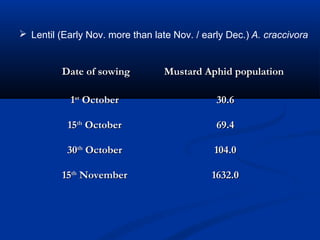
This document discusses important aphid pests and their management through cultural practices. It lists the main aphid species that infect various crops like mustard, cabbage, cotton and describes how early sowing dates can help escape damage. Plant spacing, intercropping, removal of alternate hosts, use of trap crops and resistant varieties are recommended cultural controls. The role of water, fertility, pruning and natural enemies in aphid population dynamics is also covered. Future research needs on monitoring population dynamics under different conditions is suggested.