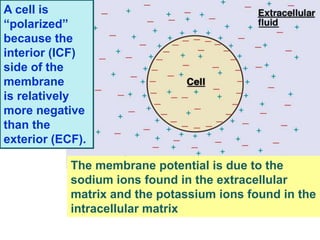
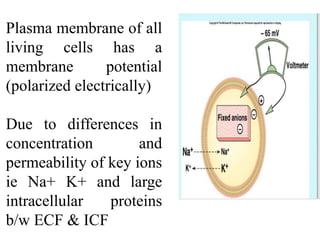
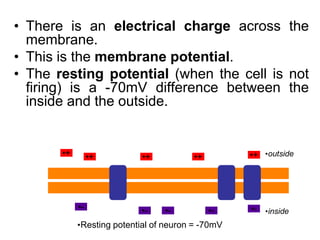
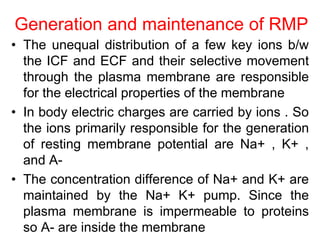
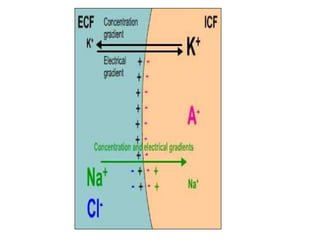
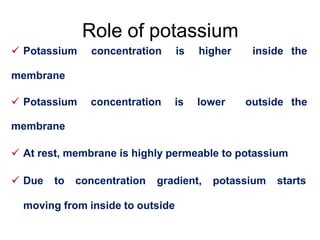
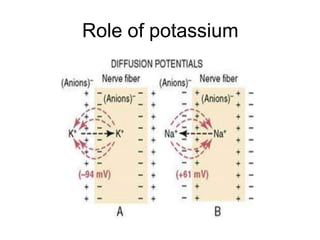
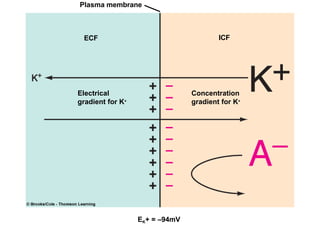
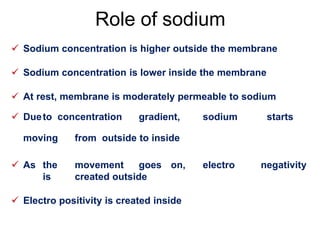
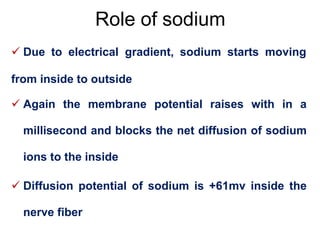
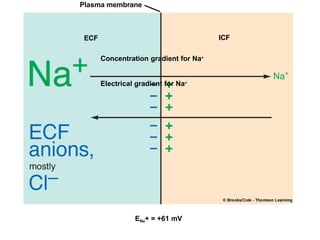
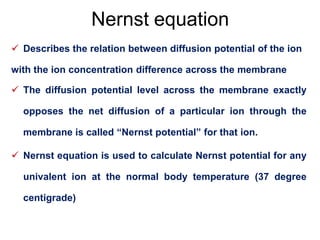
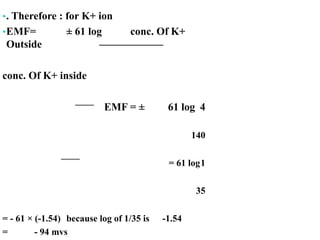
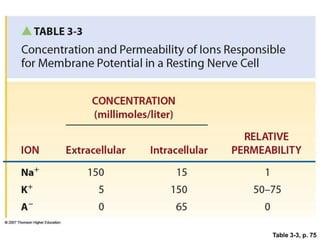
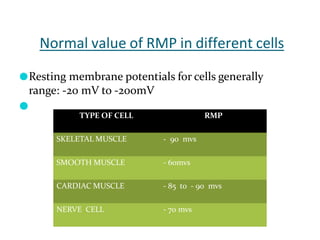
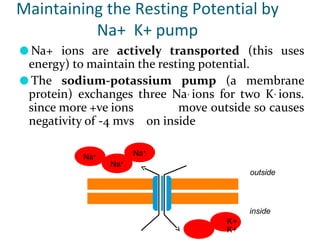
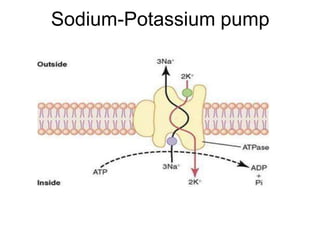
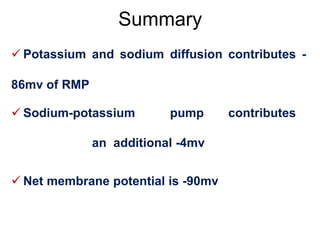
Membrane potential refers to the electric potential difference across a biological cell's membrane, created by the uneven distribution of ions such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). The resting membrane potential (RMP) is typically around -70mV in neurons, maintained through the selective permeability of the membrane and the activity of the sodium-potassium pump. Key equations, including the Nernst and Goldman equations, describe the relations and calculations for diffusion potentials of these ions, which influence cellular excitability and function.