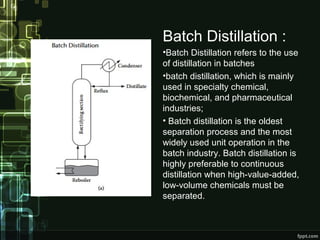
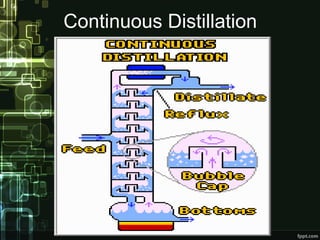
Distillation is a process of separating components of a liquid mixture based on their boiling points. It involves heating the mixture to form vapors and then cooling the vapors to form separate liquids. Distillation has been used since ancient times and is widely used today in industries like petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. Common applications include producing alcoholic beverages through fermentation and distillation of the resulting dilute ethanol solutions. Various types of distillation exist like batch, continuous, fractional, and vacuum distillation.