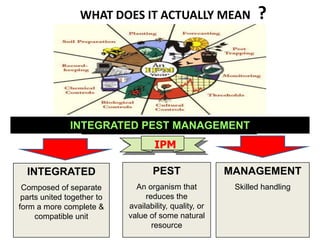
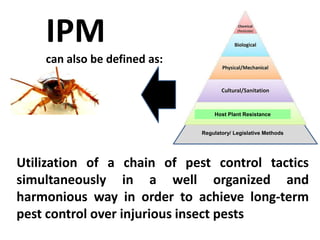
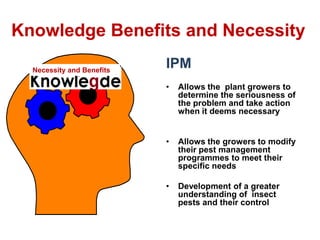
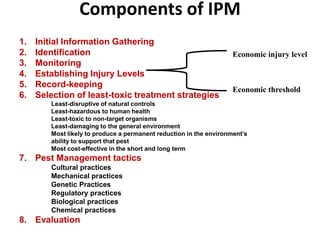
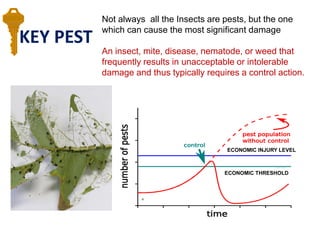
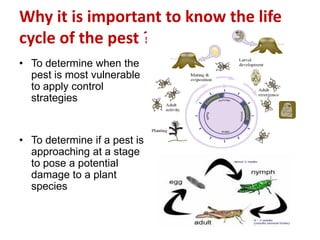
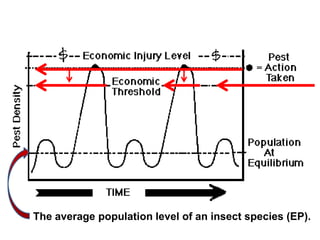
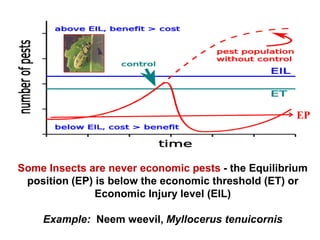
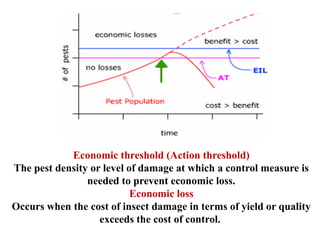
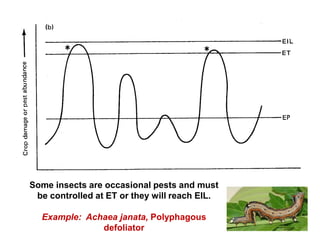
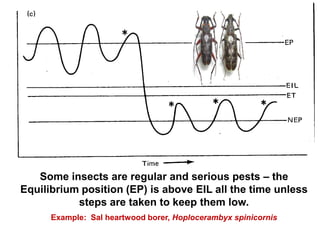
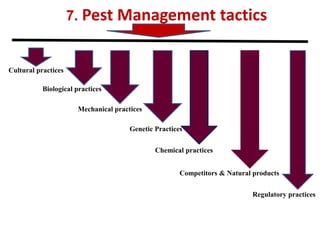
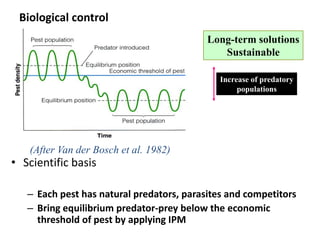
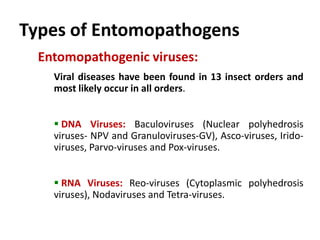
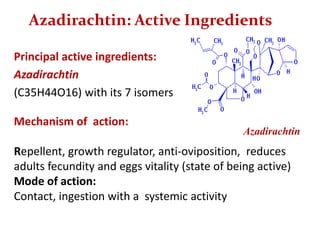
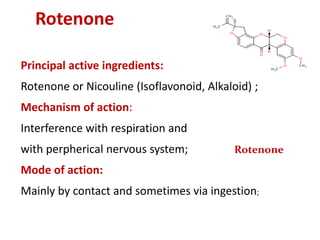
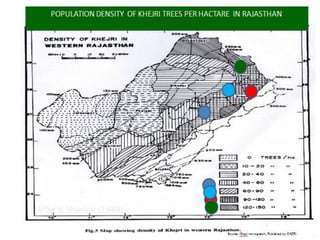
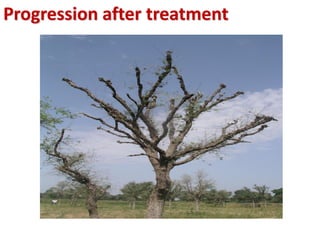
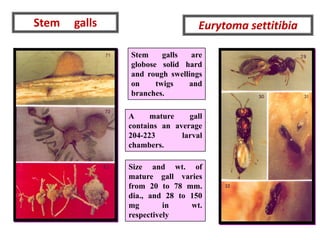
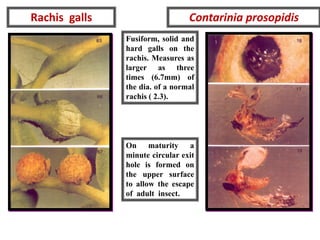
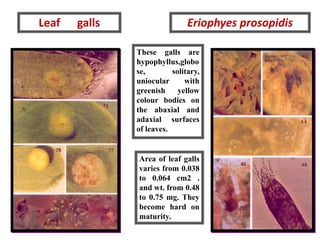
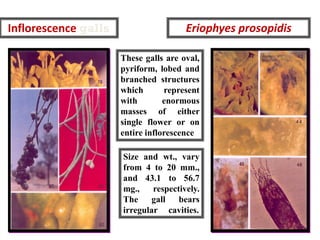
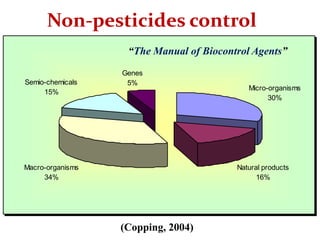
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) utilizes various pest control tactics together in a harmonious way to achieve long-term pest control. The key components of IPM include gathering initial information, correctly identifying pests, monitoring pest populations, establishing economic injury levels, record keeping, selecting least-toxic treatment strategies, and evaluating treatments. Cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical practices are among the pest management tactics used in IPM. The logic and necessity of IPM includes potential economic benefits from reduced pesticide use, environmental benefits from decreased contamination, and knowledge benefits from a better understanding of pests and their management.