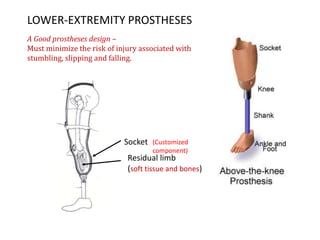
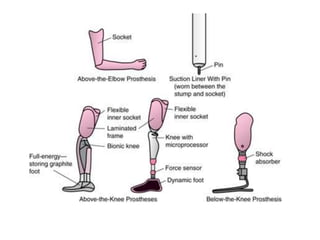
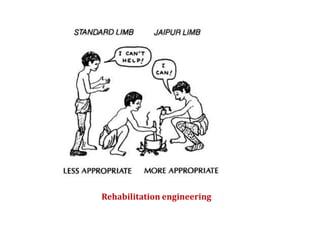
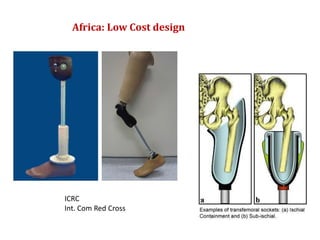
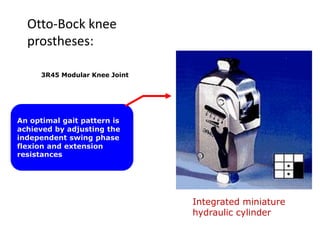
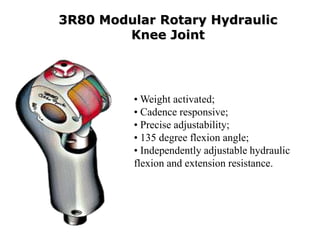
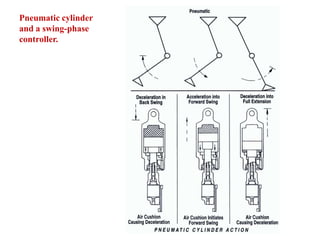
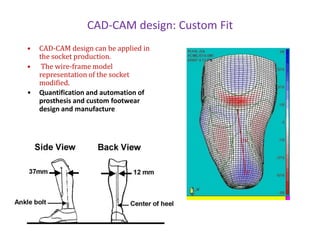
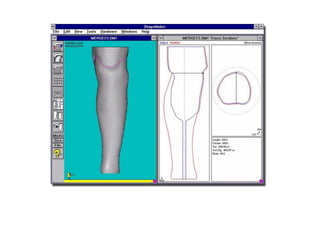
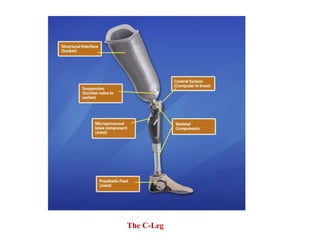
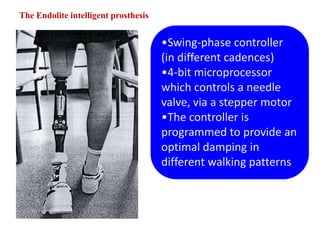
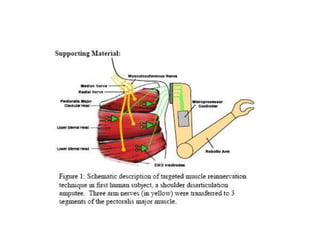
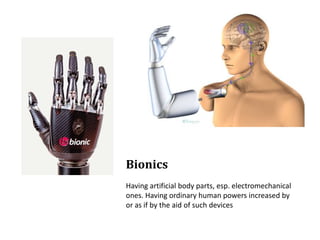
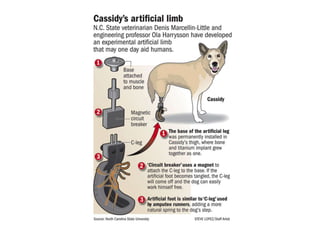
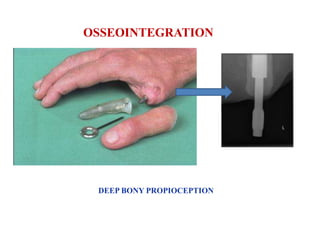
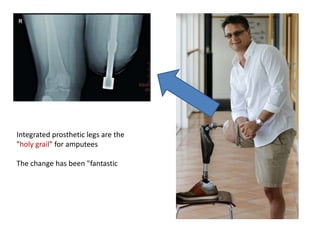
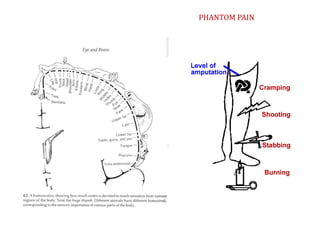
The document summarizes the evolution of artificial limbs from ancient Egypt to modern times. It discusses some of the earliest known prosthetics from ancient Egypt dating back to 2750-2625 BC. It then outlines key developments in prosthetics throughout history from ancient Greece and Rome to modern innovations like the Jaipur Foot, microprocessor knees, myoelectric arms, and cutting edge research into areas like osseointegration and mind-controlled prosthetics.