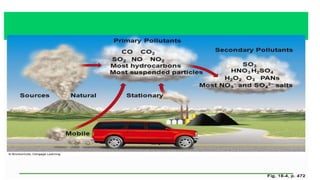
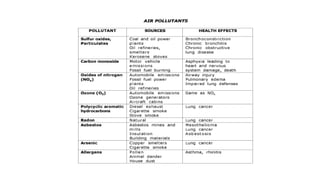
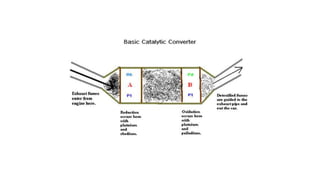
Air pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the atmosphere, causing health issues and environmental damage. There are two types of pollutants: primary, emitted directly from sources, and secondary, formed when other pollutants react. Sources include anthropogenic activities like vehicles, power plants, and agriculture as well as natural sources like wildfires. Effects of air pollution include respiratory illnesses, global warming, acid rain, and harm to wildlife. Control measures involve source reduction through alternatives to private vehicles, low emission fuels, and planting trees to absorb pollutants.