Embed presentation
Downloaded 51 times

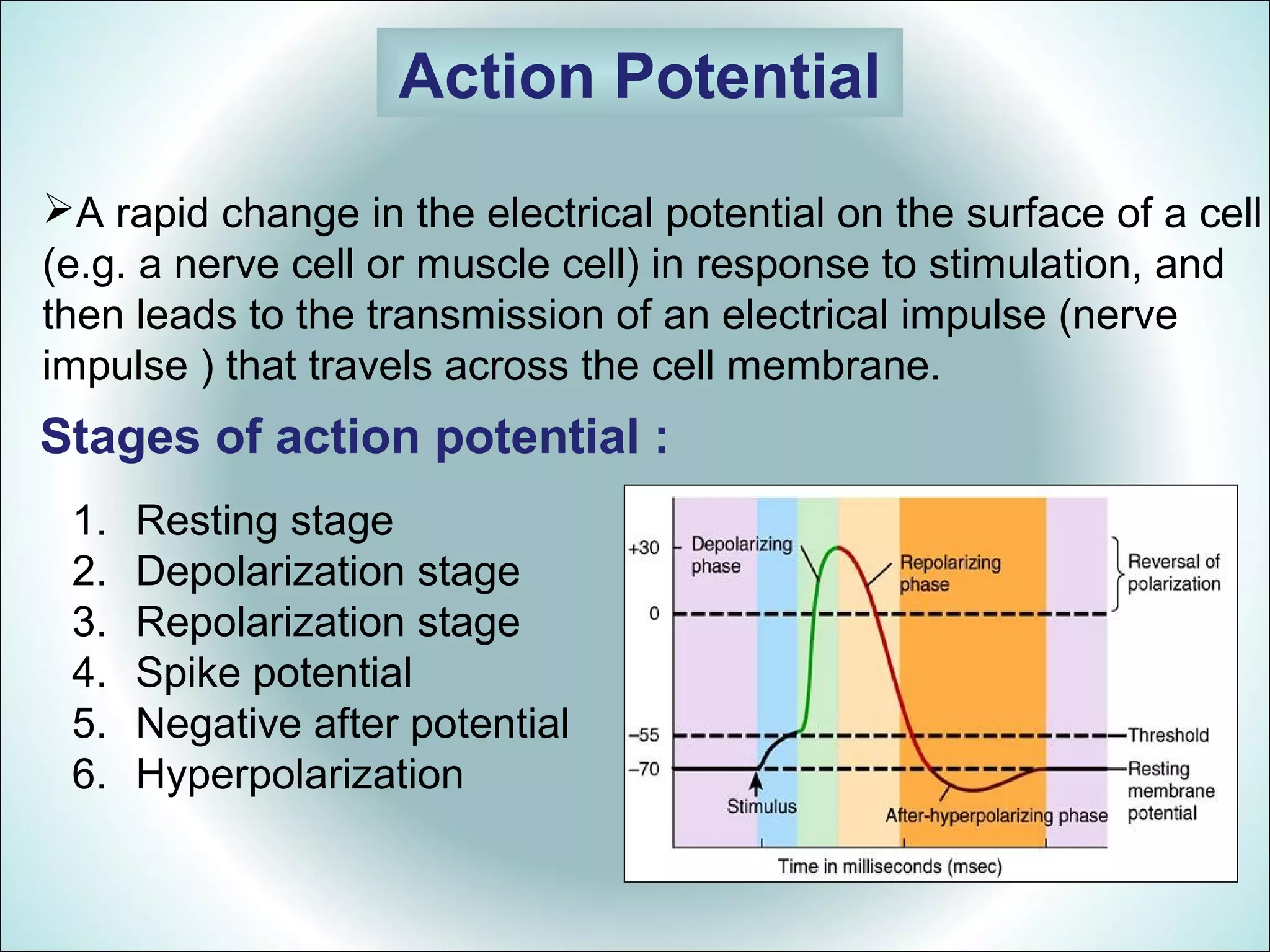
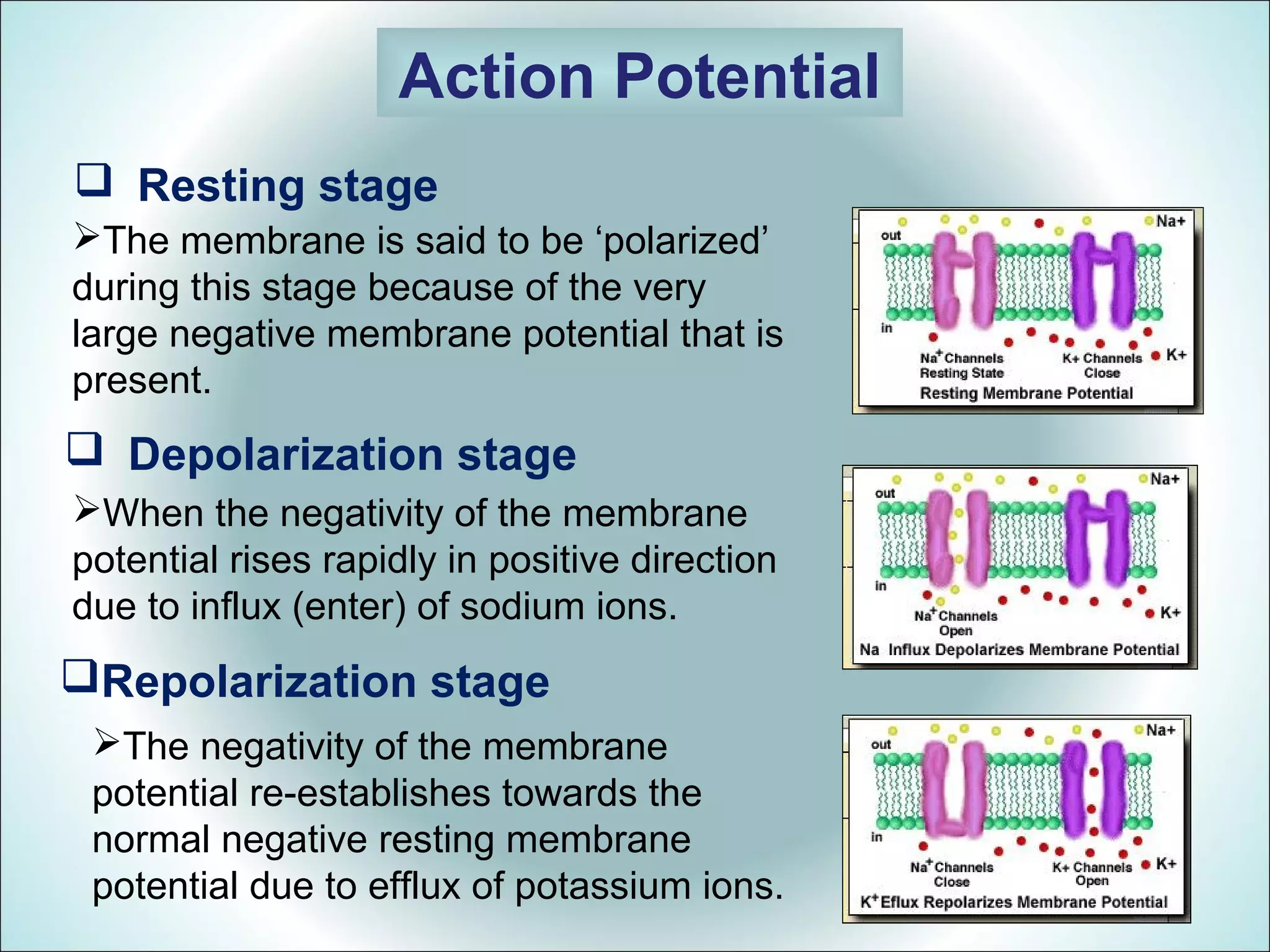
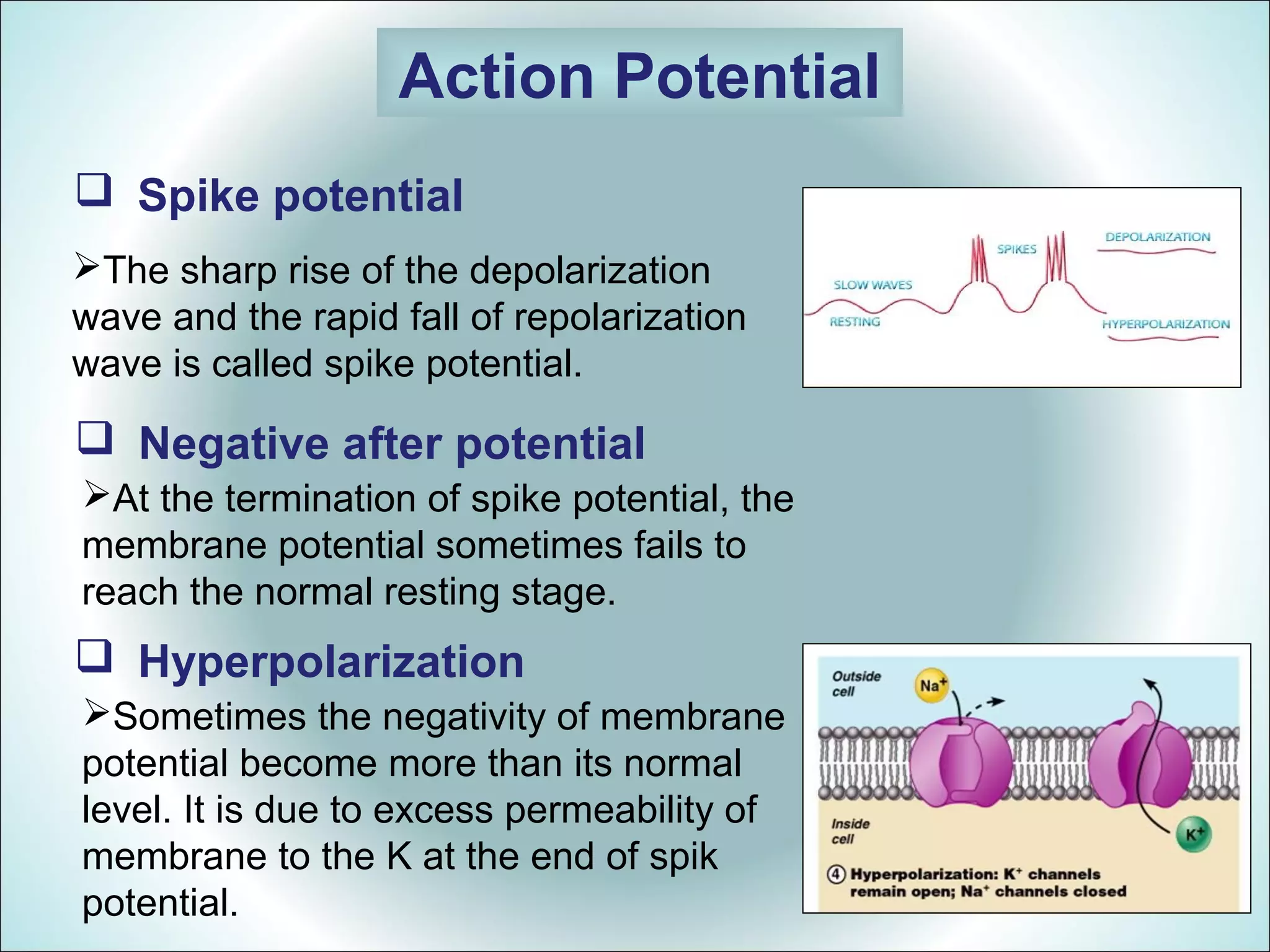
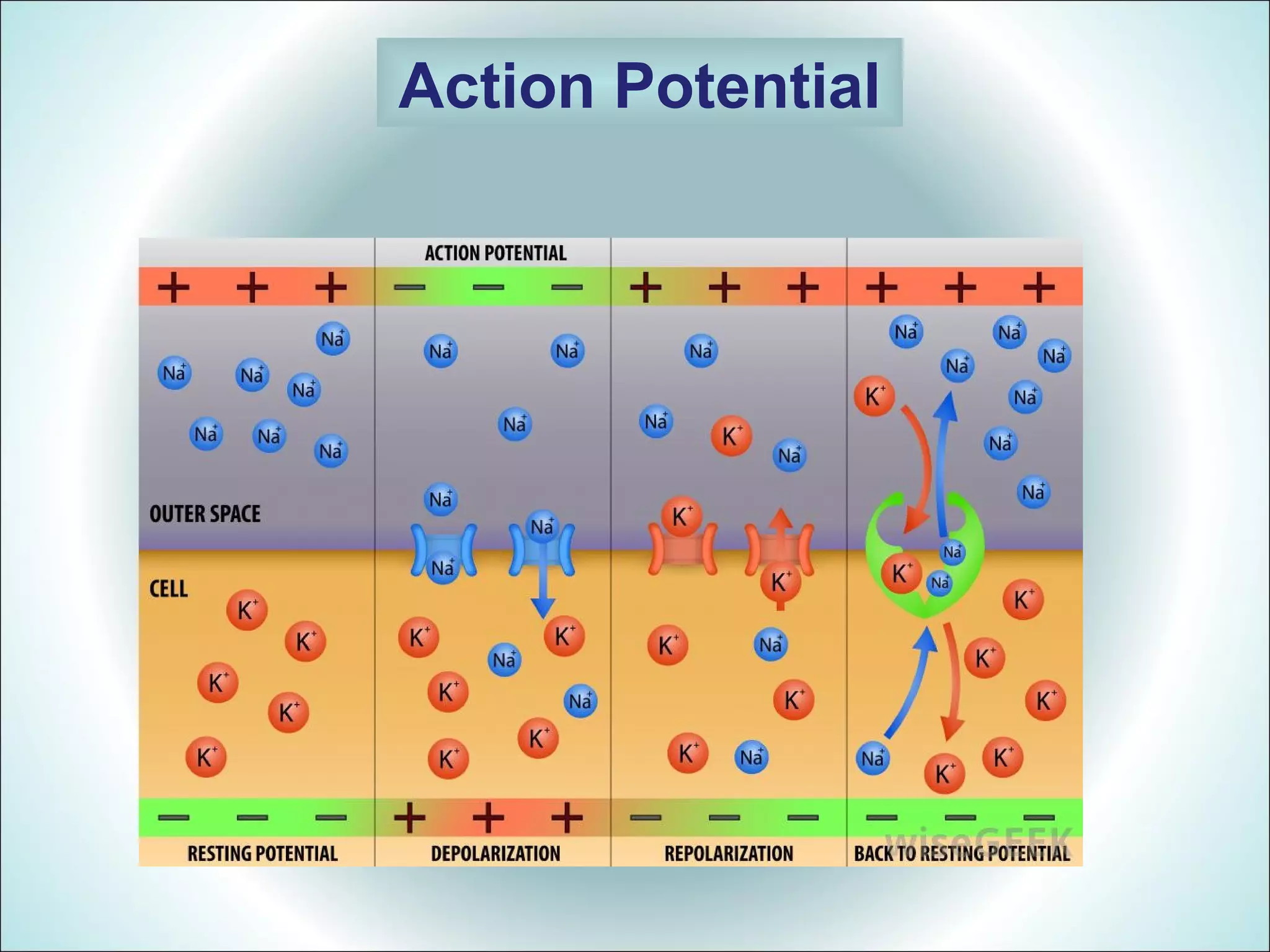



An action potential is a rapid change in the electrical potential of a nerve or muscle cell membrane in response to stimulation. It allows electrical impulses to travel across the cell membrane. There are six stages of an action potential: 1) Resting stage with a large negative potential, 2) Depolarization from sodium ion influx, 3) Repolarization by potassium ion efflux, 4) A spike potential from the sharp depolarization and repolarization waves, 5) A negative after potential where the potential does not fully return to resting, and 6) Sometimes hyperpolarization where the potential becomes more negative than resting due to excess potassium permeability.






