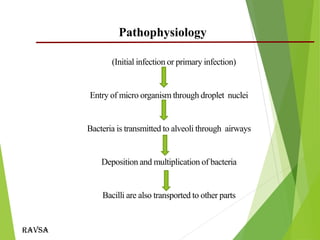
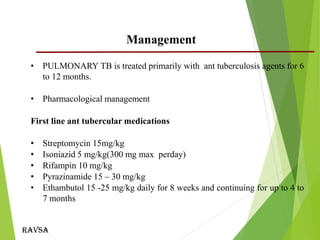
This document provides an outline and overview of tuberculosis in children. It discusses key points such as risk factors including household contact with TB cases, age less than 5 years, HIV infection, and malnutrition. The causative agent is typically Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is transmitted through inhalation of droplets. Clinical signs can include fever, weight loss, and cough. Diagnosis involves history, examination, tuberculin skin testing, and bacteriological confirmation when possible. Management consists of pharmacological treatment with first-line antitubercular medications for 6-12 months. Nursing care focuses on administration of medications, monitoring for side effects, education, and isolation to prevent transmission.