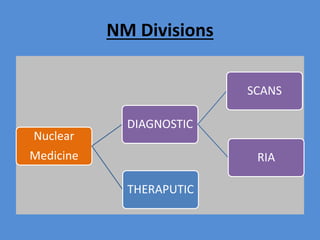
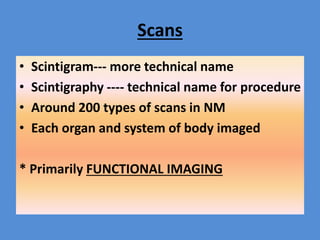
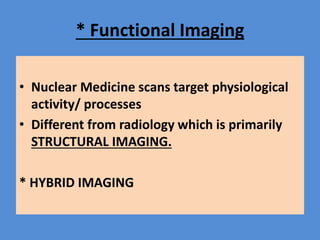
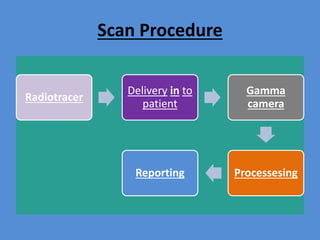
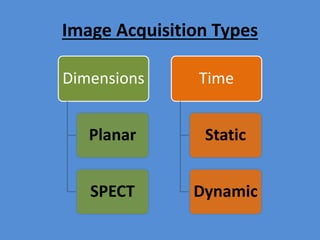
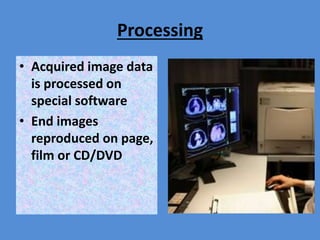
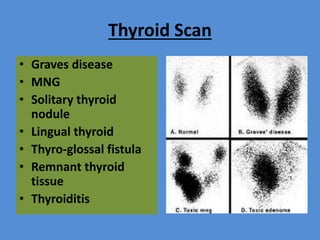
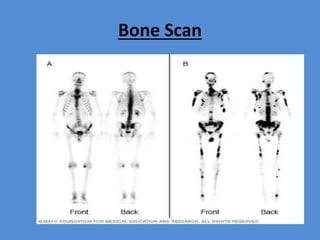
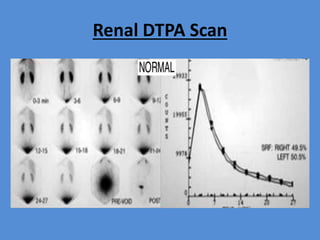
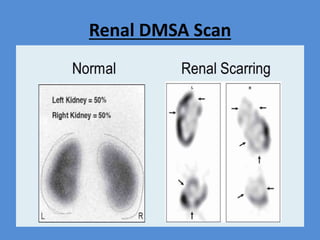
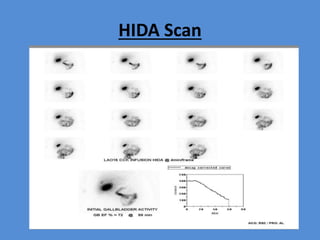
Nuclear medicine is a branch of medicine that uses radioactive tracers and imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases. It involves introducing radioactive substances into the patient's body and using a gamma camera to image their distribution and function within organs and tissues. Common nuclear medicine procedures include thyroid scans, bone scans, renal scans, and hepatobiliary scans to evaluate organ function. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an advanced nuclear medicine technique gaining importance in cancer imaging and care.