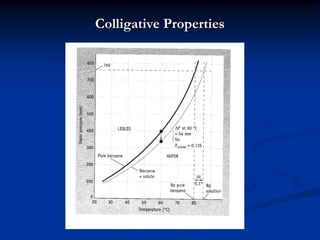
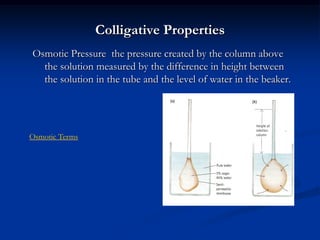
Colligative properties depend only on the number of dissolved particles in solution and not on their identity. The key colligative properties are vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. Vapor pressure lowering occurs because solute particles decrease the number of solvent particles that can evaporate from the surface. Boiling point elevation and freezing point depression occur because adding solute particles lowers the vapor pressure of the solvent, requiring more energy for evaporation or freezing. The degree of change in boiling point or freezing point depends on the molality of the solution.














































































![Study Questions
Define the following terms:
[Colligative properties, Osmotic pressure, vapour pressure, ideal solution, real solution, molar mass, electrolyte,
weight mass, gravity, molality, molarity, etc]
Respond to the following questions:
Explain the processes of the main colligative properties of the pharmaceutical materials and how the
properties vary with named factors
What is gravity and how does it affect the movement of material substance
Group work discussional questions:
Give a detailed account of the variables that can be considered in the quantification of solutes in solution
system
How many grams of a solution, that is 76.3% by mass KBr, would contain 38.95 g of KBr?
What is the ppm and molality of a solution containing 75.0 g of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, in 200.0 g of water?
How many grams of CuSO4 are needed to make 350.0 mL of a solution that contains 10.5 mg/mL of Cu2+ ion?
Calculate the molarity of the resulting solution.
Automobile battery acid is 38% H2SO4 and has a density of 1.29 g/mL. Calculate the molality of this
solution.
If 27.0 g of LiBr are dissolved in 50.0 g of water, the percent of LiBr by mass is
If 15.0 g of KNO3 is added to 75g of water, what is the mass percent of KNO3 in the solution?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-colligativeproperties-180825211533/85/Colligative-Properties-88-320.jpg)