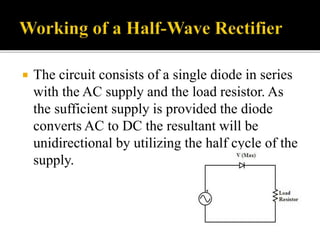
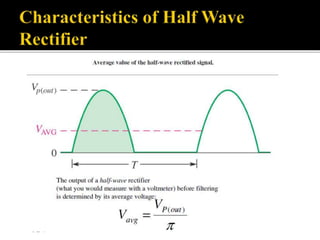
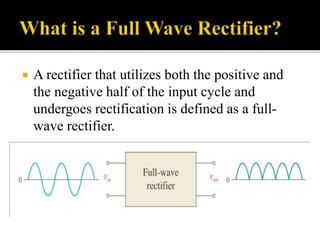
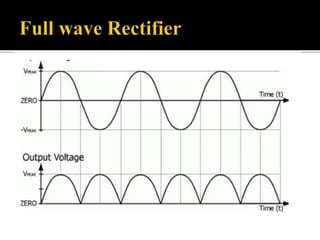
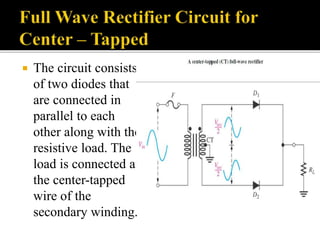
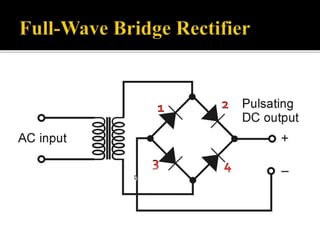
The document explains the principles and components of half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, detailing how each type converts AC to DC. It describes half-wave rectification using a single diode and the resulting pulsating DC output, highlighting efficiency and ripple factors, while also discussing the configurations and advantages of full-wave bridge rectifiers involving four diodes. Overall, it emphasizes the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and applications of these rectifier circuits in power supply systems.