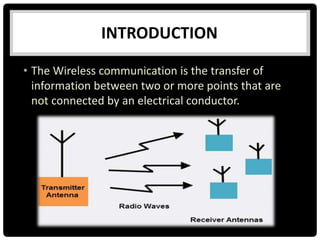
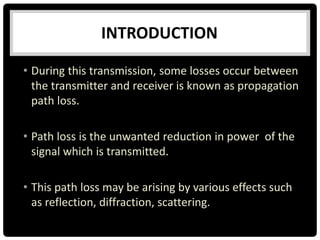
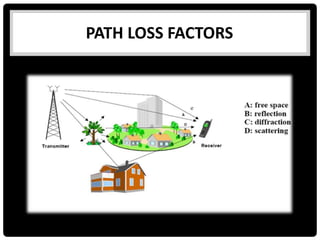
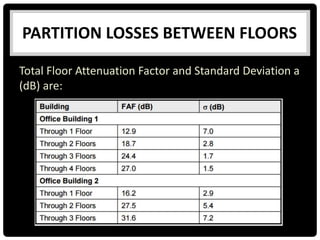
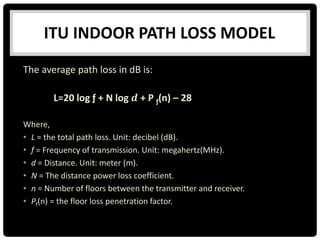
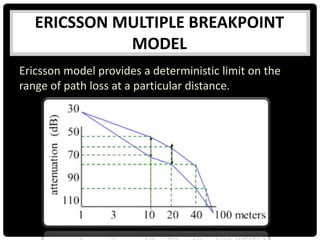
This document summarizes several indoor propagation models. It begins with introducing path loss factors like reflection, diffraction, and scattering. It then describes the ITU indoor path loss model, log-distance path loss model, and Ericsson multiple breakpoint model. The ITU model calculates path loss based on frequency, distance, and floor number. The log-distance model uses a path loss exponent to estimate loss over distance. The Ericsson model provides upper and lower loss bounds based on measurements in an office building.