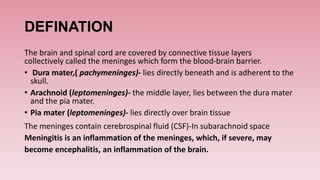
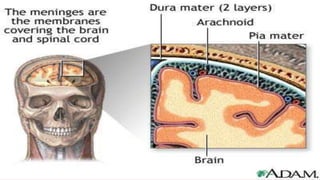
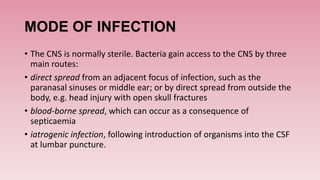
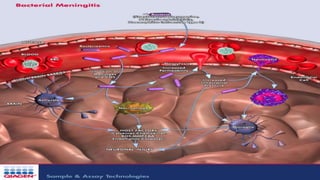
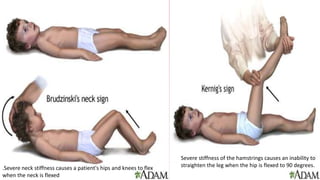
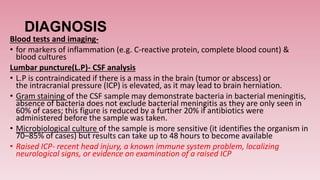
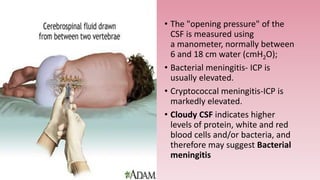
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, which are the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Bacteria can reach the meninges through the bloodstream, direct contact from a site of infection like the sinuses or ears, or iatrogenically through procedures like lumbar puncture. Symptoms include fever, headache, neck stiffness, and altered mental status. Diagnosis involves analyzing cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture for signs of infection like increased white blood cells. The most common causes of bacterial meningitis are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae.