Embed presentation
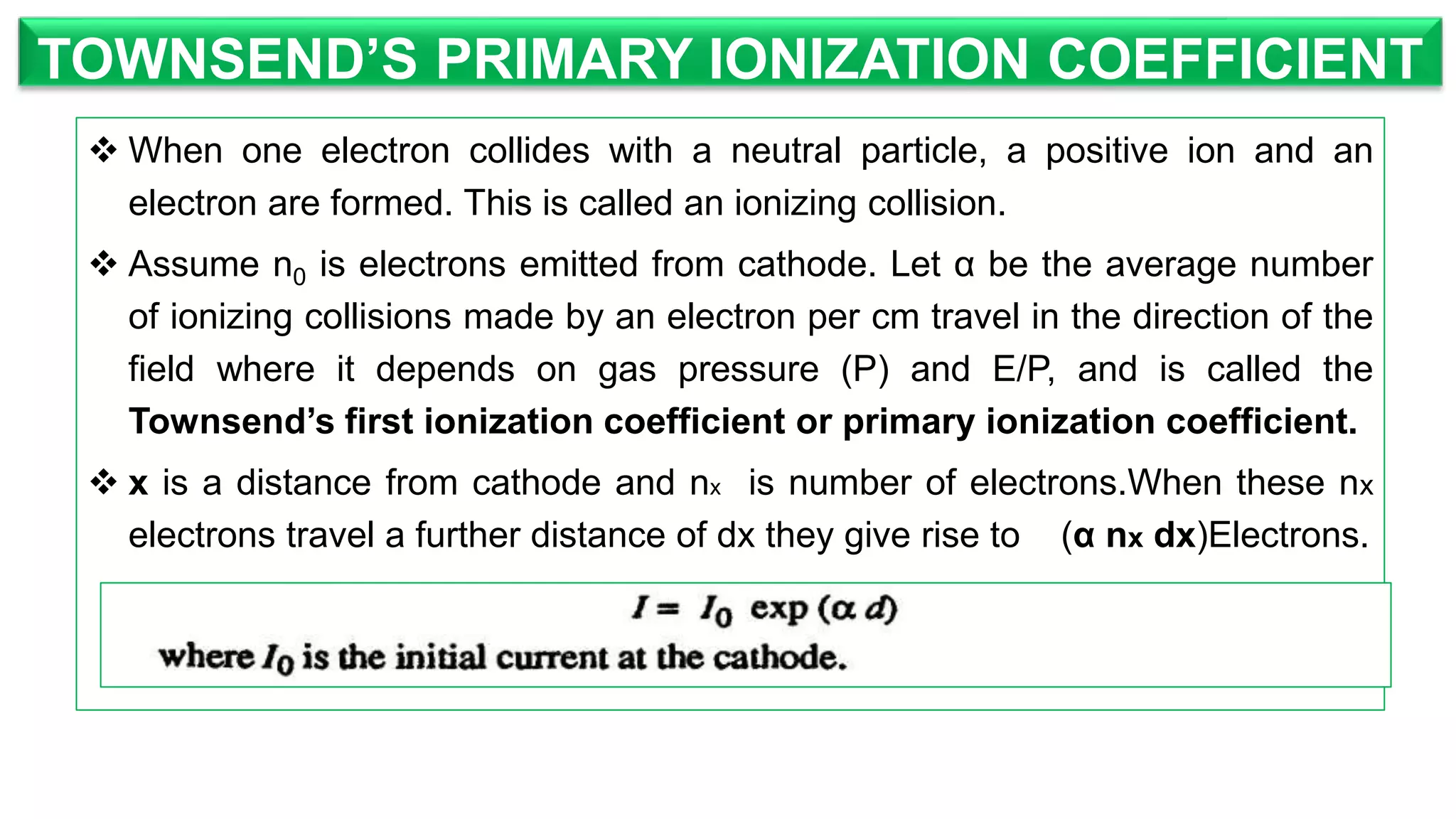
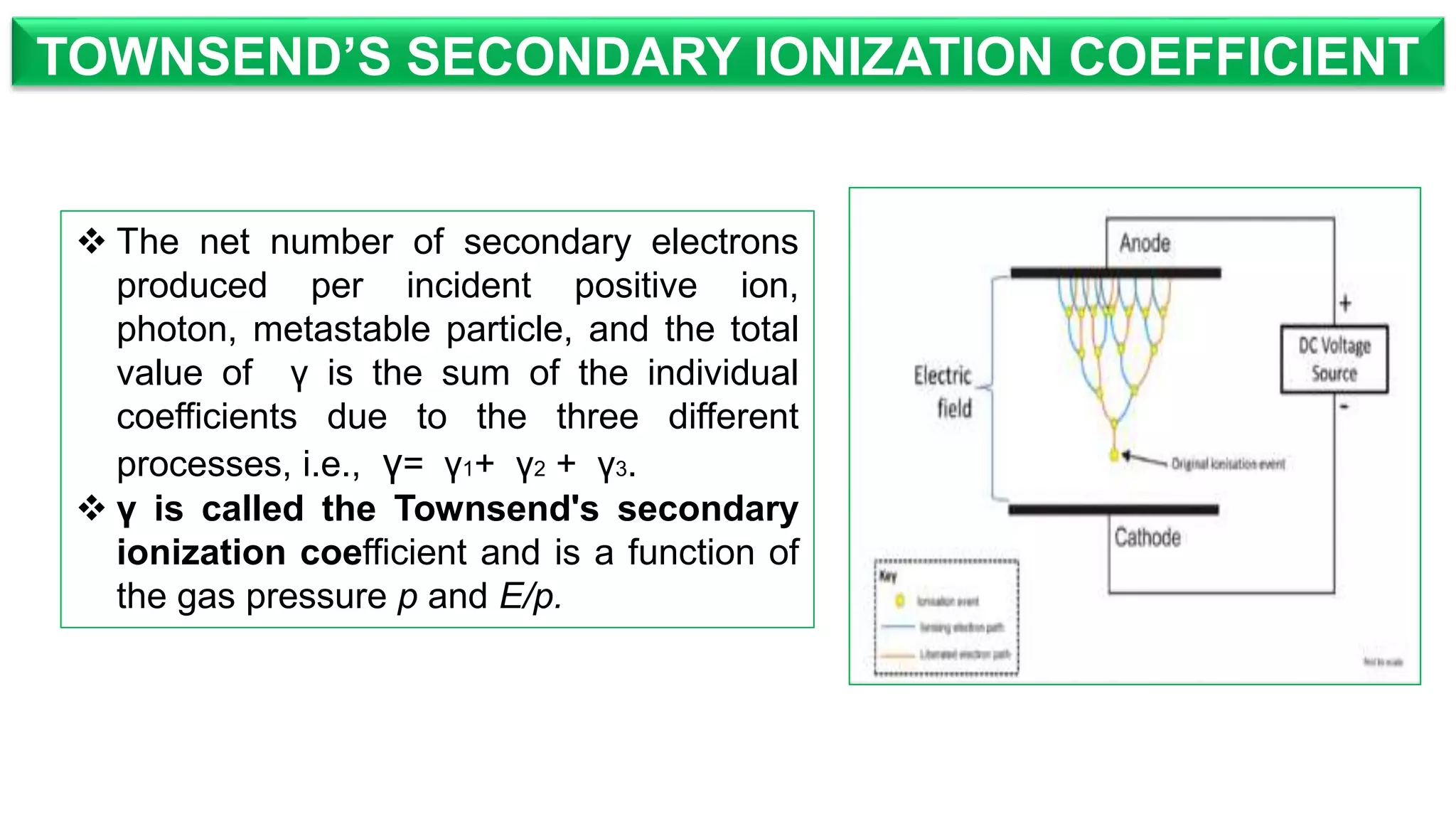

The document discusses high voltage engineering, specifically focusing on Townsend's ionization coefficients related to gas breakdown. It explains ionizing collisions that create positive ions and electrons, and distinguishes between primary (α) and secondary (γ) ionization coefficients, outlining the processes that lead to gas breakdown. Additionally, it highlights the factors affecting these coefficients and their dependence on gas pressure.




