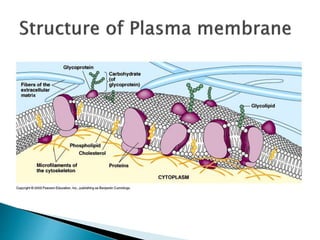
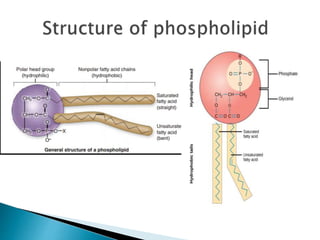
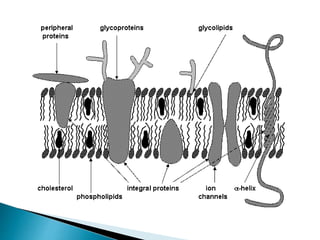
The cell membrane is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. They form a bilayer with different types concentrated on either side. Cholesterol modulates membrane fluidity and prevents small molecules from crossing. Membrane proteins carry out functions like transport and signaling, and can be integral or peripheral. Carbohydrates attached to proteins or lipids on the external surface form the glycocalyx and enable cell adhesion, recognition, and responses.