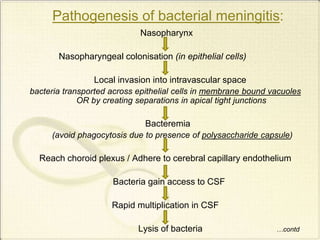
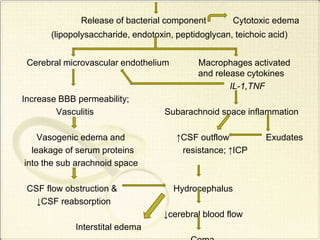
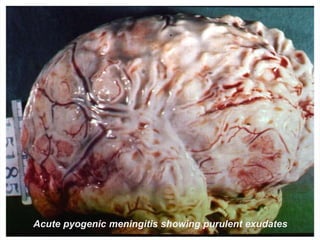
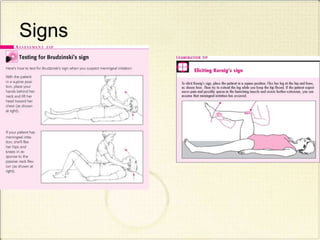
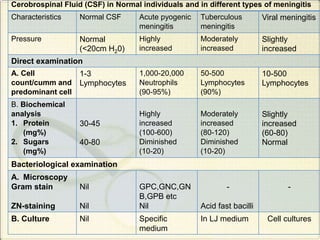
Meningitis refers to inflammation of the membranes (meninges) surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is generally caused by viral or bacterial infections, though chemical meningitis can occur from injection of irritants into the subarachnoid space. The main types are acute pyogenic (bacterial), aseptic (usually viral), and chronic (often tuberculous or fungal). Common causative agents include bacteria like Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and viruses such as enterovirus. Bacteria typically enter the CSF through the blood or direct implantation. This causes an inflammatory response and increased CSF pressure that can lead to complications like hydrocephalus or brain damage if left untreated