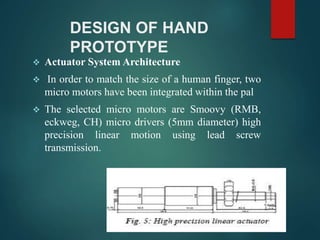
The document discusses the design of a biomechatronic hand prototype. It introduces biomechatronics and prosthetics as artificial replacements for missing body parts. It then describes the design of the hand prototype, including the use of micro motors and lead screws for finger actuation. Position and force sensors are integrated to provide feedback. Experimental tests analyzed the force exerted by individual fingers. Advantages include independence for handicapped individuals while disadvantages are high costs and limited load capacity. Current research institutions in the field are also listed before concluding with challenges in implementing neural control interfaces.