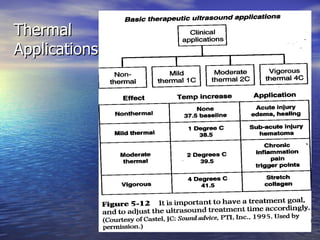
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to produce either thermal or non-thermal effects in tissues. It works by using a transducer that converts electrical energy into longitudinal sound waves through the piezoelectric effect. These waves can be used for diagnostic imaging or to accelerate tissue healing by increasing blood flow and the activity of immune cells through both thermal and non-thermal mechanisms of action. The document provides details on ultrasound wave properties, transducer types, intensities, and clinical applications.