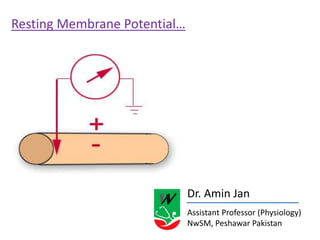
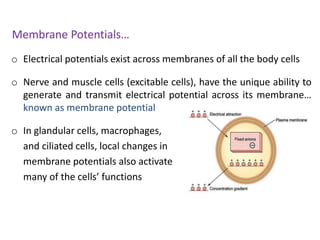
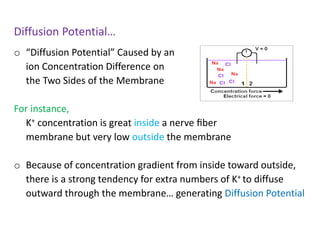
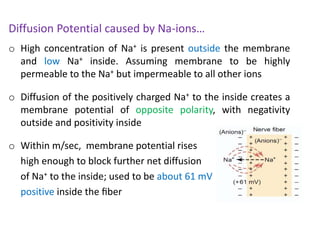
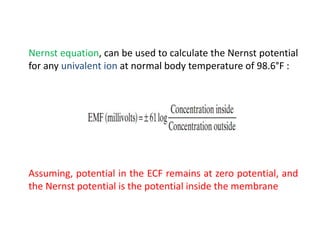
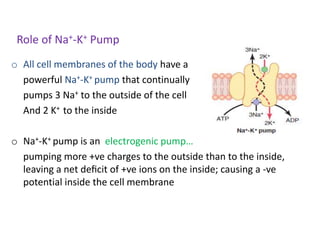
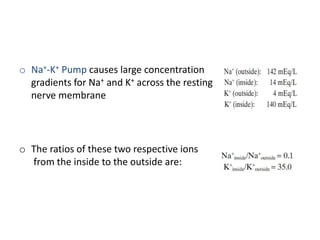
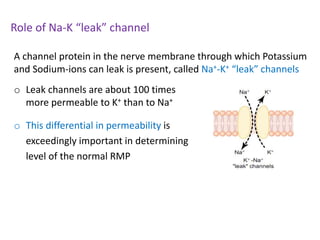
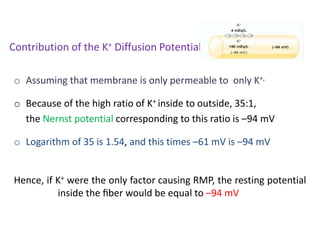
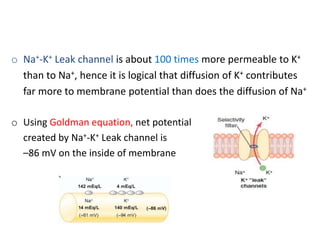
The document discusses resting membrane potential and its determinants. It begins with questions about cations involved and their contributions. It then provides details on diffusion potential, Nernst potential, the role of the sodium-potassium pump and leak channels. The resting membrane potential arises from potassium diffusion potential of -94 mV, sodium diffusion potential of +61 mV, and an additional -4 mV from the sodium-potassium pump, totaling around -90 mV.