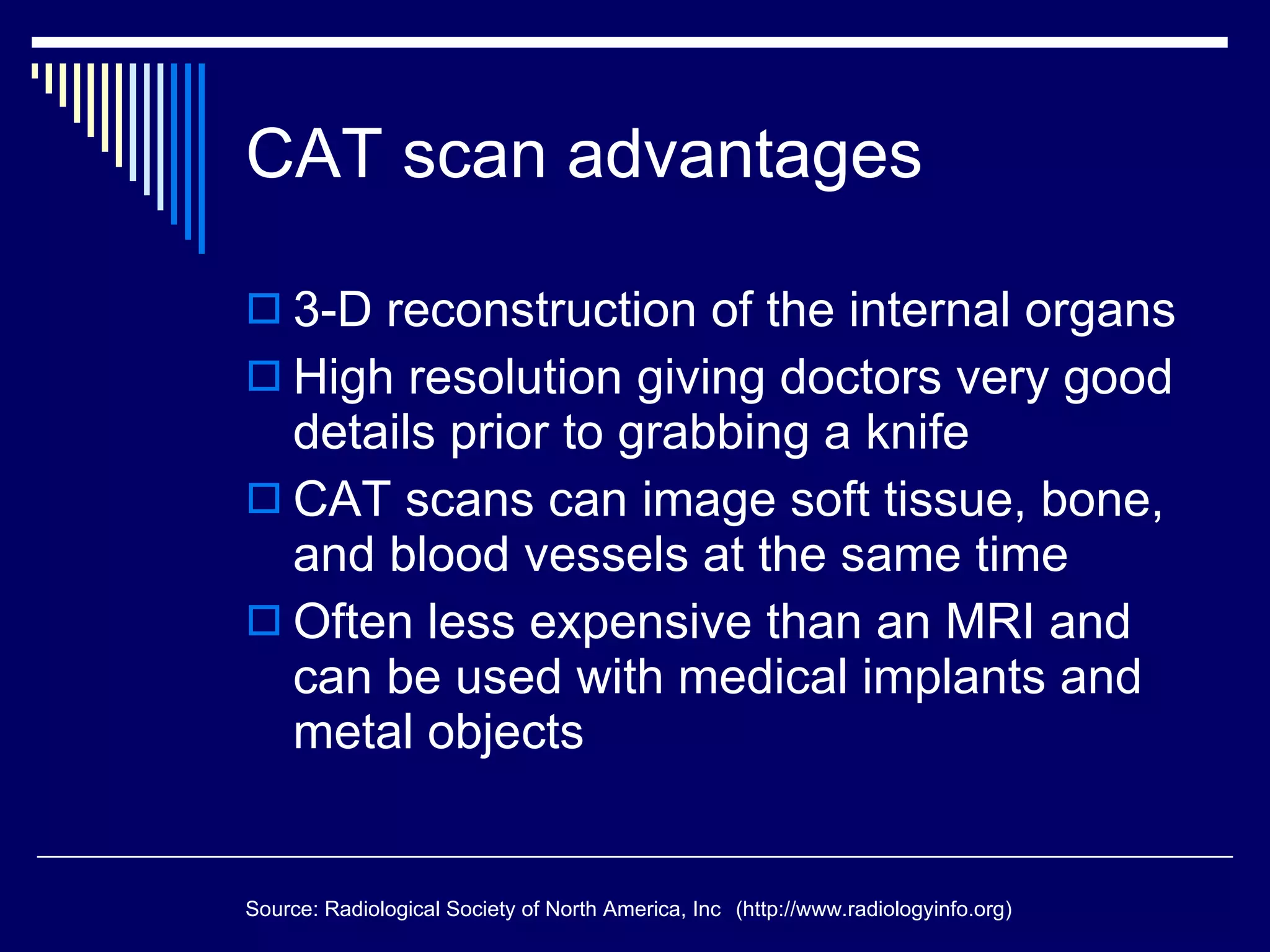
Nuclear physics has led to several important medical applications of diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment. Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT) scans use X-rays to produce cross-sectional images of the body with high resolution. Positron emission tomography (PET) scans use radioactive tracers injected into the body to detect metabolic activity and locate tumors. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues without using ionizing radiation. Radiation therapies like gamma knife radiosurgery, linear accelerators, and proton therapy also apply principles of nuclear physics to precisely target high doses of radiation to cancerous tumors.