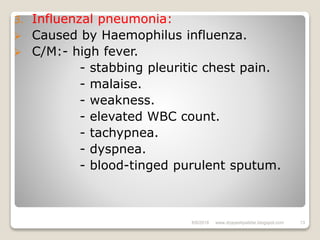
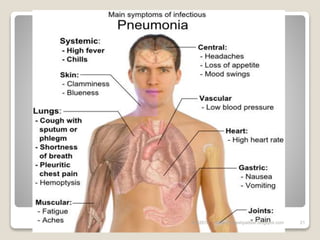
Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition caused by various microorganisms. It discusses the definition, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, types, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, classification, medical management, nursing management, and potential complications of pneumonia. The document provides an overview of pneumonia with definitions of key terms and descriptions of common causes, symptoms, diagnostic tests, and treatment approaches.