This document discusses the cyclotron, a type of particle accelerator. It begins with an introduction and overview of key topics like principles, construction, diagrams, workings, calculations, applications, and limitations. Some key points made are:
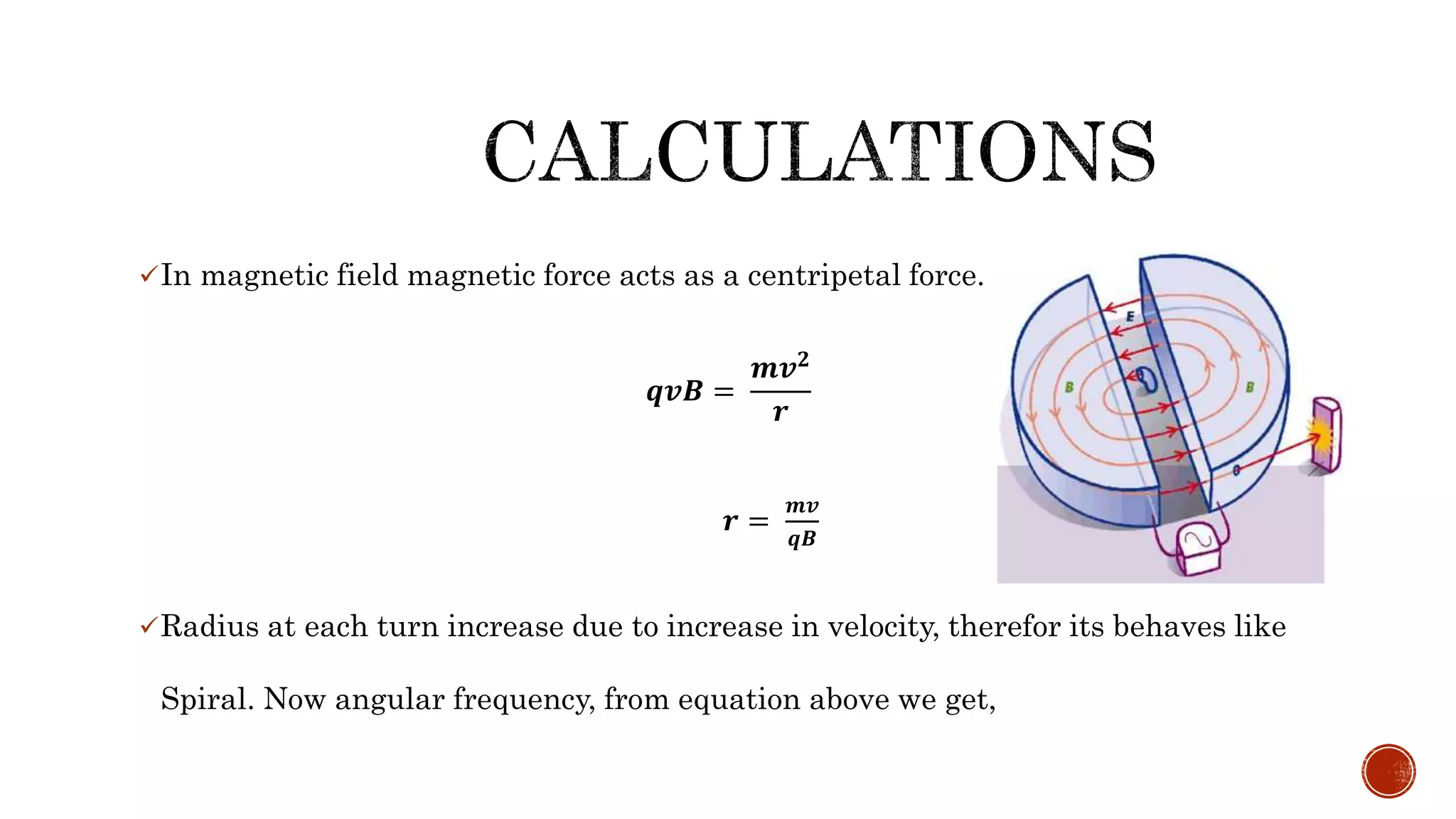
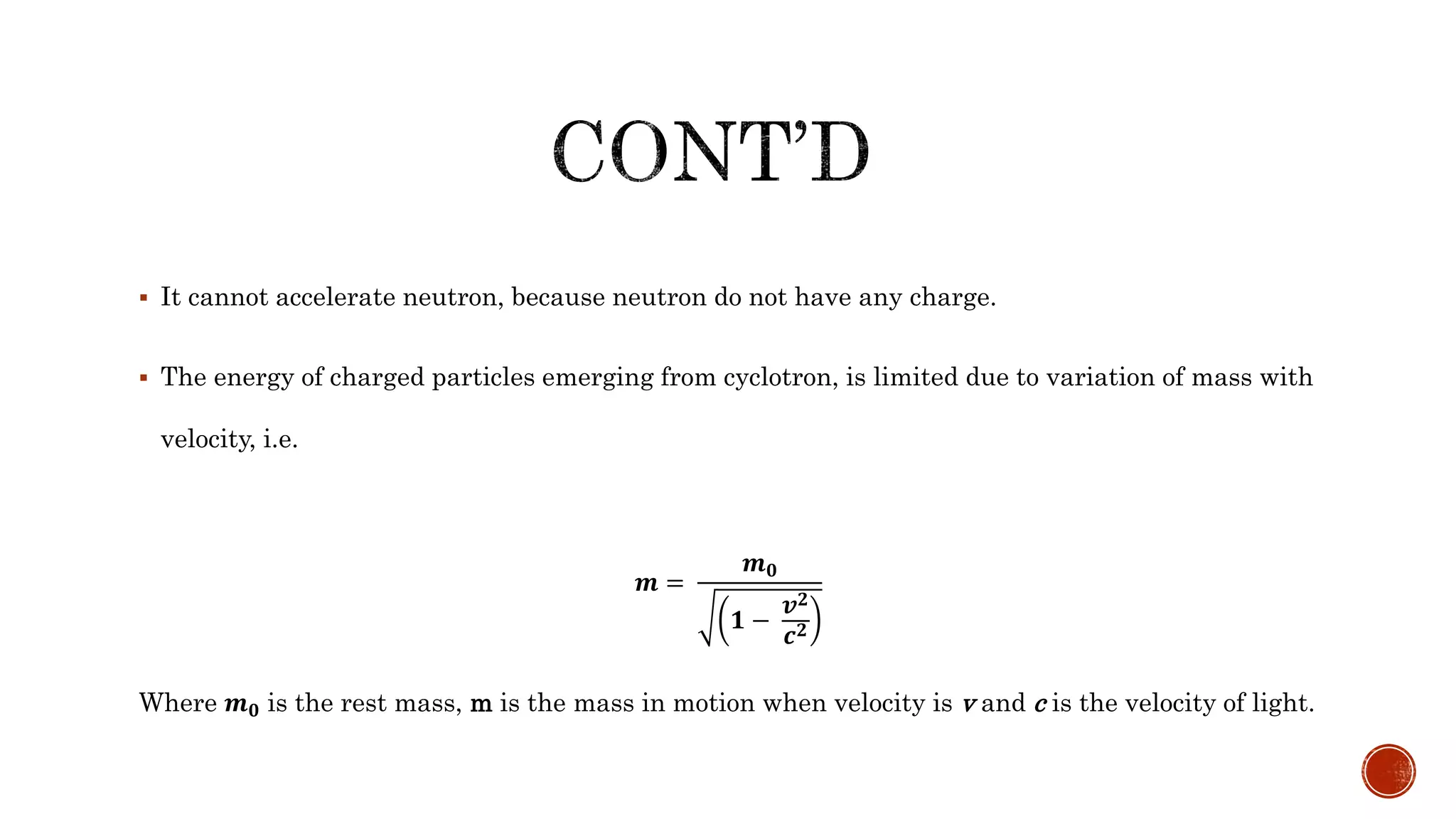
- A cyclotron accelerates charged particles like protons and deuterons using electric and magnetic fields, generating energies from 1 MeV to over 100 MeV.
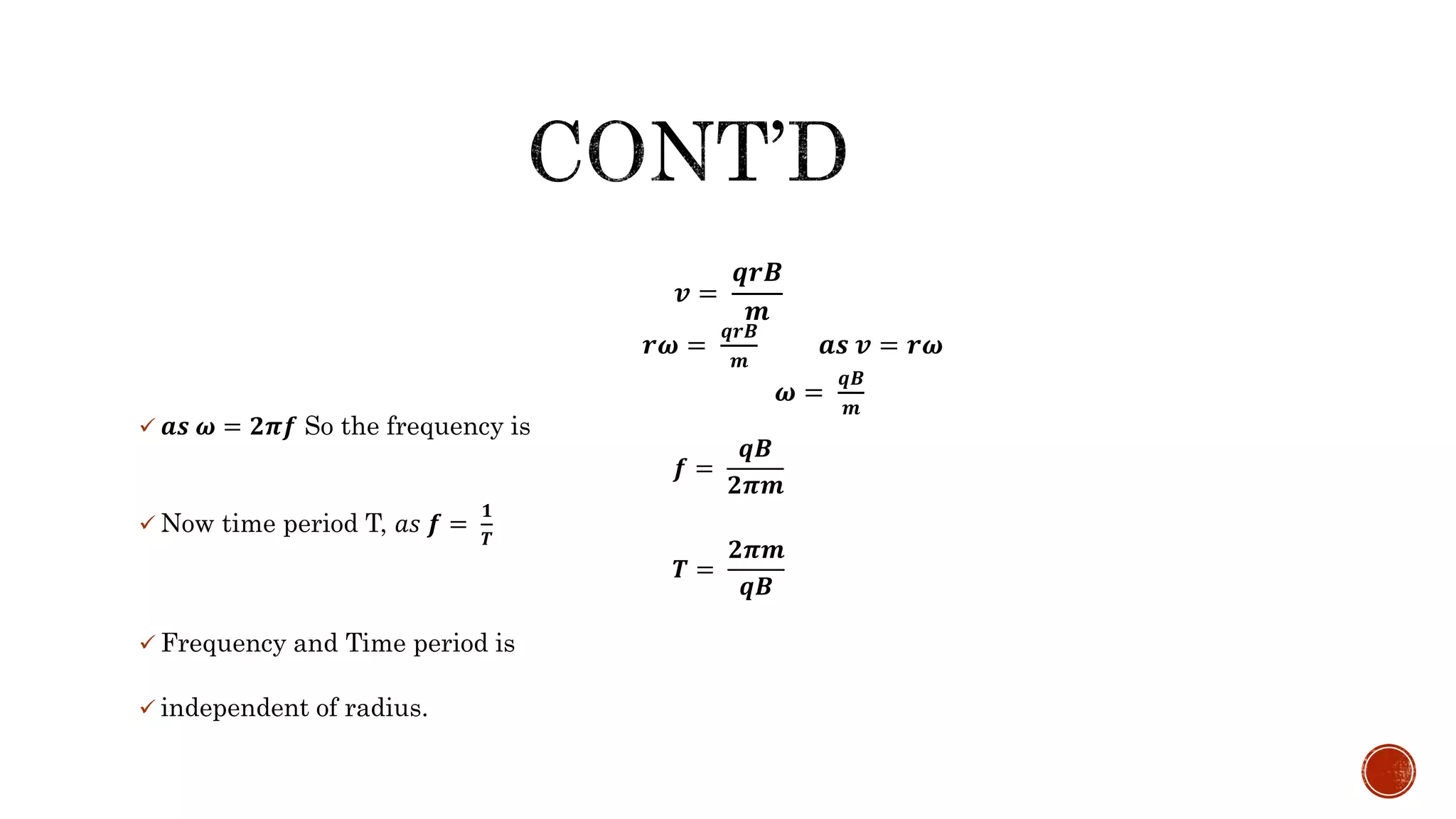
- It works on the principle that a charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field experiences a force causing it to travel in a circular path, with increasing radius and velocity over time due to an oscillating electric field.
- Important applications of cyclotrons include production of beams for nuclear physics experiments and cancer particle therapy.