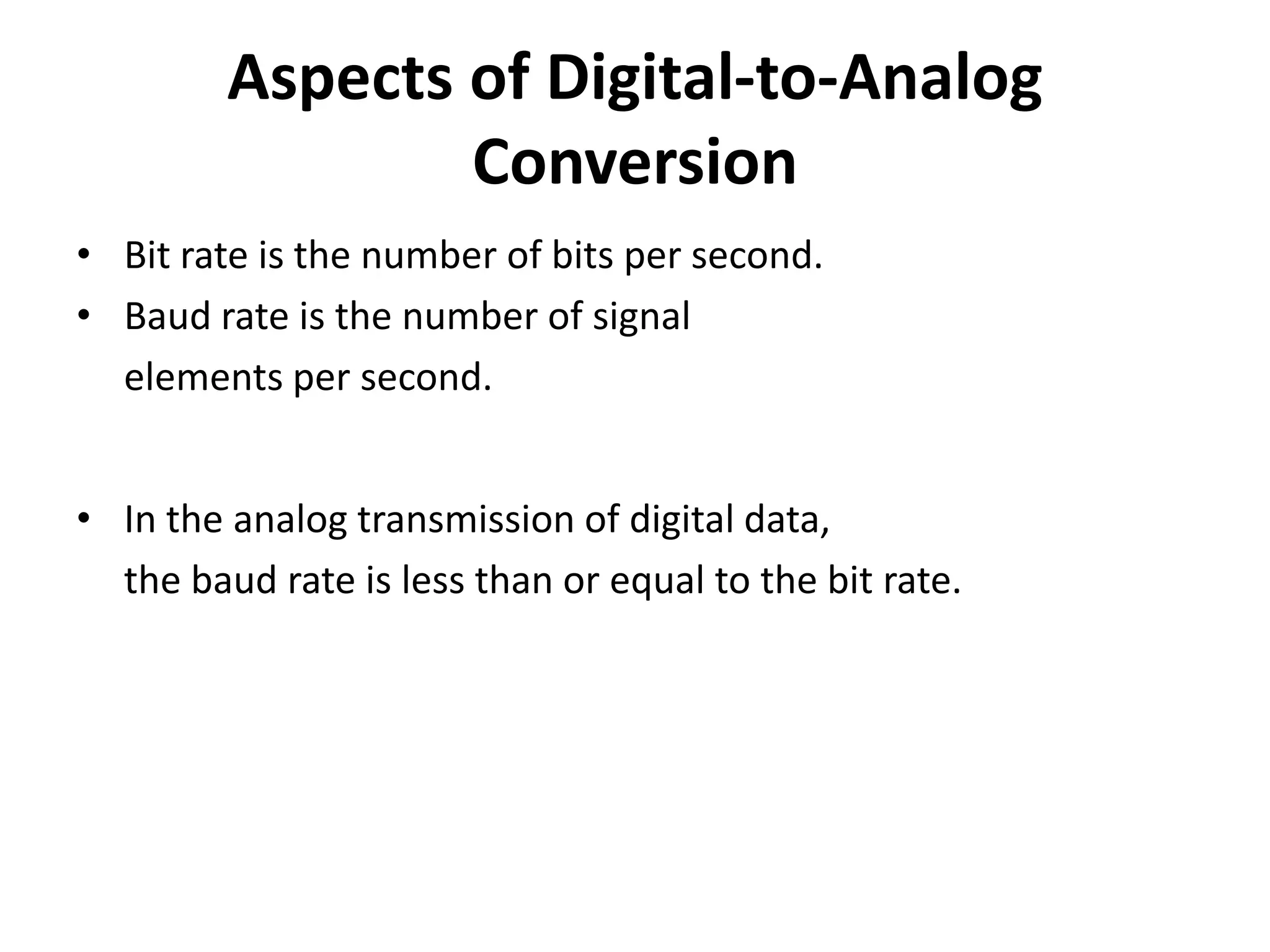
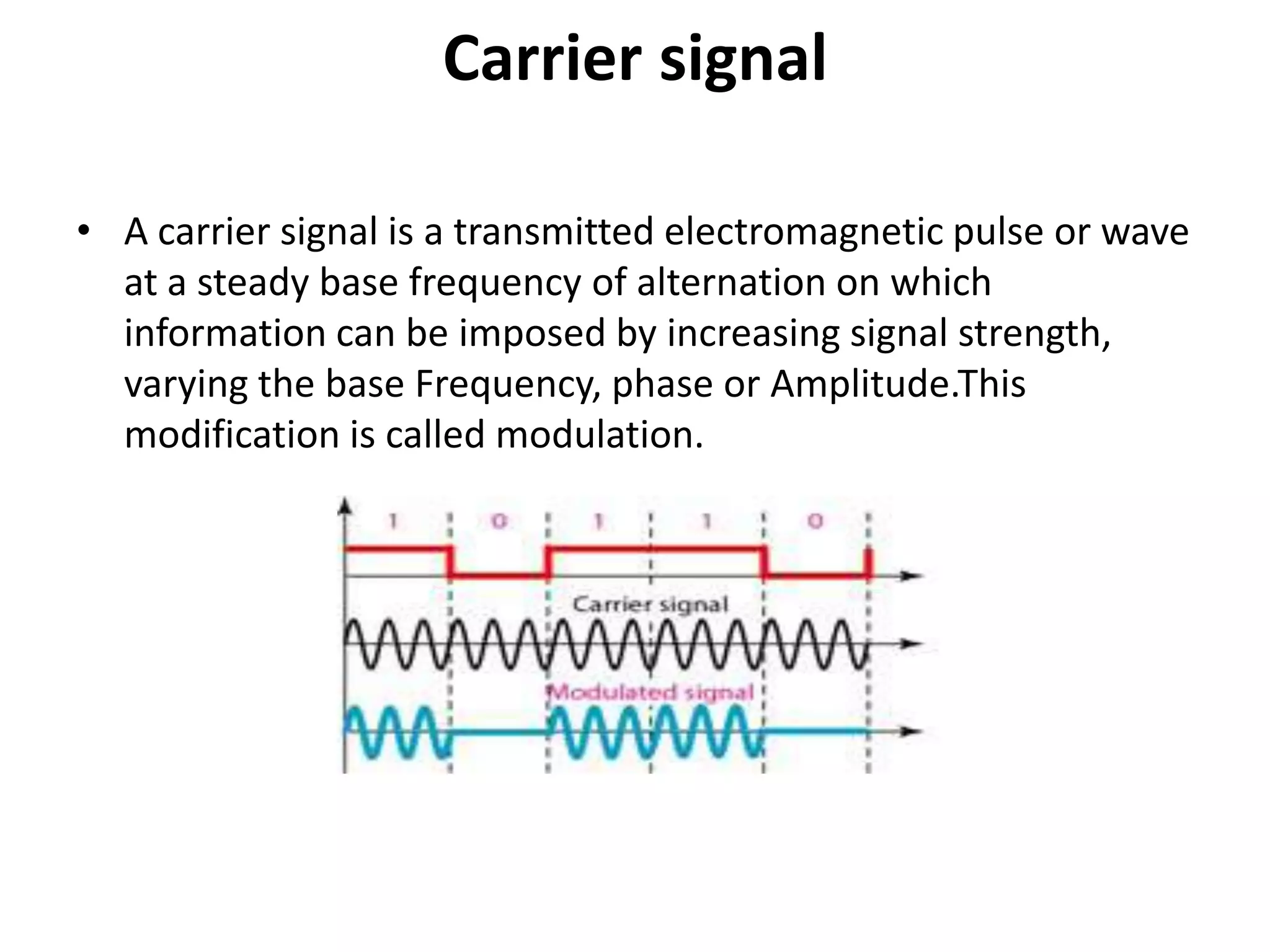
This document discusses different digital modulation techniques:
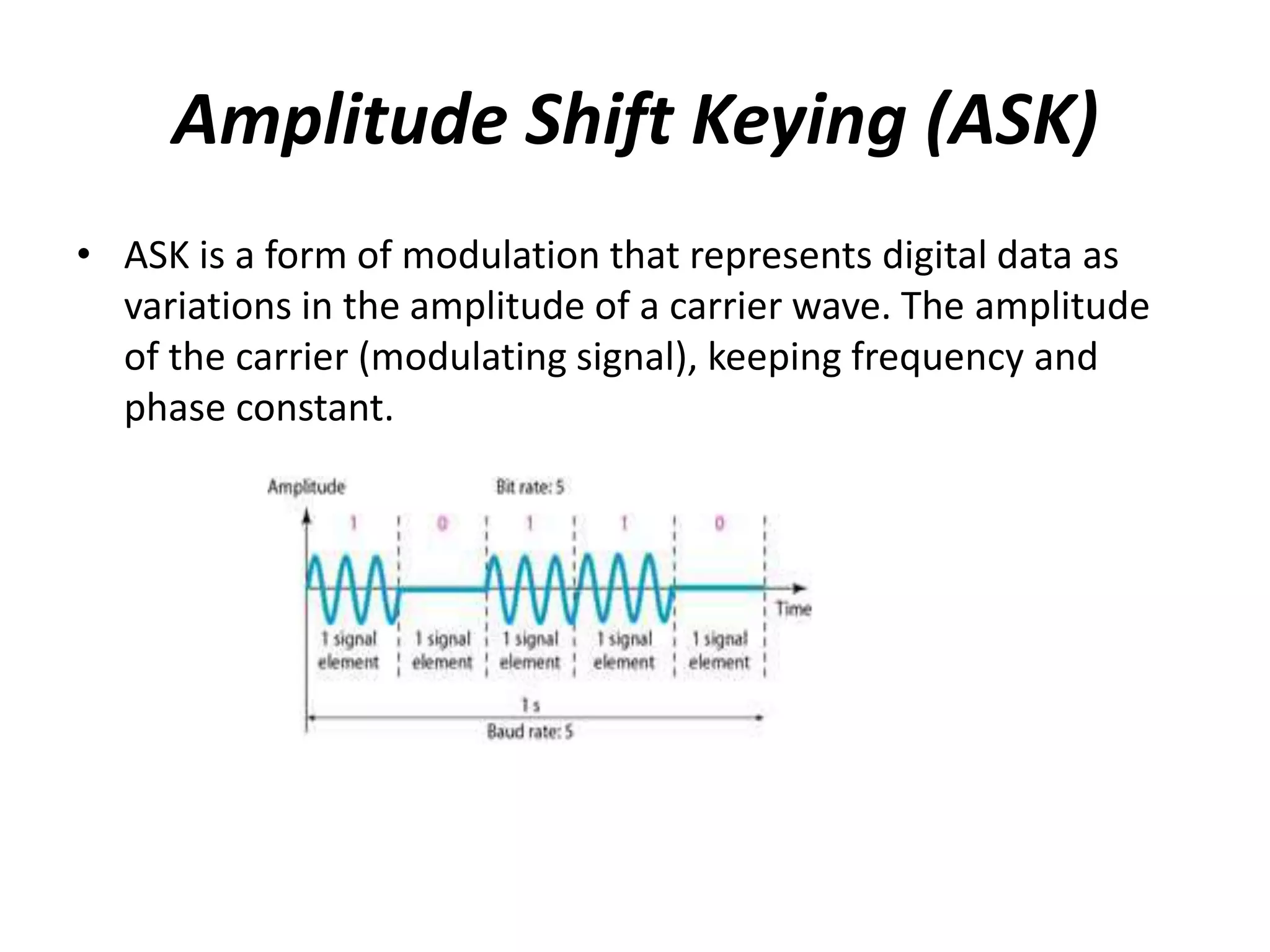
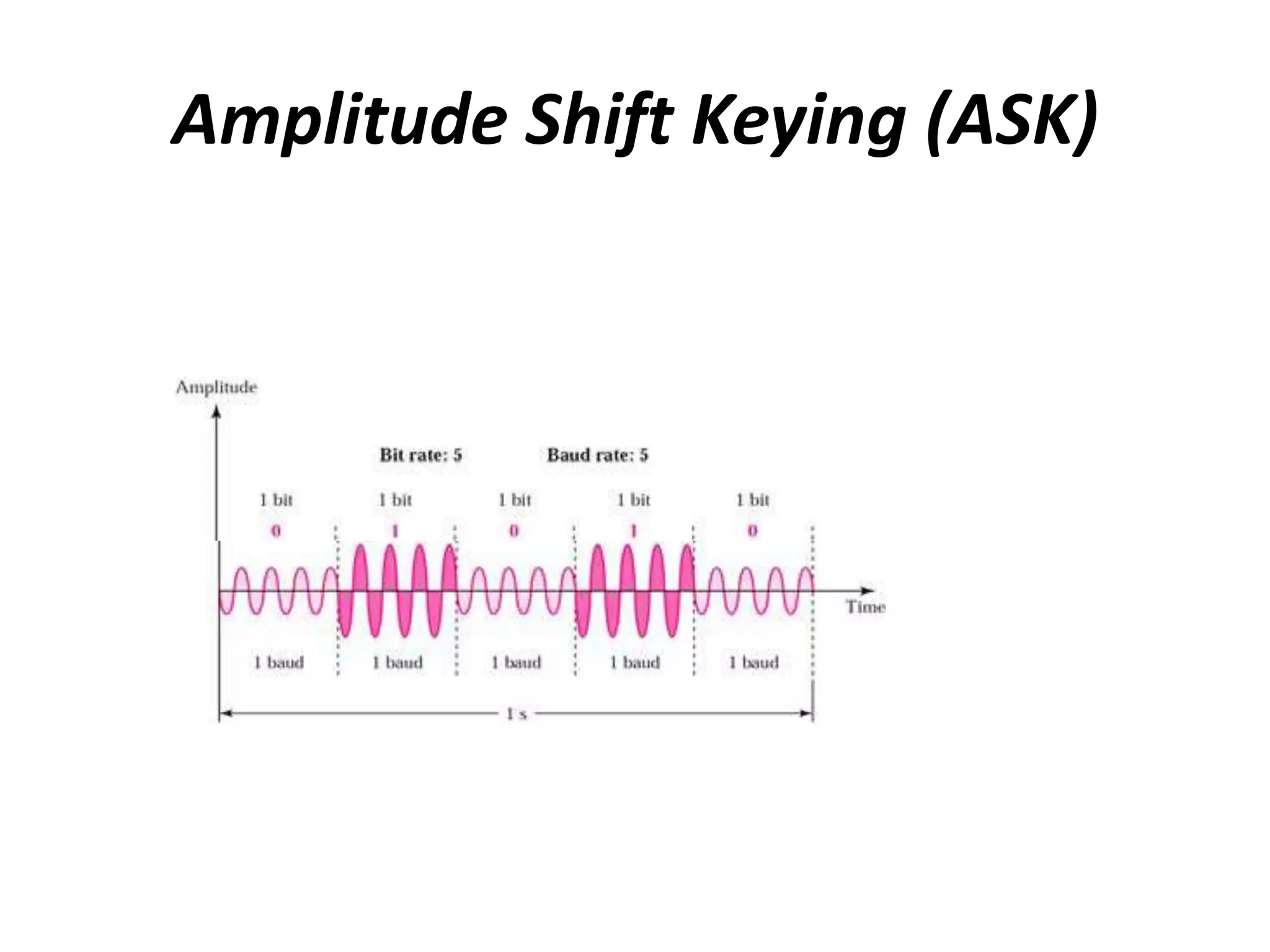
1) Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave, keeping frequency and phase constant. It has simple modulation/demodulation but is highly sensitive to noise.
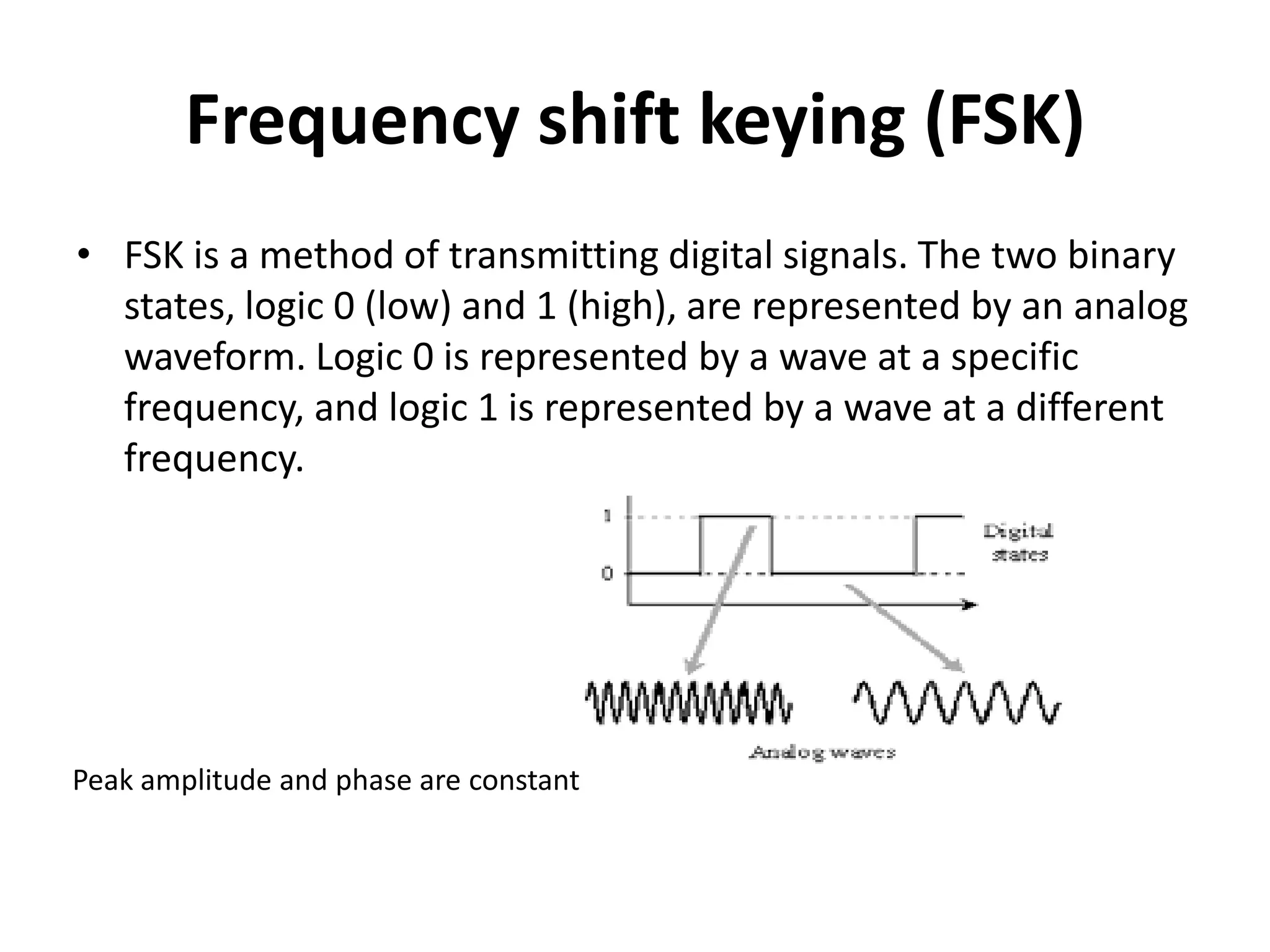
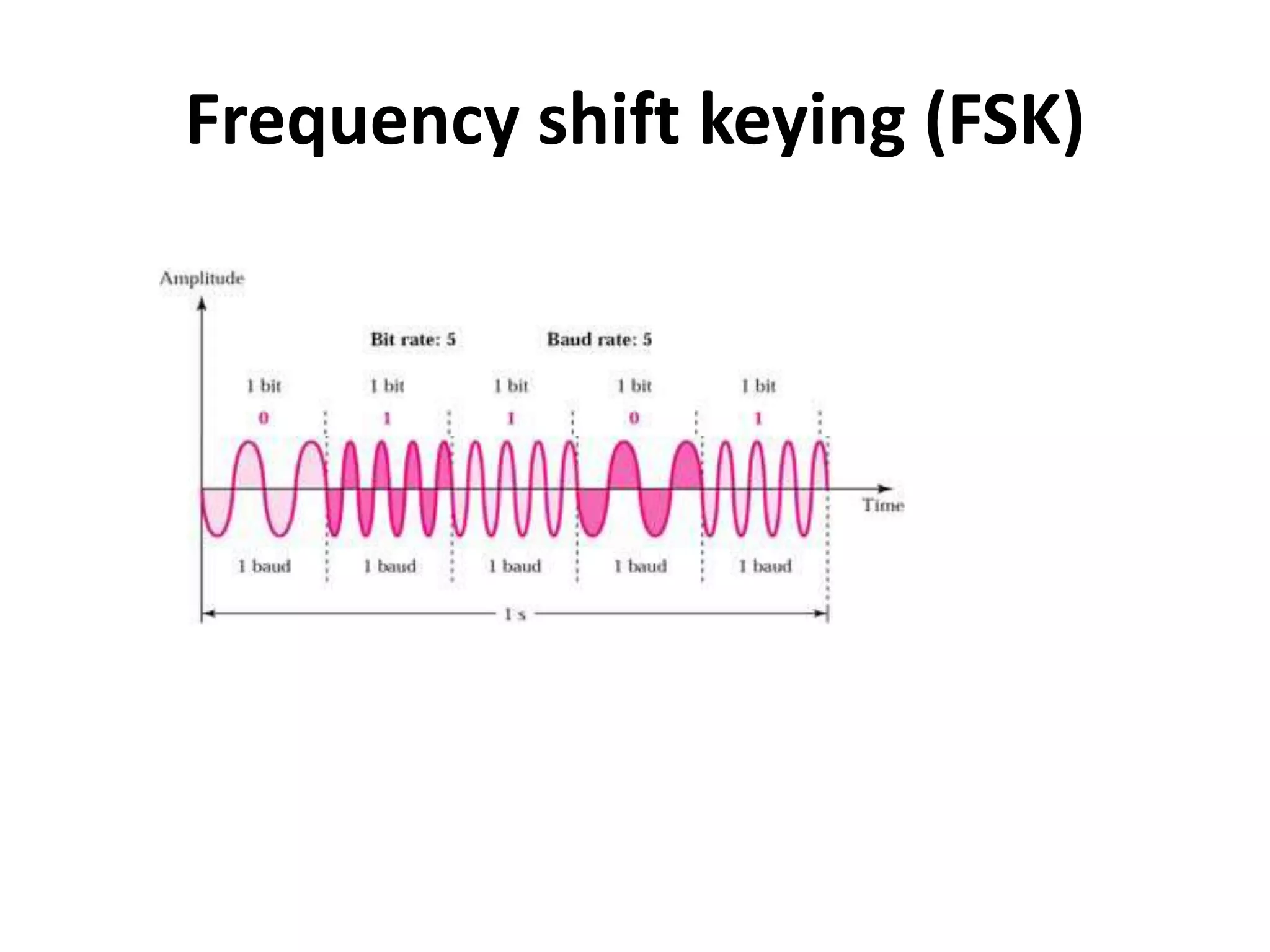
2) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) represents binary digits by transmitting two different frequencies, with the peak amplitude and phase held constant.
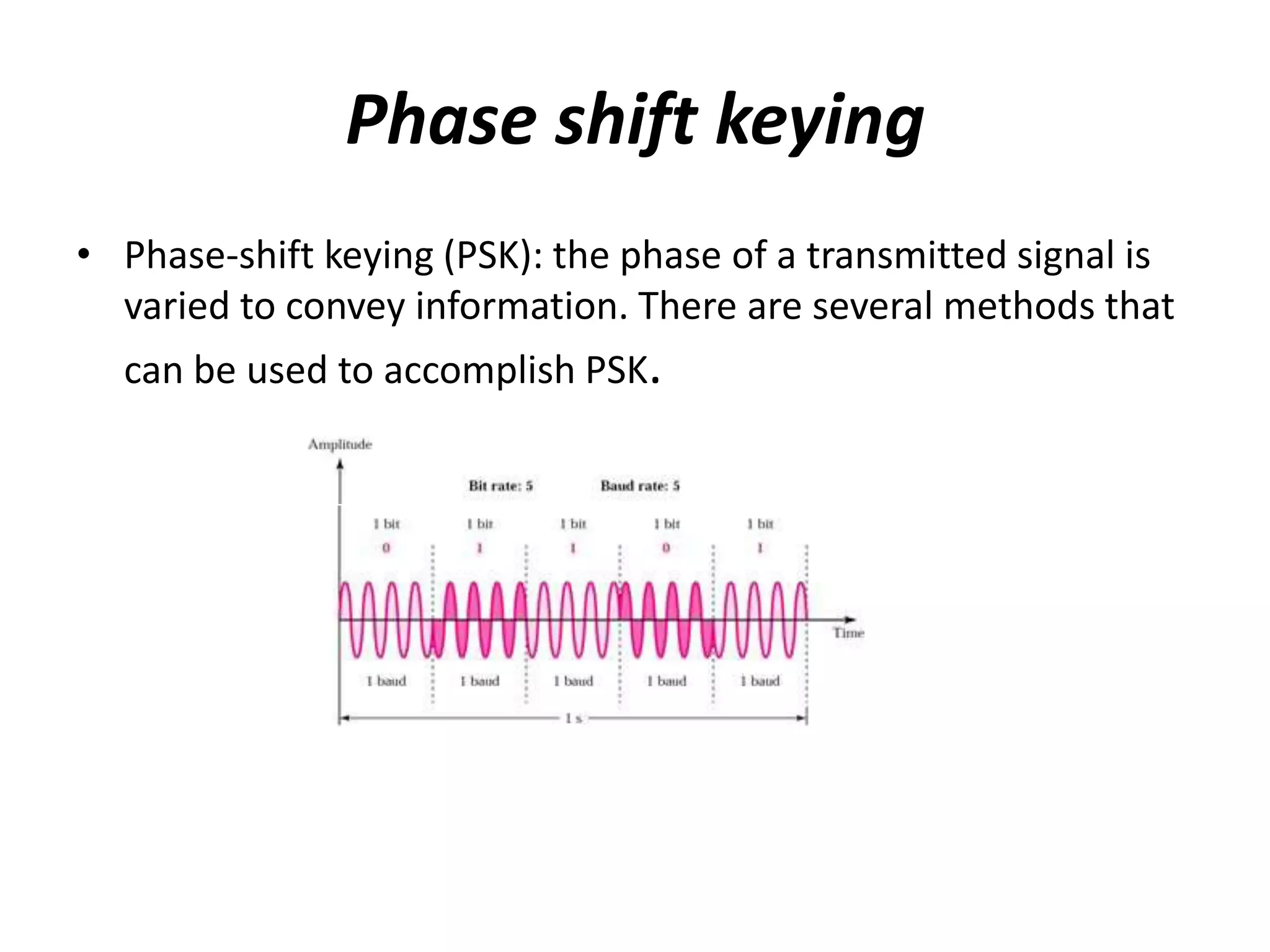
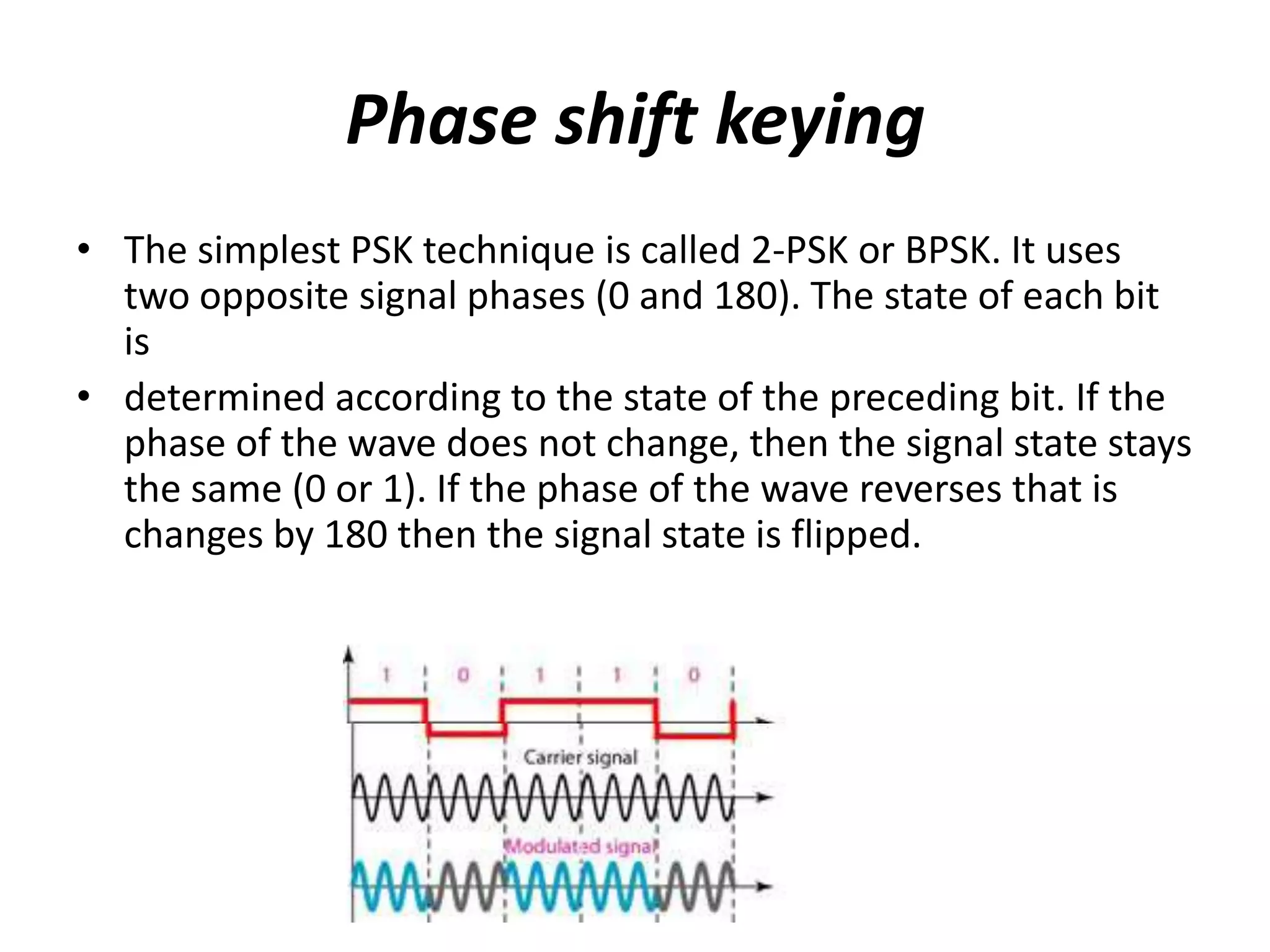
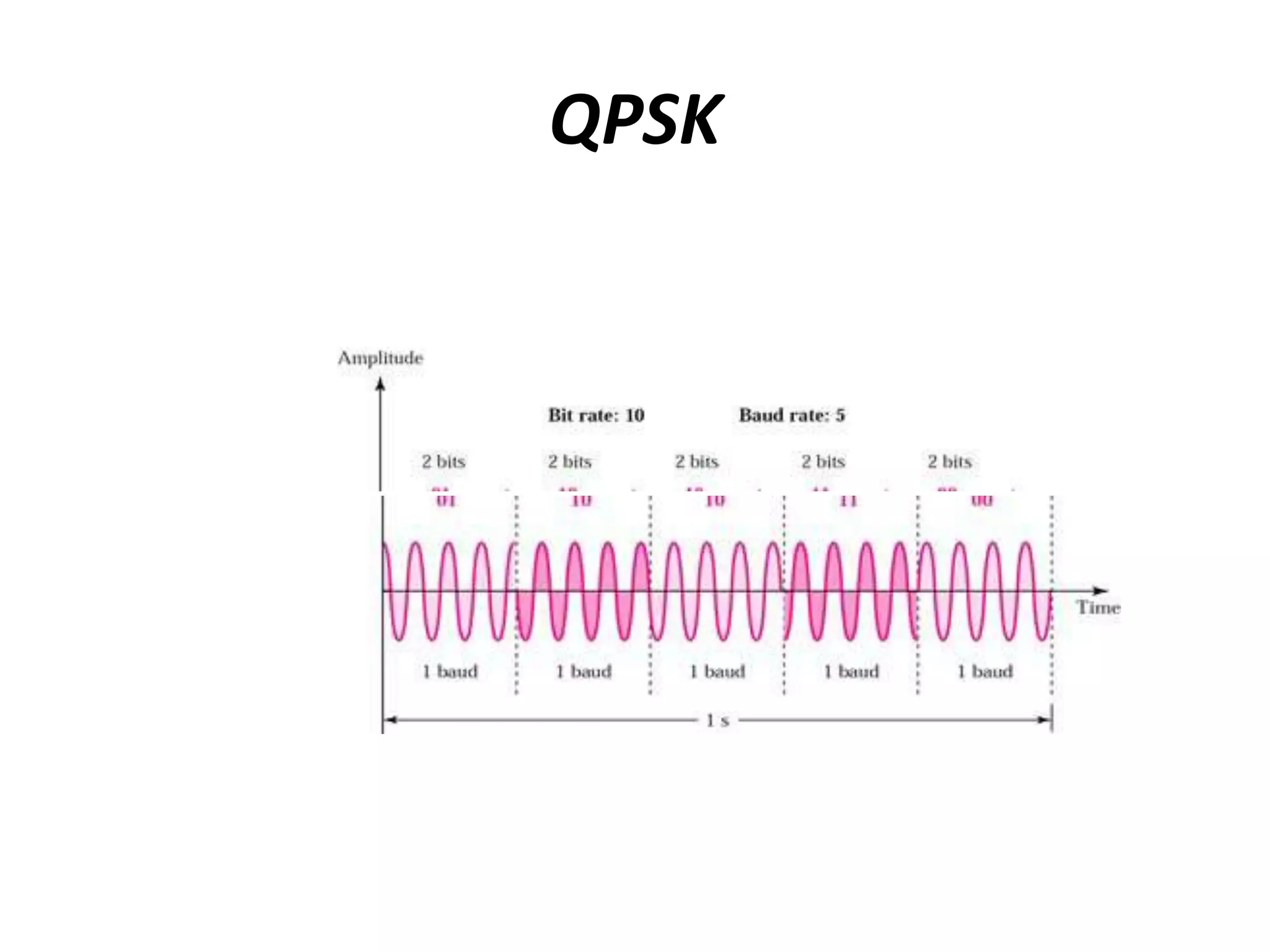
3) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) varies the phase of a transmitted signal to convey information, with the simplest method being BPSK using two opposite phases. PSK has good noise immunity and no bandwidth limitation.