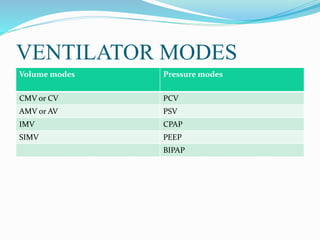
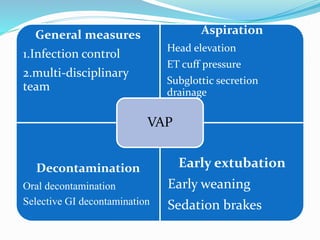
Mechanical ventilation is a method used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing by using physical devices. It can be used to treat acute respiratory failure, provide prophylactic support, or induce hyperventilation. There are two main types: negative pressure ventilation which applies lower pressure outside the chest and positive pressure ventilation which applies higher pressure inside the lungs. Common ventilator modes include assist control, SIMV, pressure control, and pressure support. Proper monitoring, settings, and care are needed to prevent complications while the patient is ventilated.