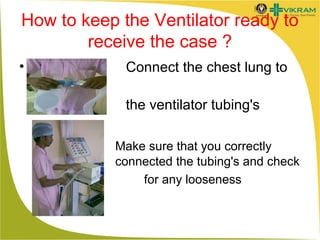
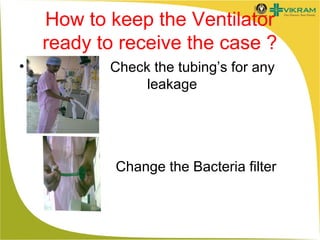
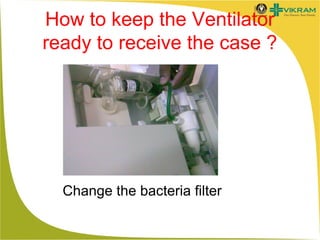
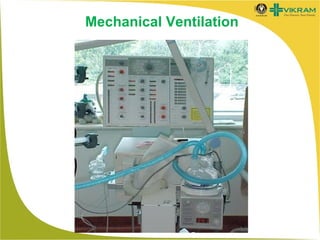
Mechanical ventilation involves using a machine to assist or replace spontaneous breathing. It is commonly used in ICUs for patients with acute respiratory failure or distress. Some key points:
- There are two main types - negative pressure ventilation uses suction to pull air into the lungs, while positive pressure ventilation pushes air into the lungs.
- Indications for use include respiratory acidosis, hypoxemia, increased work of breathing, and neurological/pulmonary conditions.
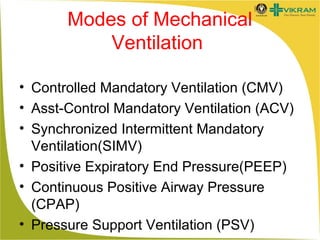
- Common modes include controlled mandatory ventilation (CMV), assisted-control (AC), and synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV).
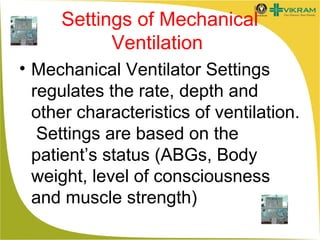
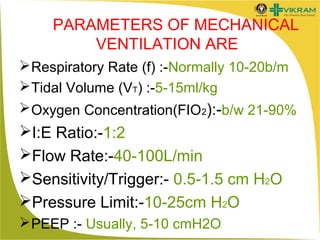
- Settings are based on parameters like respiratory rate, tidal volume, oxygen concentration, and pressures.


![History
The roman physician Galen may have been the
first to describe mechanical ventilation: "If you take
a dead animal and blow air through its larynx
[through a reed], you will fill its bronchi and watch
its lungs attain the greatest distention.” Vesalius
too describes ventilation by inserting a reed or
cane into the trachea of animals. In 1908 George
Poe demonstrated his mechanical respirator by
asphyxiating dogs and seemingly bringing them
back to life.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilation-131223004609-phpapp01/85/Mechanical-ventilation-5-320.jpg)