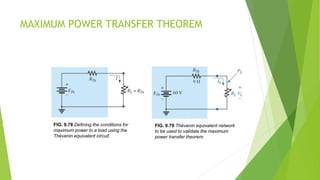
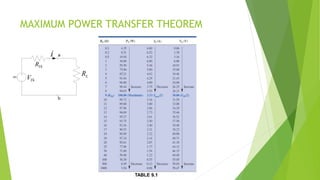
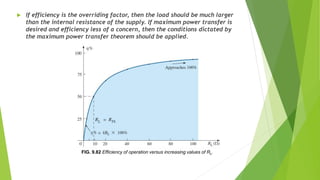
1) The maximum power transfer theorem states that maximum power is delivered to a load when its resistance equals the internal resistance of the voltage source, as represented by the Thevenin equivalent circuit.
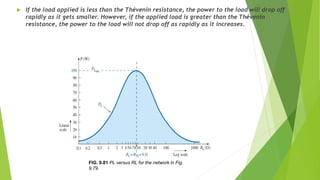
2) When the load resistance is less than the Thevenin resistance, the power delivered to the load decreases rapidly as the load resistance decreases.
3) For maximum power transfer, the load resistance should be set equal to the Thevenin resistance according to the maximum power transfer theorem.