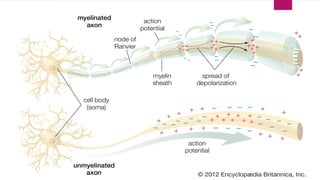
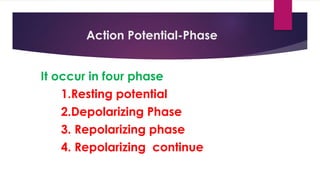
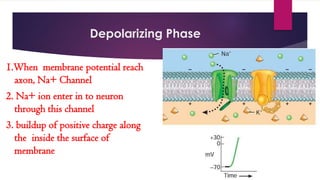
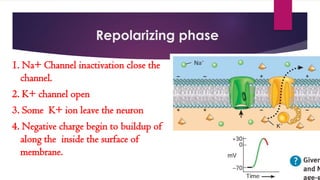
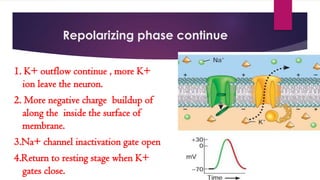
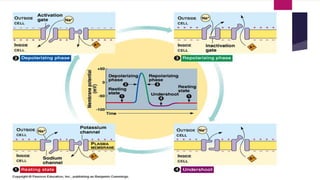
An action potential is an electrical signal that propagates along the surface of a neuron membrane due to the movement of sodium and potassium ions through specific ion channels. It occurs in four phases: 1) Resting potential with sodium and potassium channels closed, 2) Depolarization with sodium entry lowering the membrane potential, 3) Repolarization with sodium channel inactivation and potassium efflux restoring the potential, 4) Repolarization continuation with full potential restoration before returning to resting potential. This process allows an electrical signal to travel down an axon through repeated action potentials.