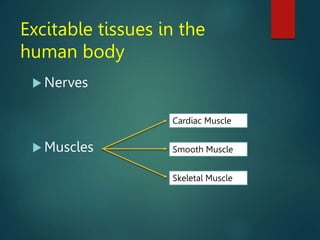
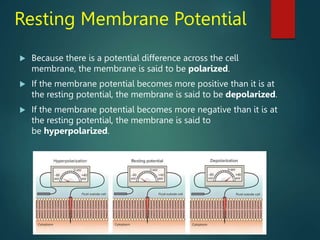
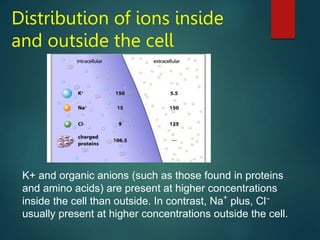
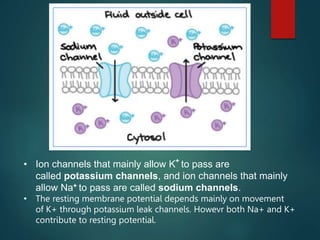
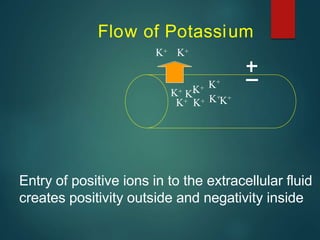
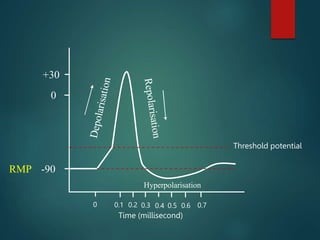
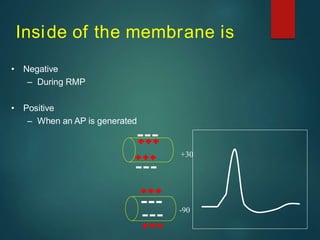
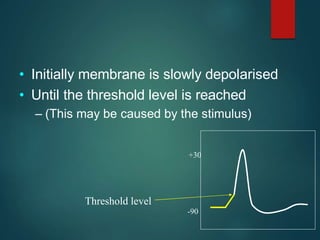
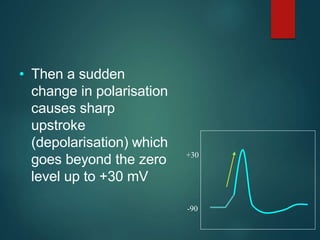
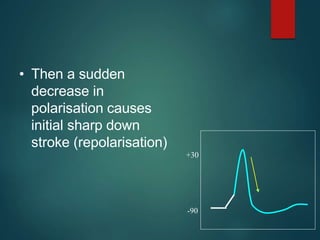
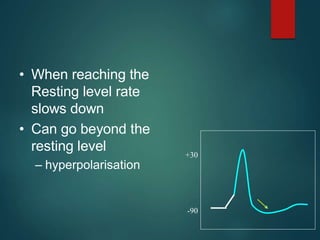
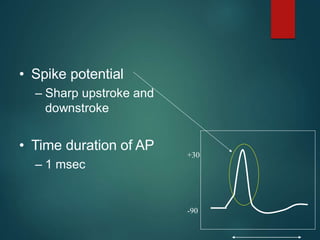
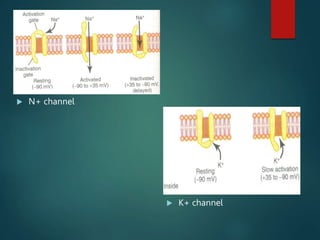
Excitable tissues are capable of generating and transmitting electrochemical impulses along cell membranes. The resting membrane potential in most neurons is around -70mV due to uneven distribution of ions like potassium and sodium across the cell membrane. When a threshold stimulus is reached, voltage-gated ion channels allow rapid sodium influx and potassium efflux, causing a brief reversal of the potential known as an action potential. This propagates the electrochemical signal along the membrane.