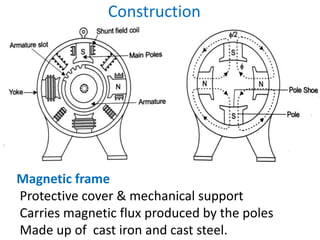
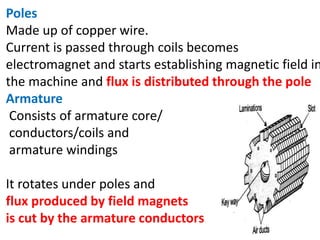
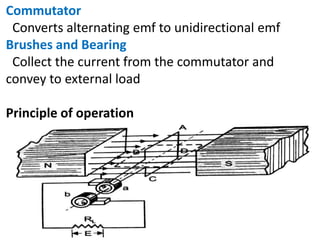
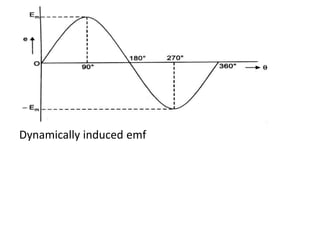
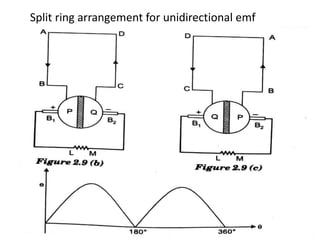
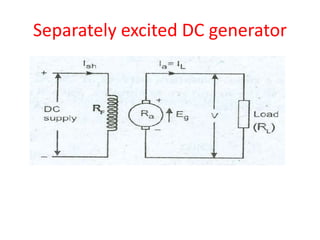
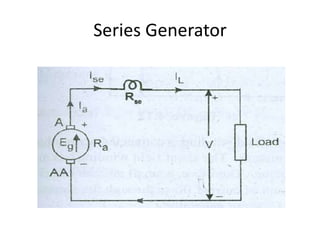
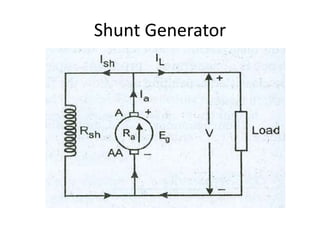
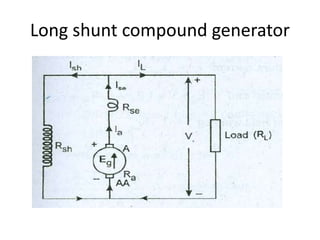
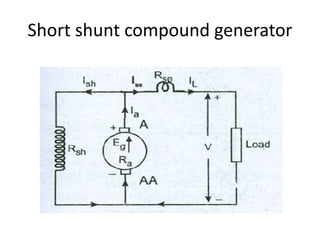
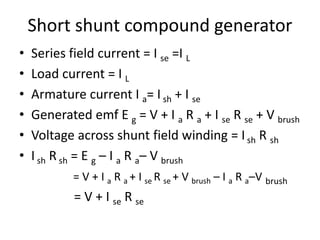
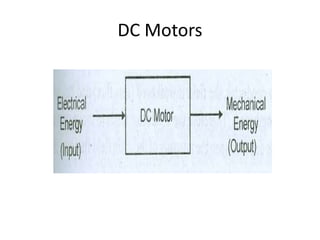
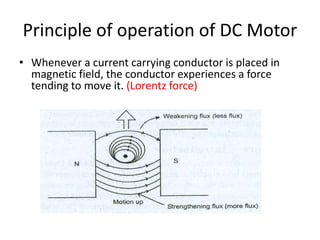
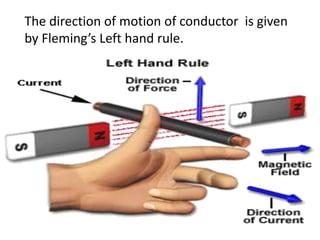
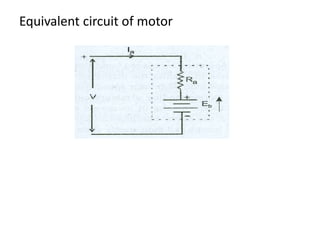
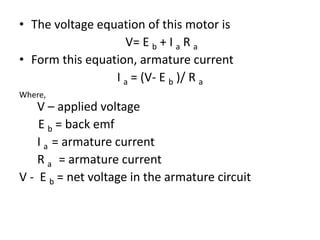
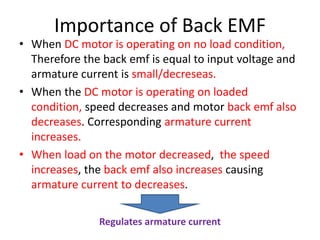
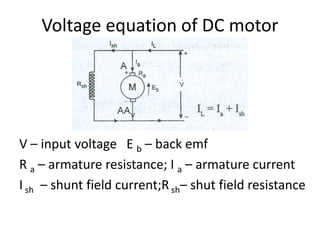
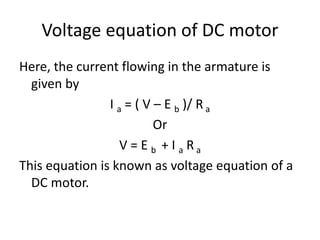
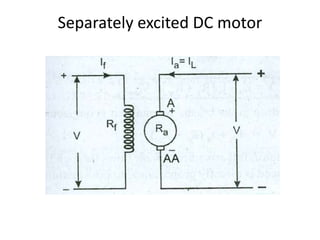
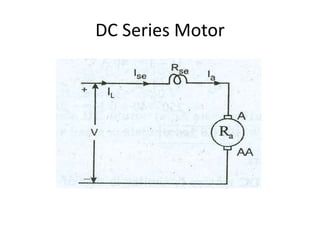
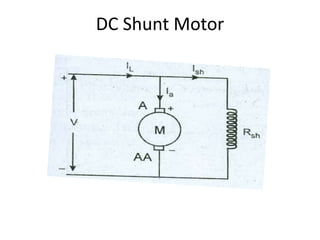
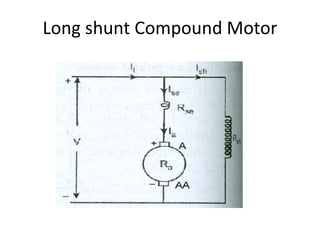
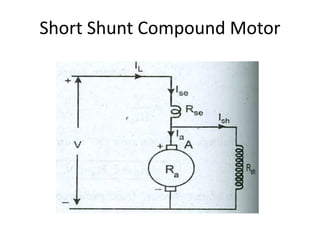
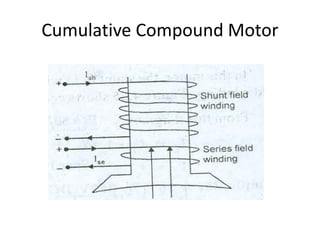
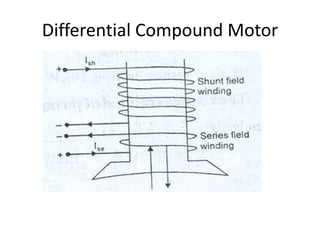
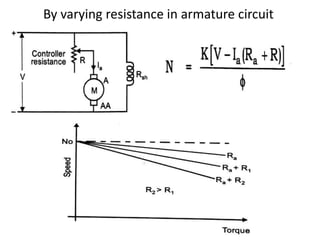
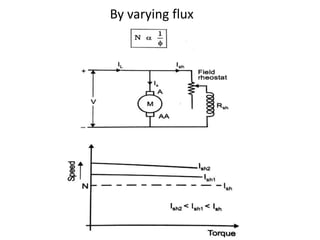
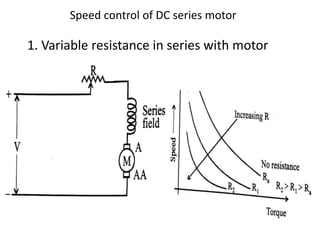
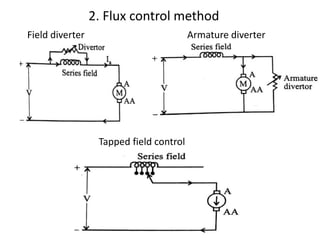
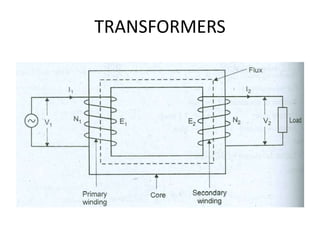
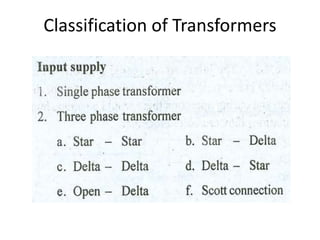
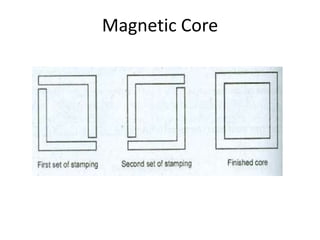
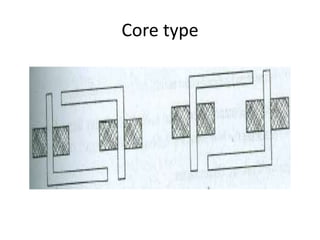
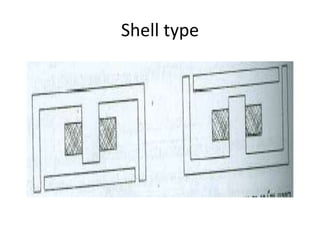
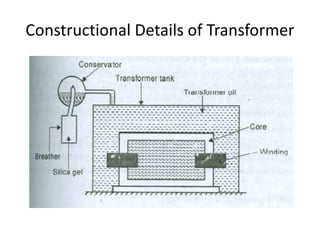
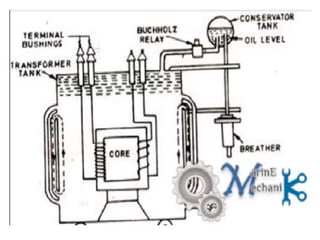
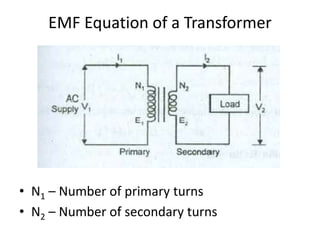
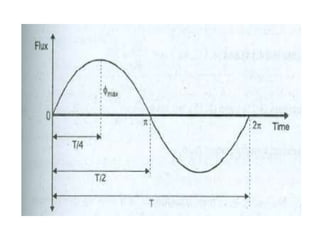
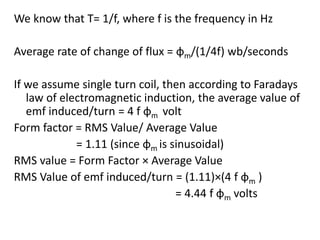
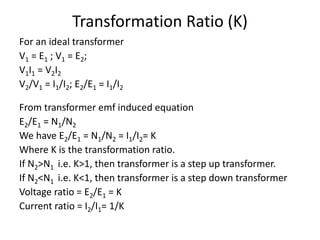
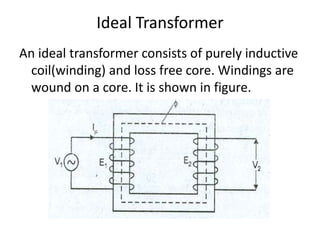
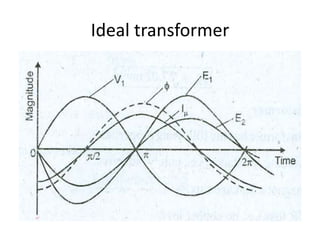
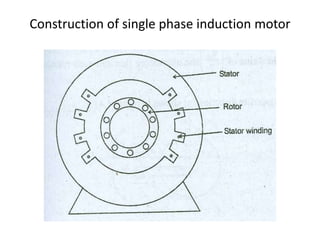
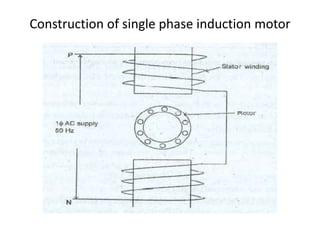
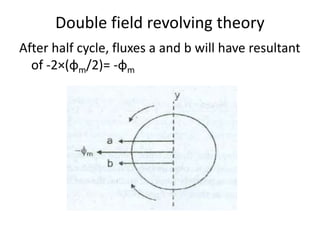
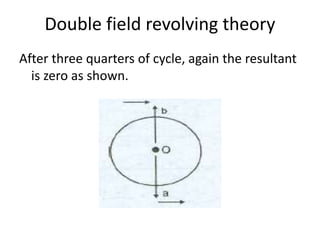
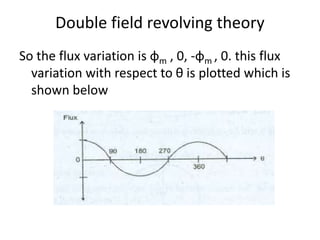
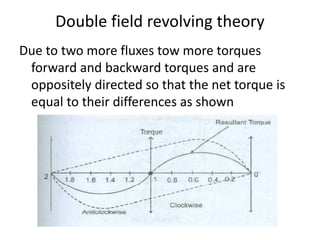
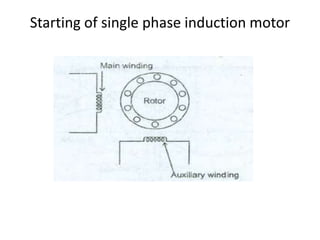
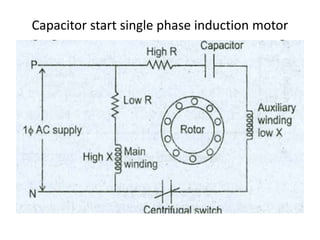
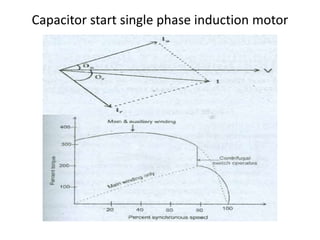
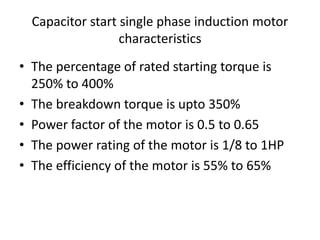
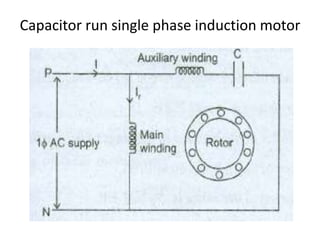
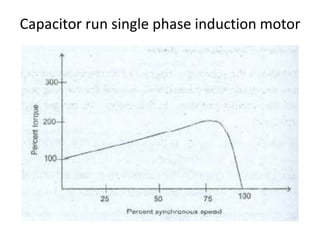
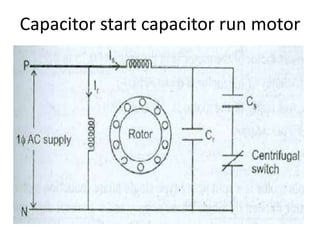
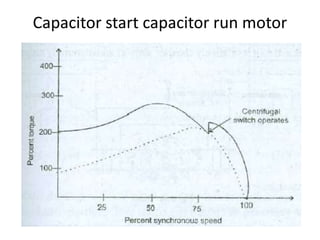
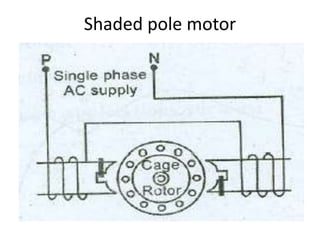
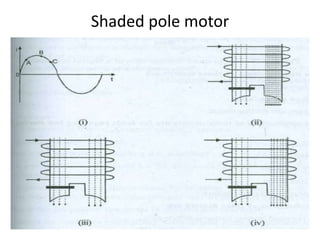
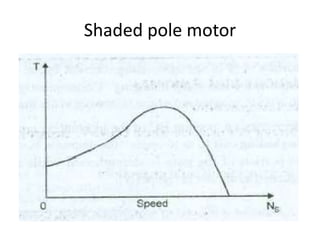
A DC generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction. It consists of a magnetic frame, field poles, an armature, and a commutator. The armature rotates under the poles, cutting the magnetic flux and inducing an EMF. The commutator converts the alternating EMF into a pulsating DC voltage. DC generators are classified as separately excited, self-excited (series, shunt, compound), depending on how the field is connected. A DC motor operates on the principle that a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a torque. It consists of an armature, field poles, a commutator, and brushes. The back EMF opposes the applied voltage