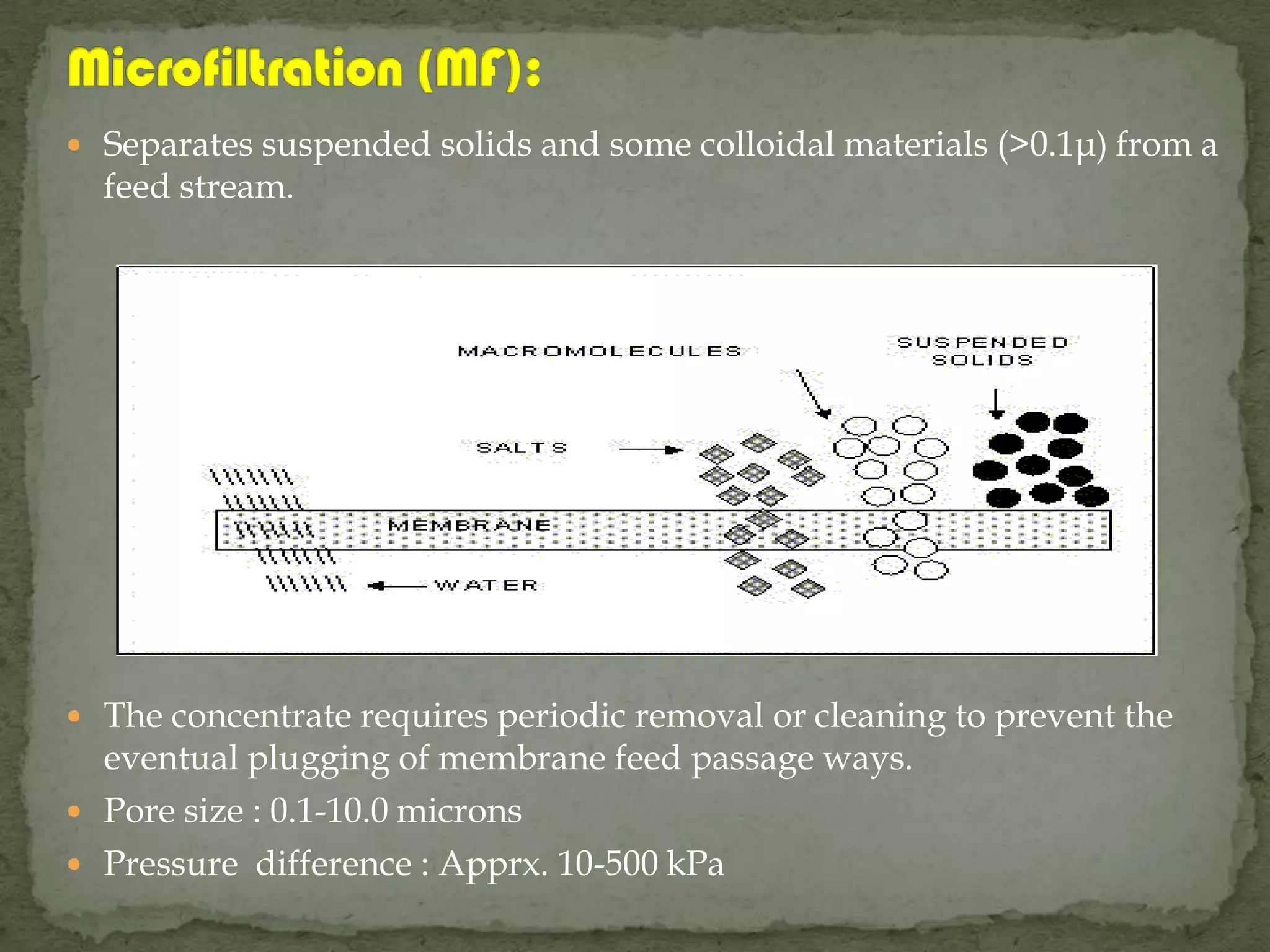
Membranes have been used for separations since the 18th century, with significant developments in the 20th century. They are semi-permeable barriers that selectively restrict the transport of molecules. Key membrane processes include microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, gas separation, and pervaporation. Membranes are used in modules and the selection of module depends on factors like membrane area, costs, and fouling control. While membranes offer advantages like mild operating conditions, challenges include membrane fouling and costs.