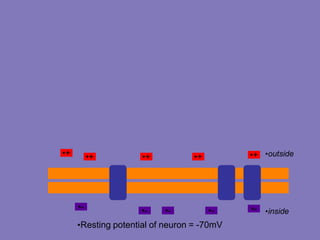
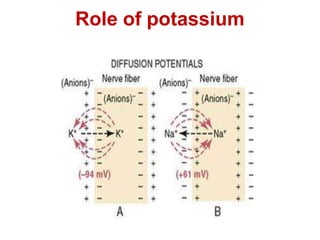
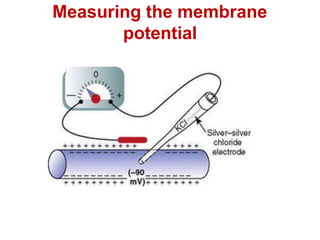
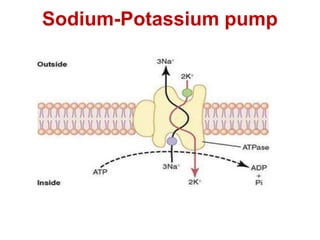
The resting membrane potential arises from three main factors: 1) Potassium diffusion produces a -86mV potential due to its higher intracellular concentration, 2) Sodium diffusion contributes a smaller potential due to its lower permeability, and 3) The sodium-potassium pump actively transports ions and contributes an additional -4mV, resulting in a total resting membrane potential of -90mV in neurons.