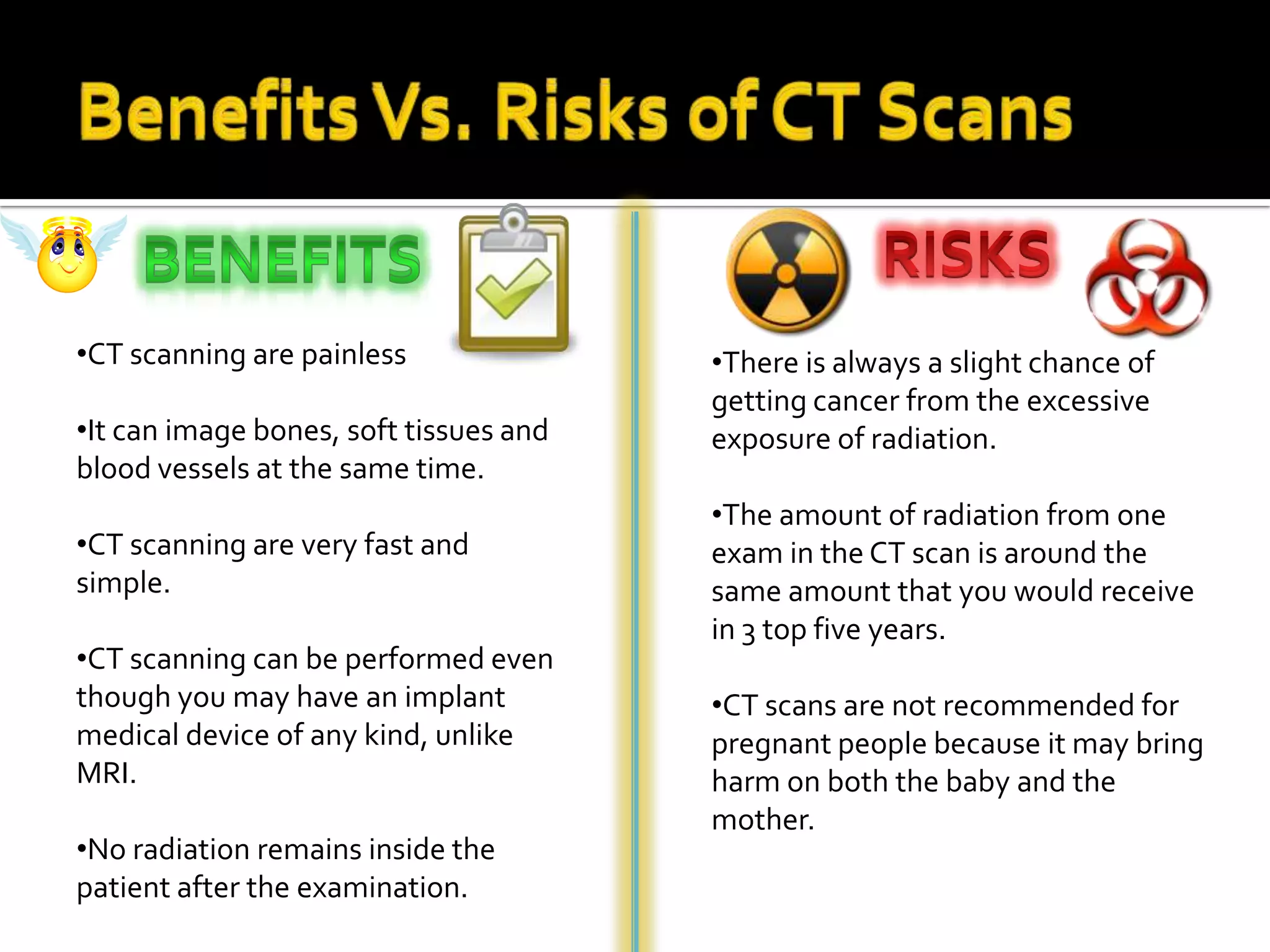
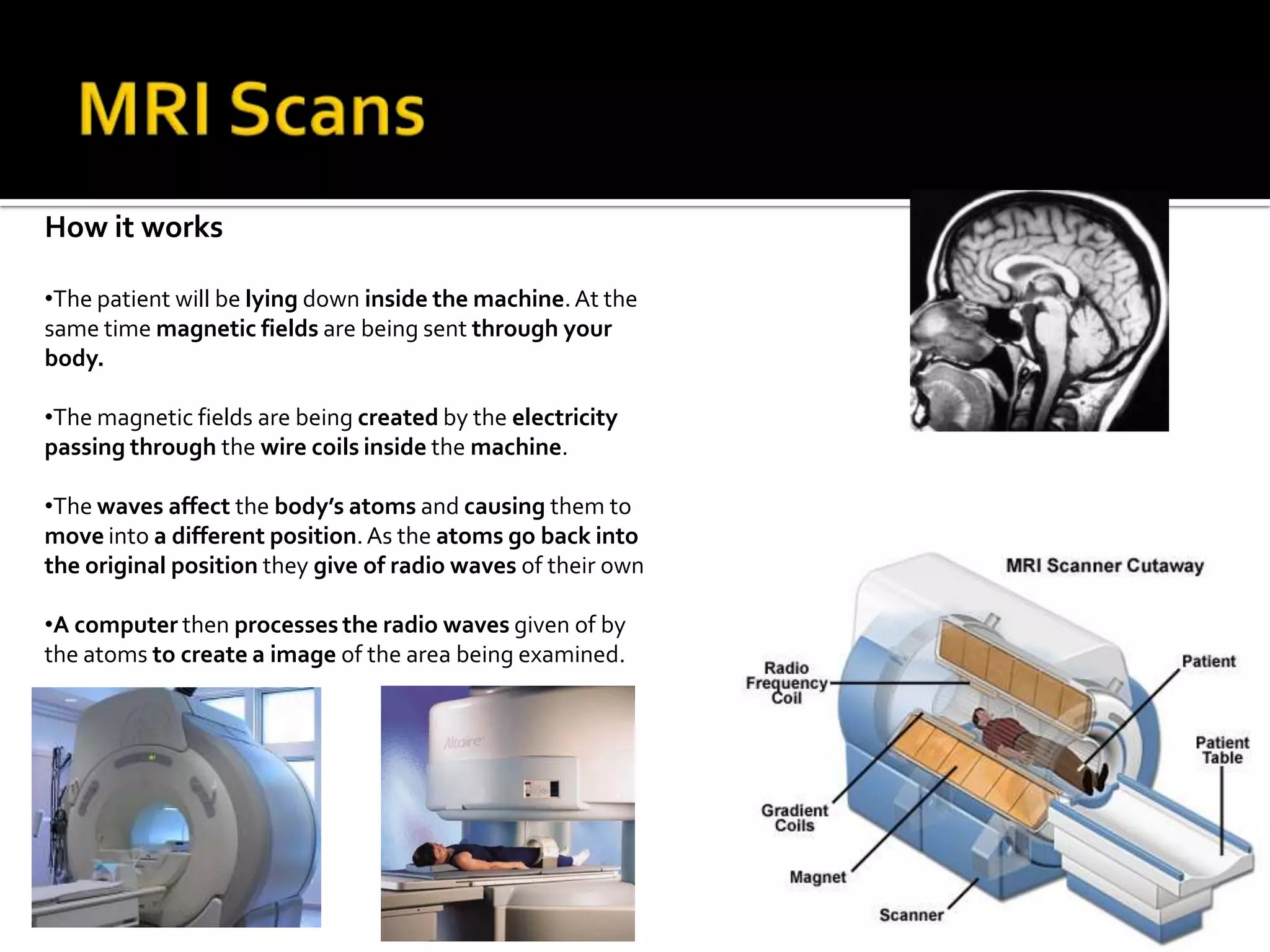
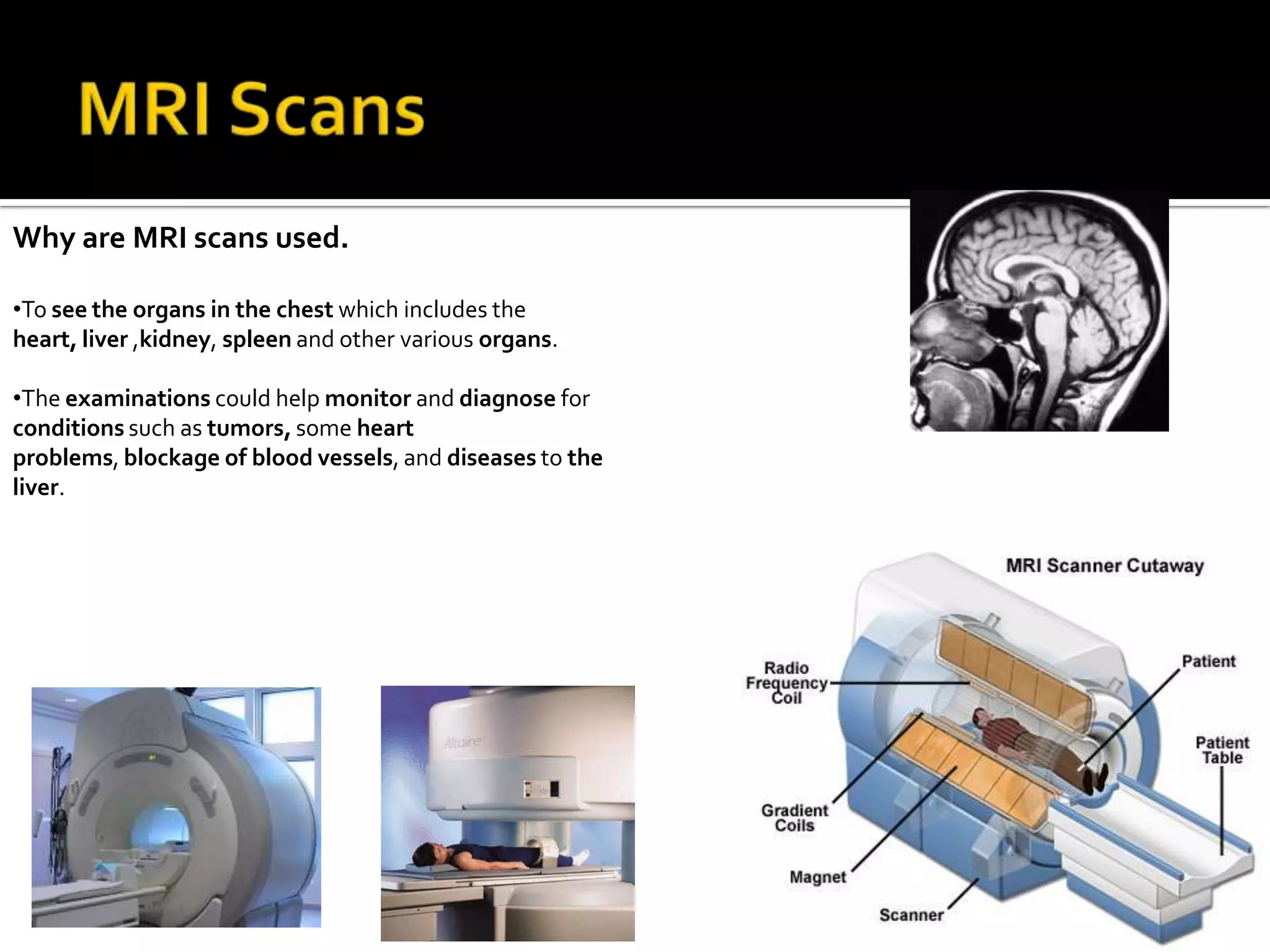
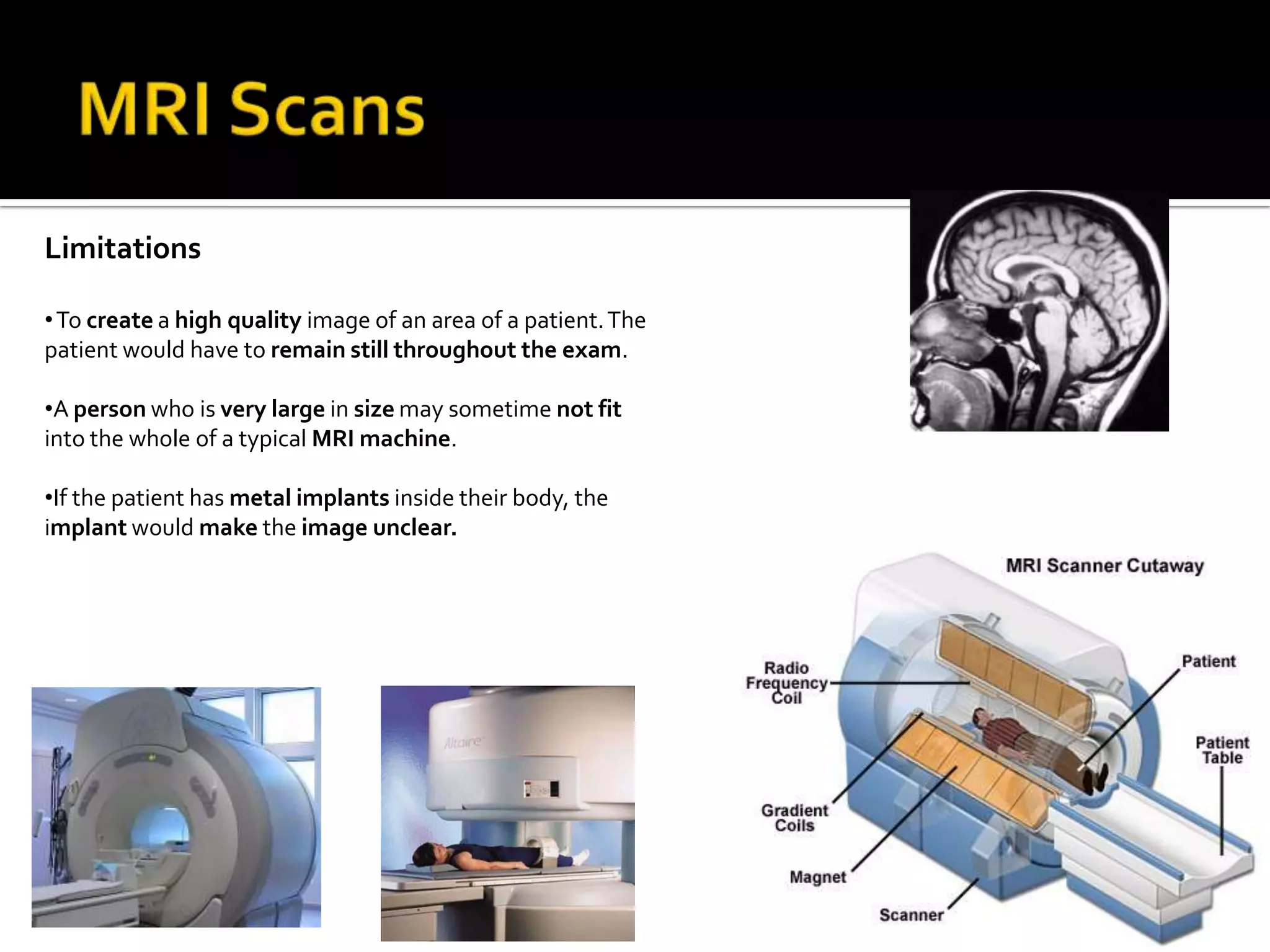
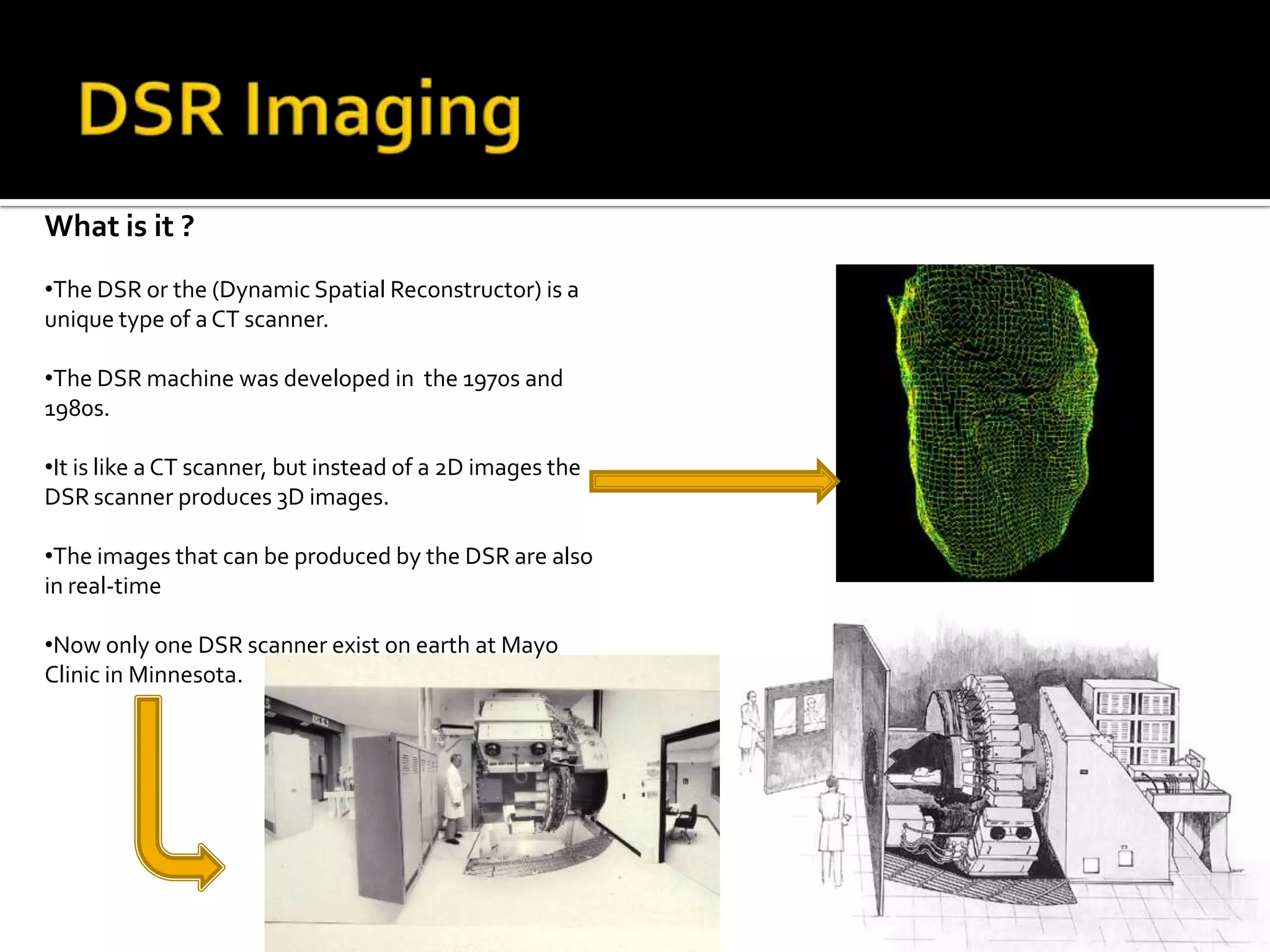
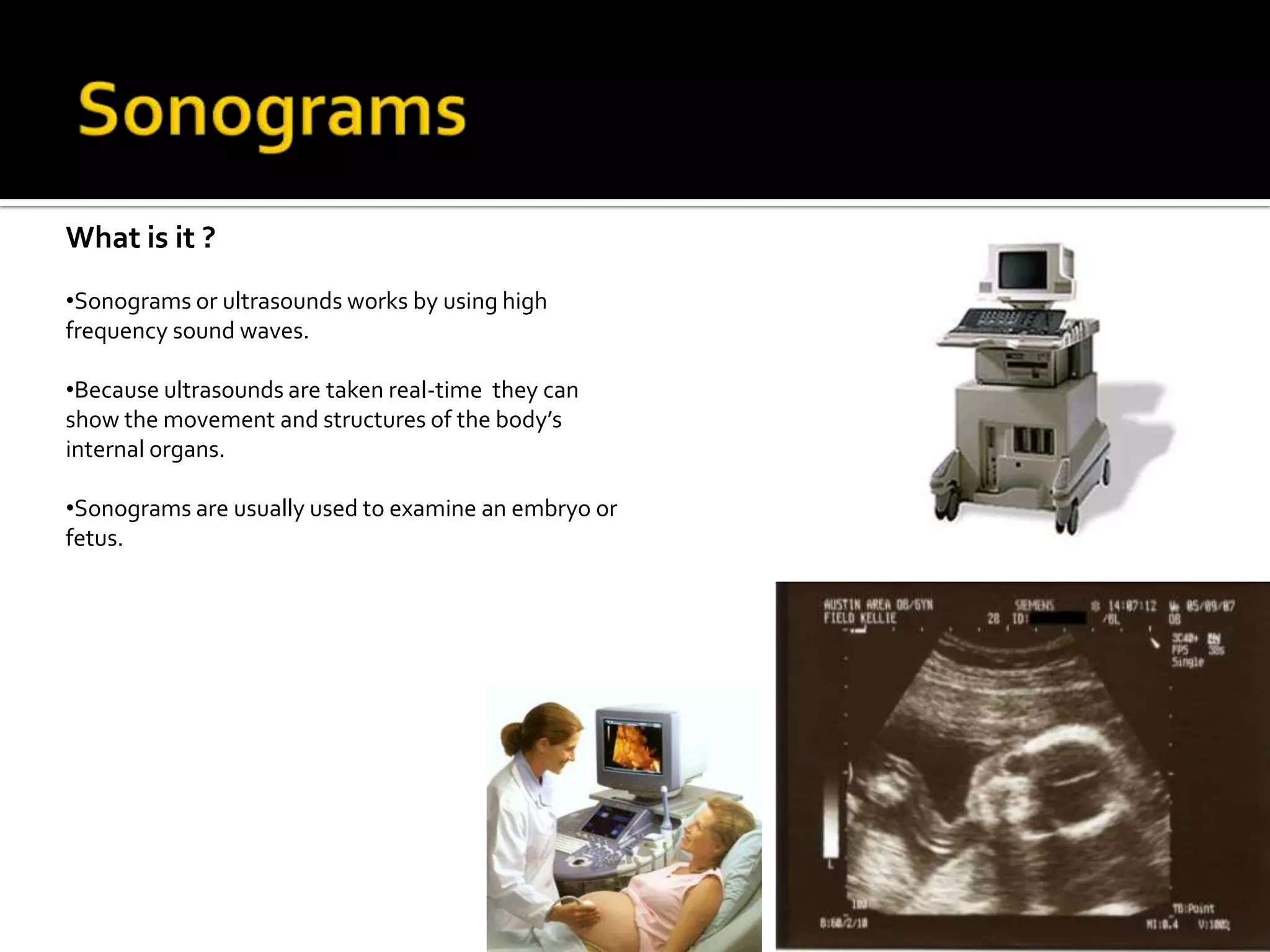
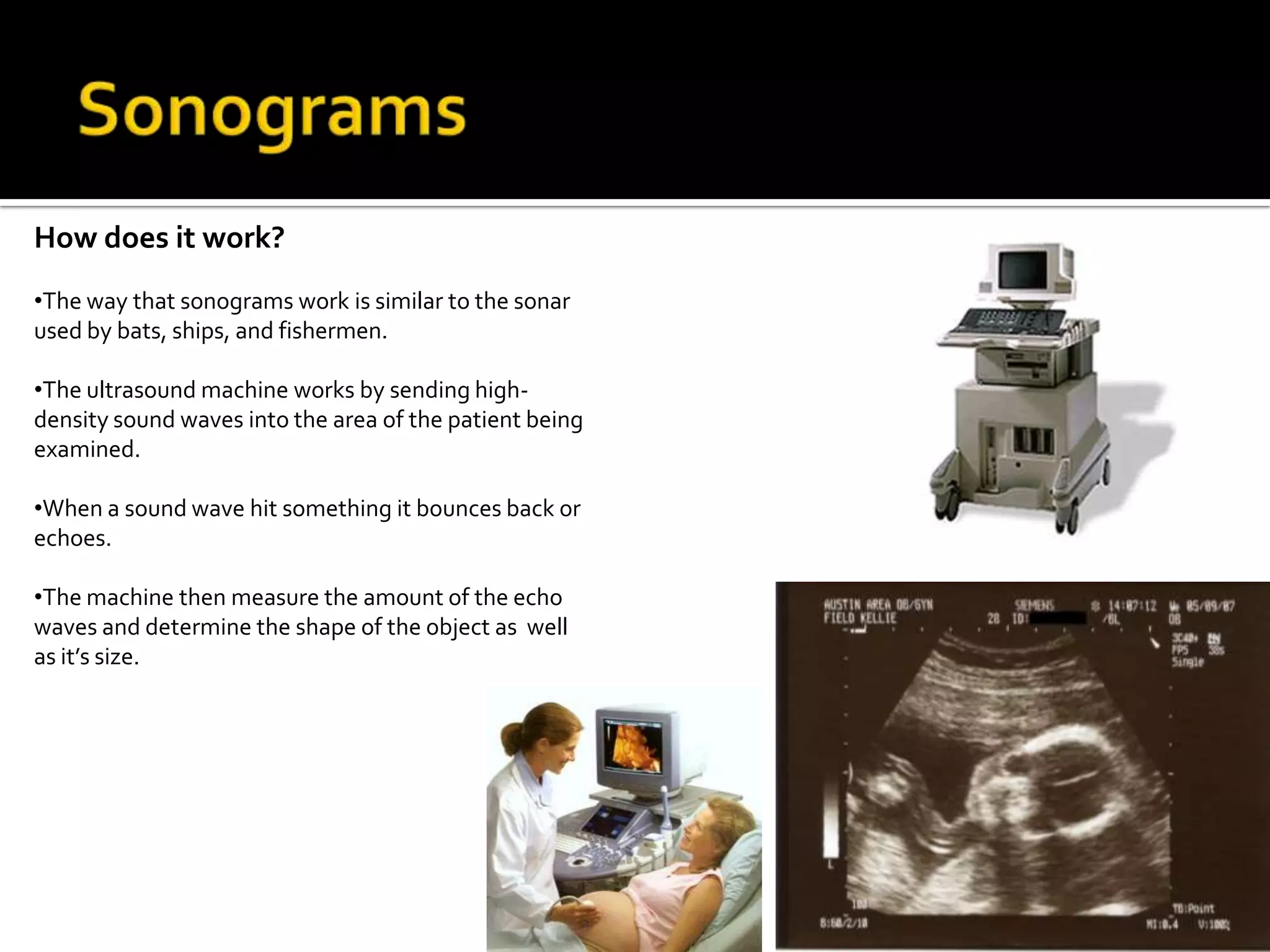
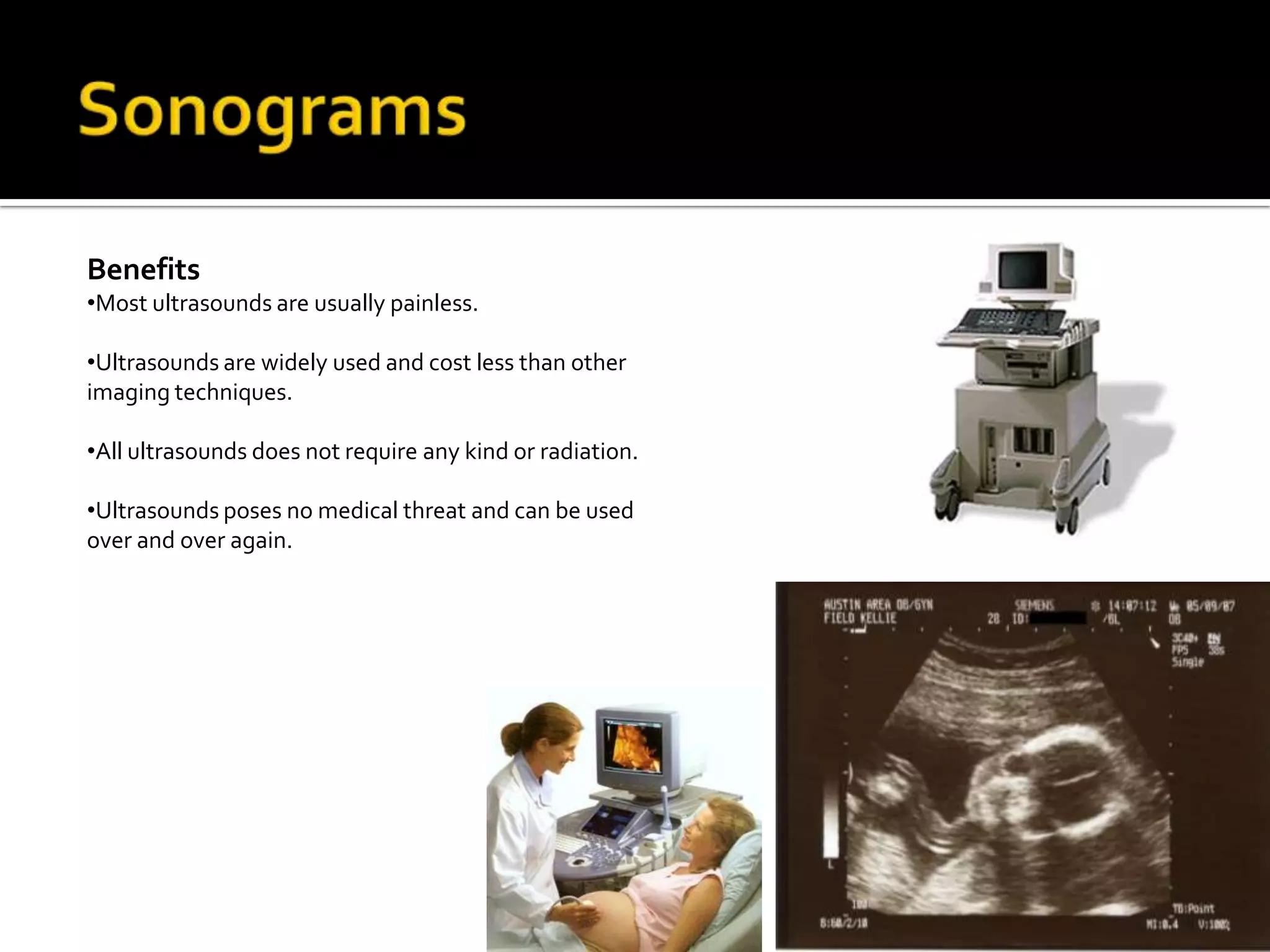
The document summarizes various medical imaging machines including CT scans, PET scans, MRI scans, DSR scans, and sonograms. CT scans use X-rays and computers to produce cross-sectional images of the body. PET scans use radioactive tracers to detect cancer and other diseases. MRI scans use magnetic fields to produce detailed images of organs and soft tissues without radiation. DSR scans produce real-time 3D images while sonograms use ultrasound to image fetuses and internal organs in real-time without radiation.