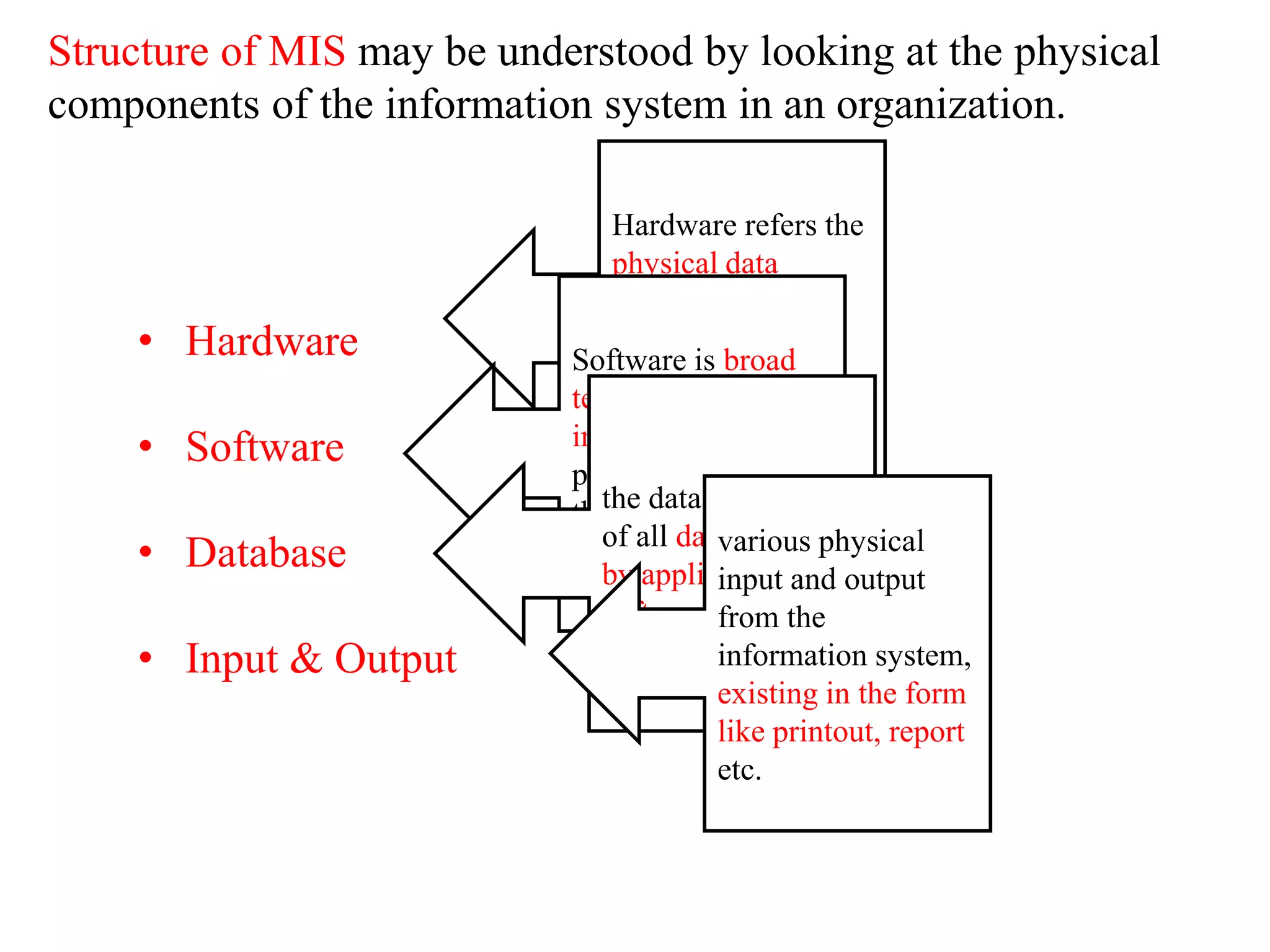
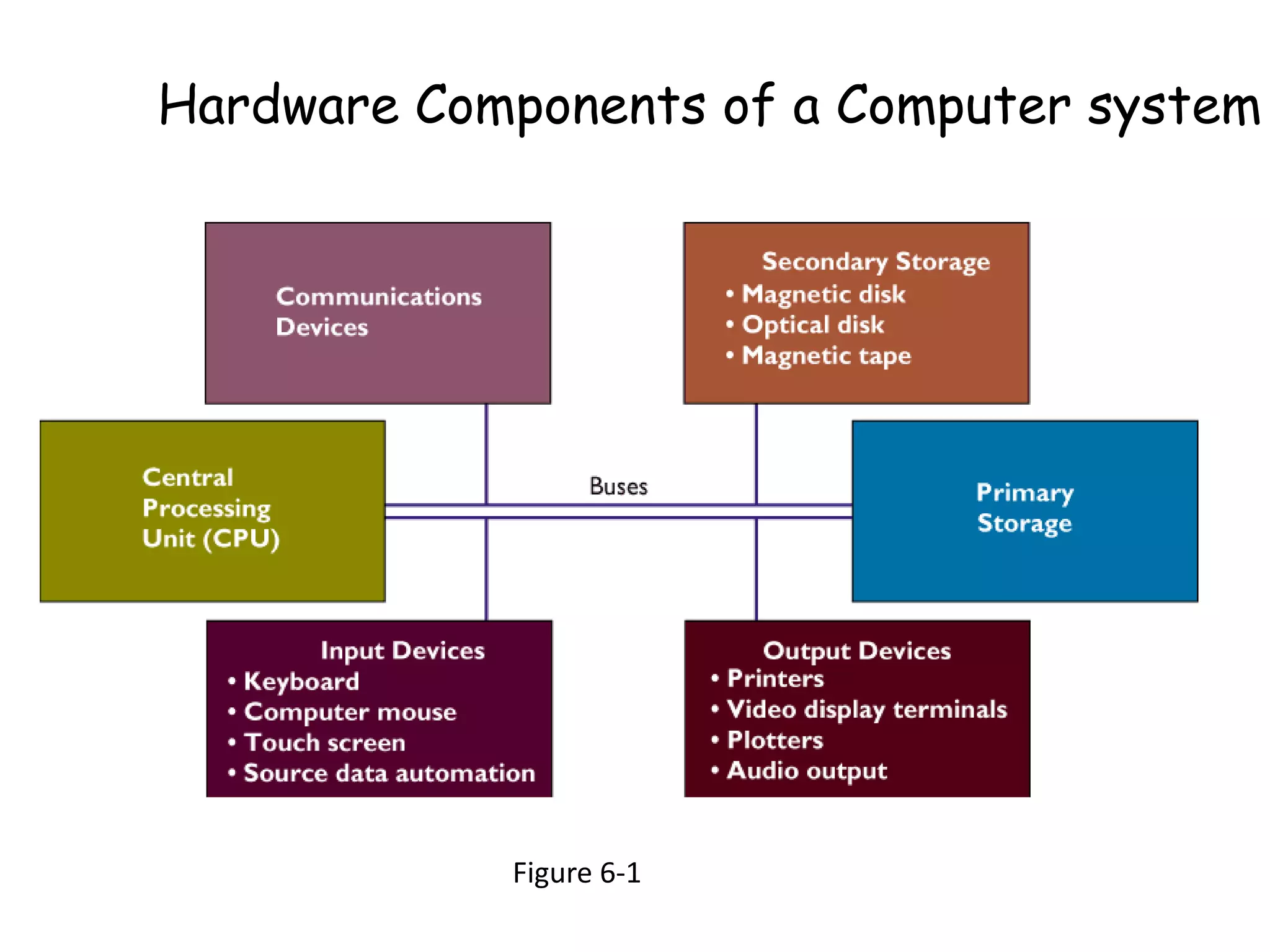
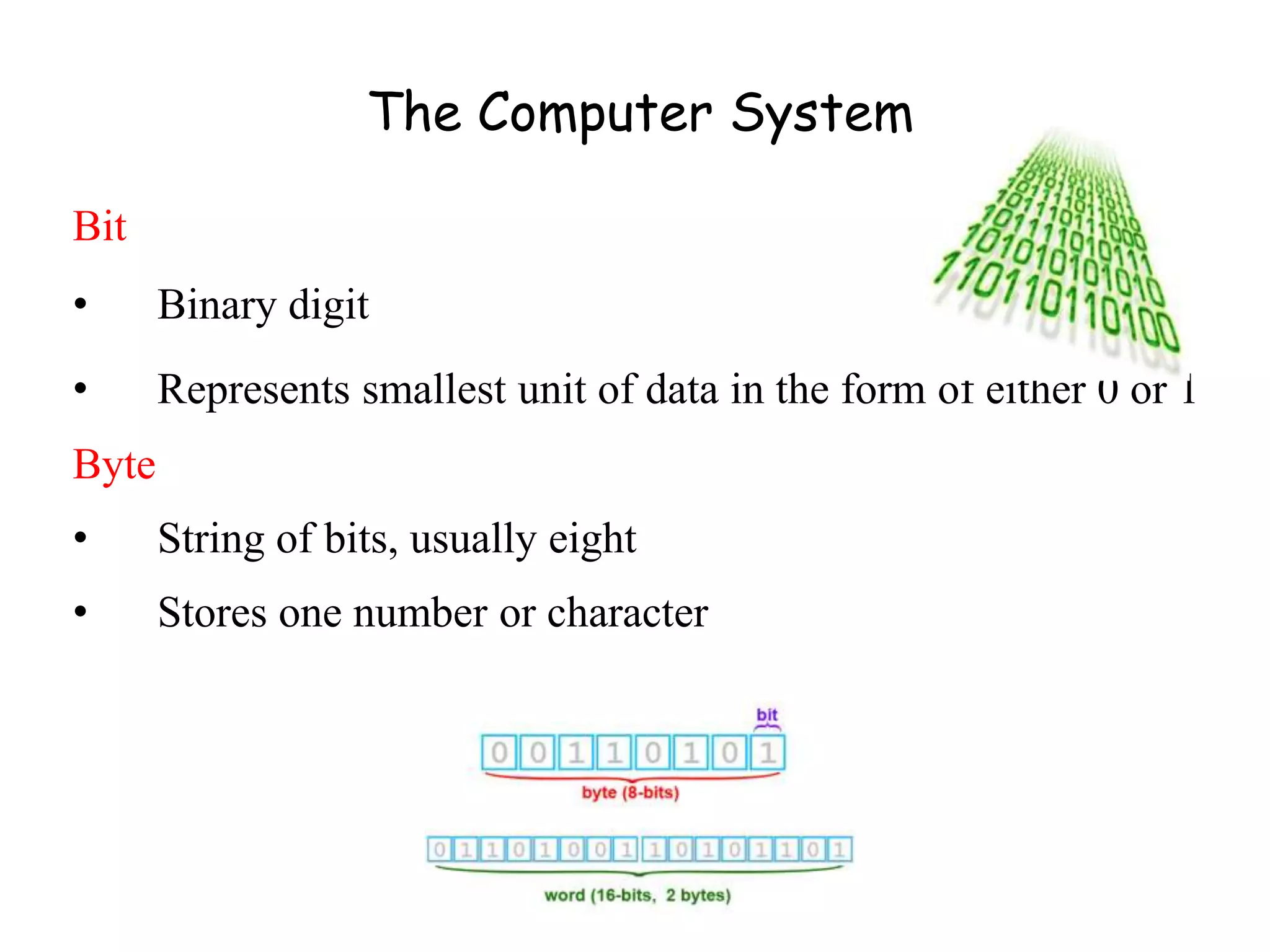
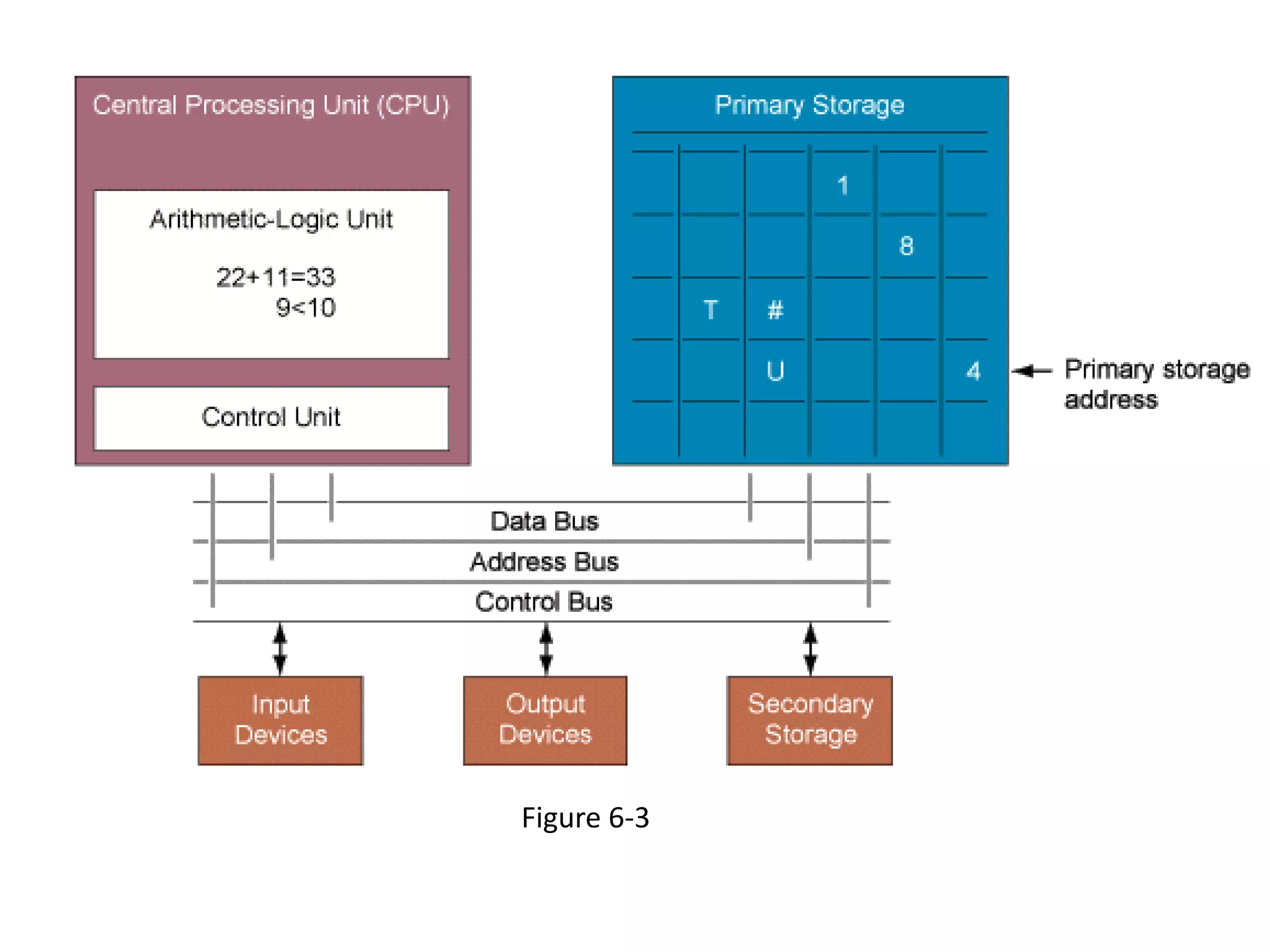
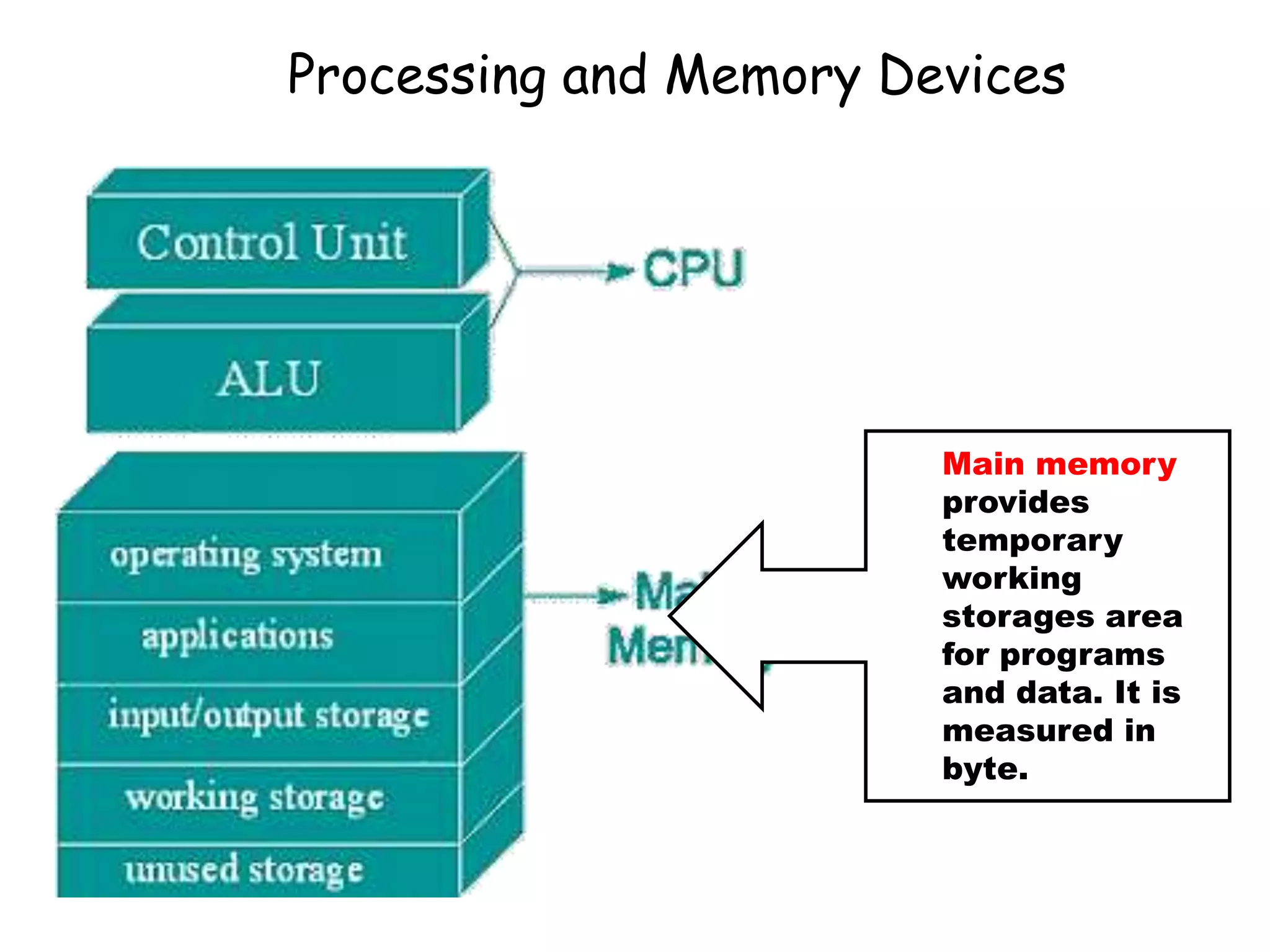
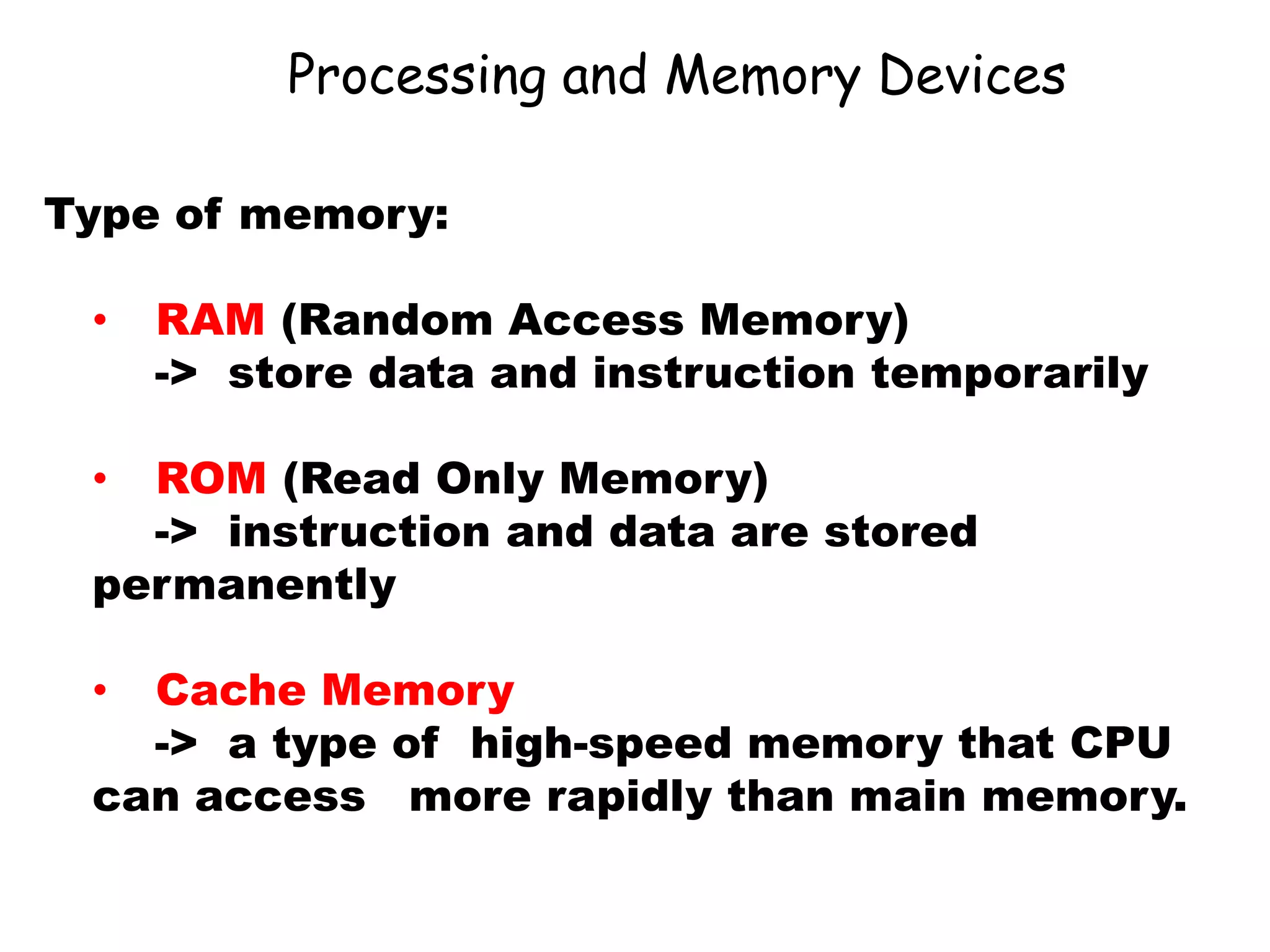
The document discusses the components of a management information system (MIS), focusing on hardware. It defines hardware as the physical components of a computer system, including processing equipment and peripheral devices. It notes that hardware supports organizational goals and objectives. Advantages of investing in computer hardware for organizations include improving productivity, increasing revenue, reducing costs, and enabling collaboration. The document outlines different types of hardware components such as the central processing unit (CPU), primary and secondary storage, and different classifications of computers including mainframes, servers, and minicomputers. It also discusses managing hardware and software assets.