- Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) uses a mask to deliver bi-level positive airway pressure to improve gas exchange and reduce work of breathing without using an invasive tube.
- NIV aims to improve gas exchange, reduce shortness of breath, avoid invasive ventilation, and reduce length of stay.
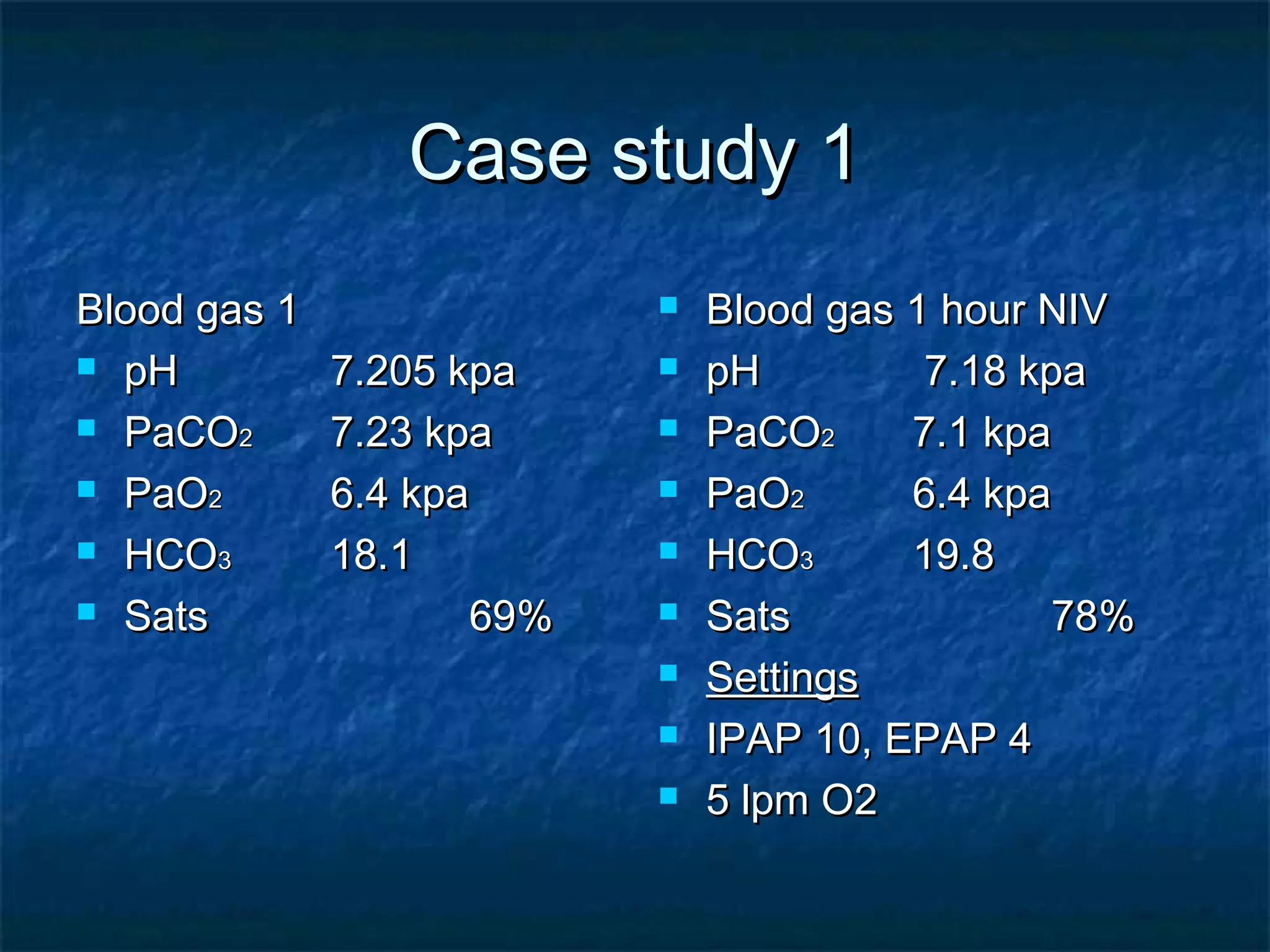
- It is indicated for type 2 respiratory failure with a pH between 7.25-7.35. Patients outside this range may require ICU care.
- Patients must be able to protect their airway, cooperate, and clear secretions. Contraindications include recent surgery or trauma, vomiting, and impaired consciousness.
- Settings are initially IPAP 10 and EPAP 4 but adjusted