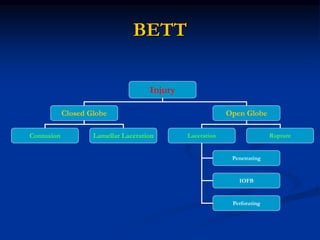
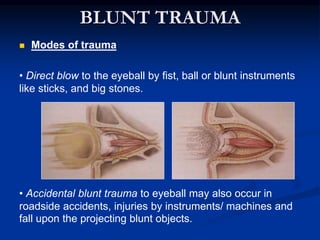
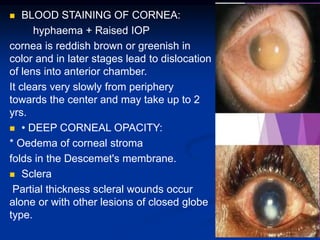
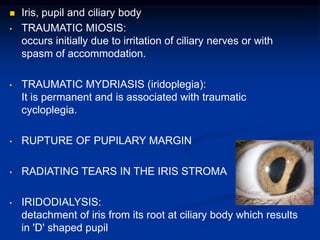
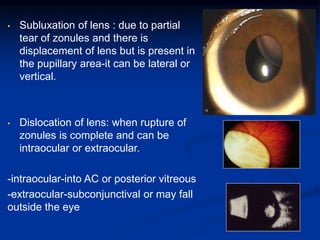
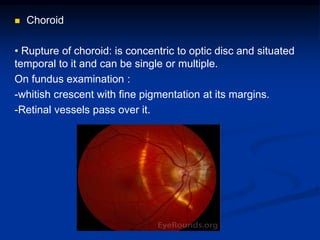
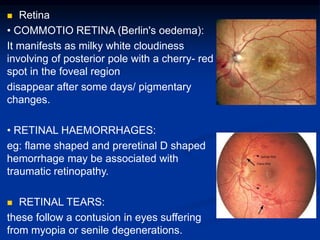
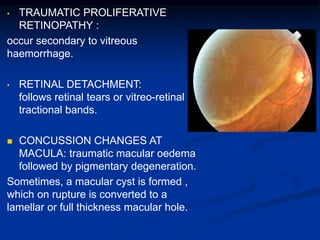
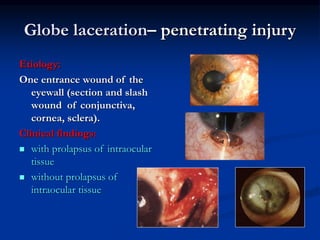
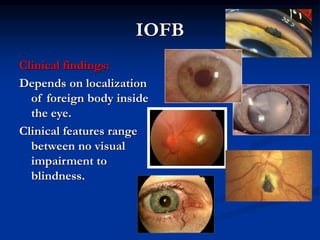
Mechanical ocular trauma can cause a wide range of eye injuries from relatively minor to vision threatening. The document defines standard terminology for different types of eye injuries using the Birmingham Eye Trauma Terminology (BETT) system. It describes closed globe injuries which involve no penetration of the eyewall, open globe injuries which involve penetration of the eyewall, and different types of open globe injuries including globe rupture, penetrating injuries, and perforating injuries. It provides details on mechanisms of injury, clinical findings, examination techniques, and treatment approaches for different injury types.