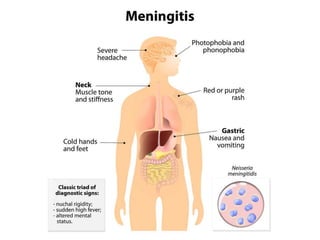
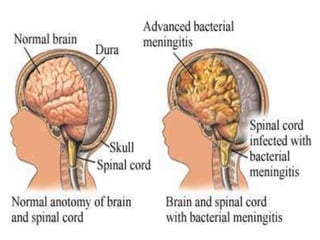
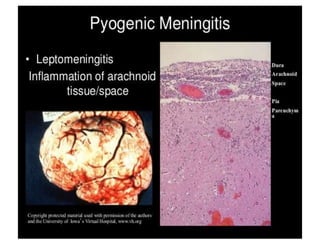
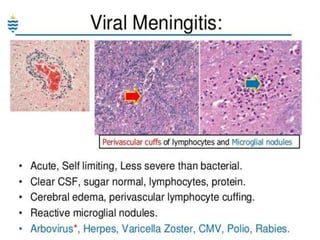
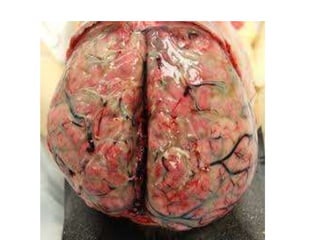
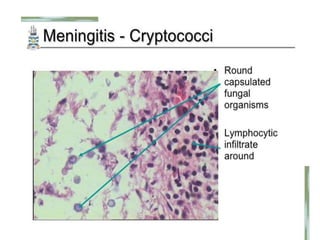
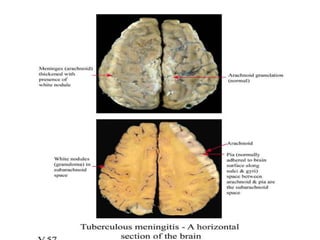
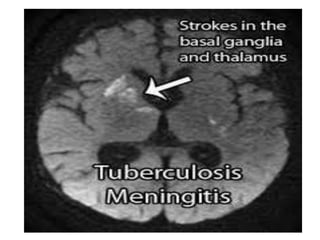
This document discusses different types of meningitis, including acute pyogenic meningitis, acute lymphocytic meningitis, and chronic meningitis. Acute pyogenic meningitis is caused by bacteria and results in inflammation of the meninges around the brain. Common causative organisms vary with age. Acute lymphocytic meningitis is usually viral and has milder symptoms that resolve more quickly. Chronic meningitis includes tuberculous and cryptococcal types, which cause long-term granulomatous inflammation that may lead to hydrocephalus. Diagnosis is based on examination of cerebrospinal fluid characteristics.