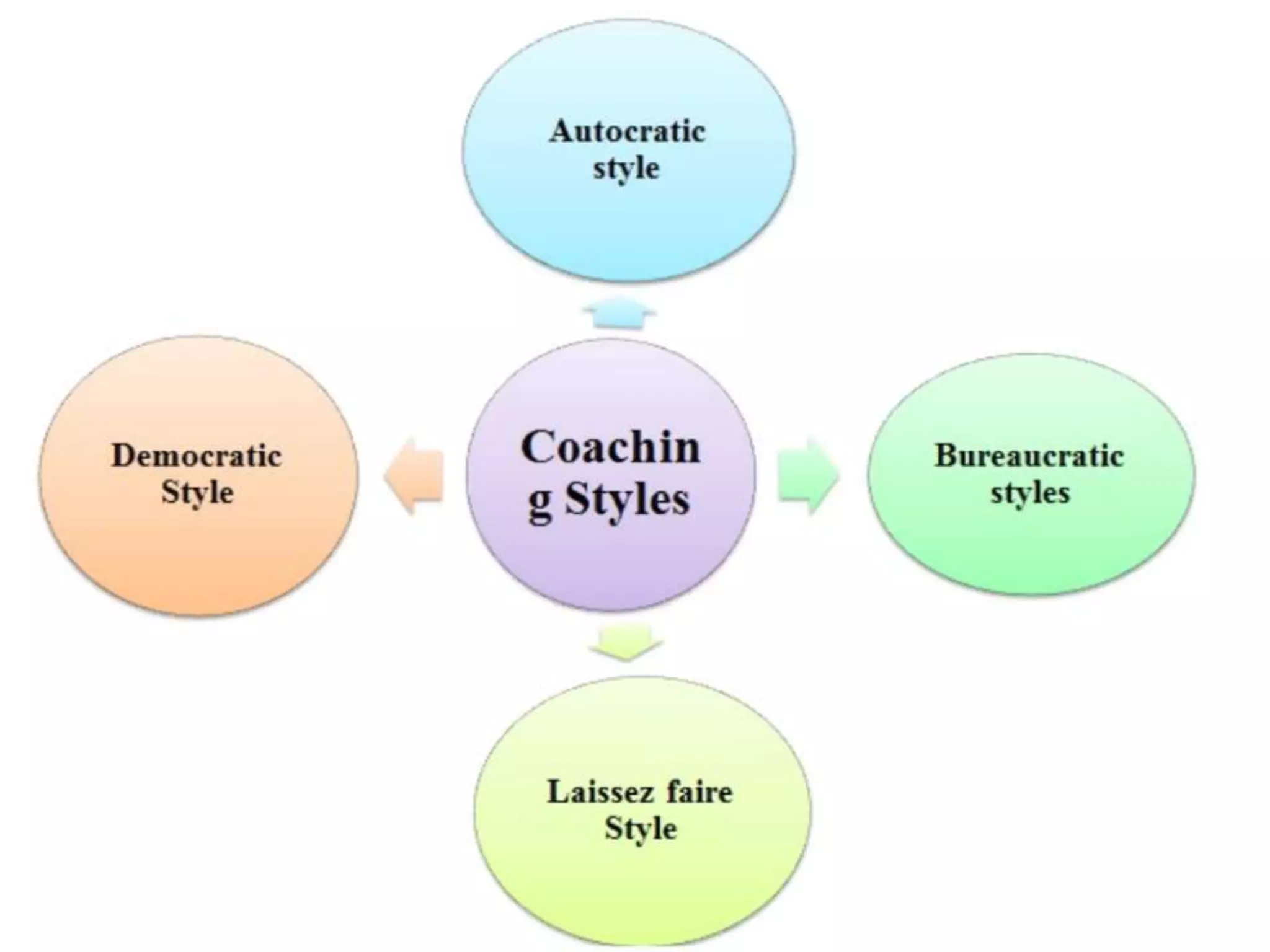
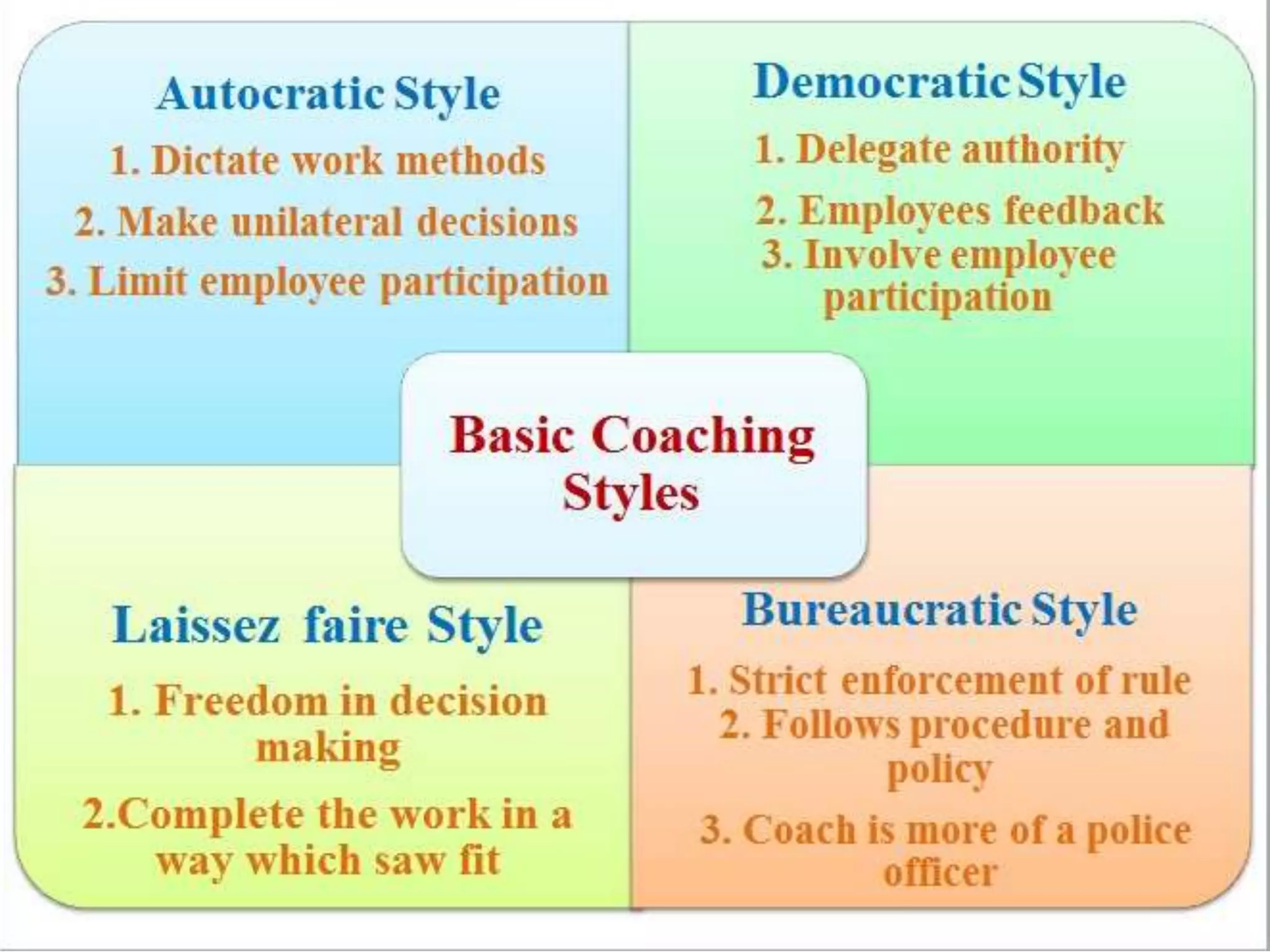
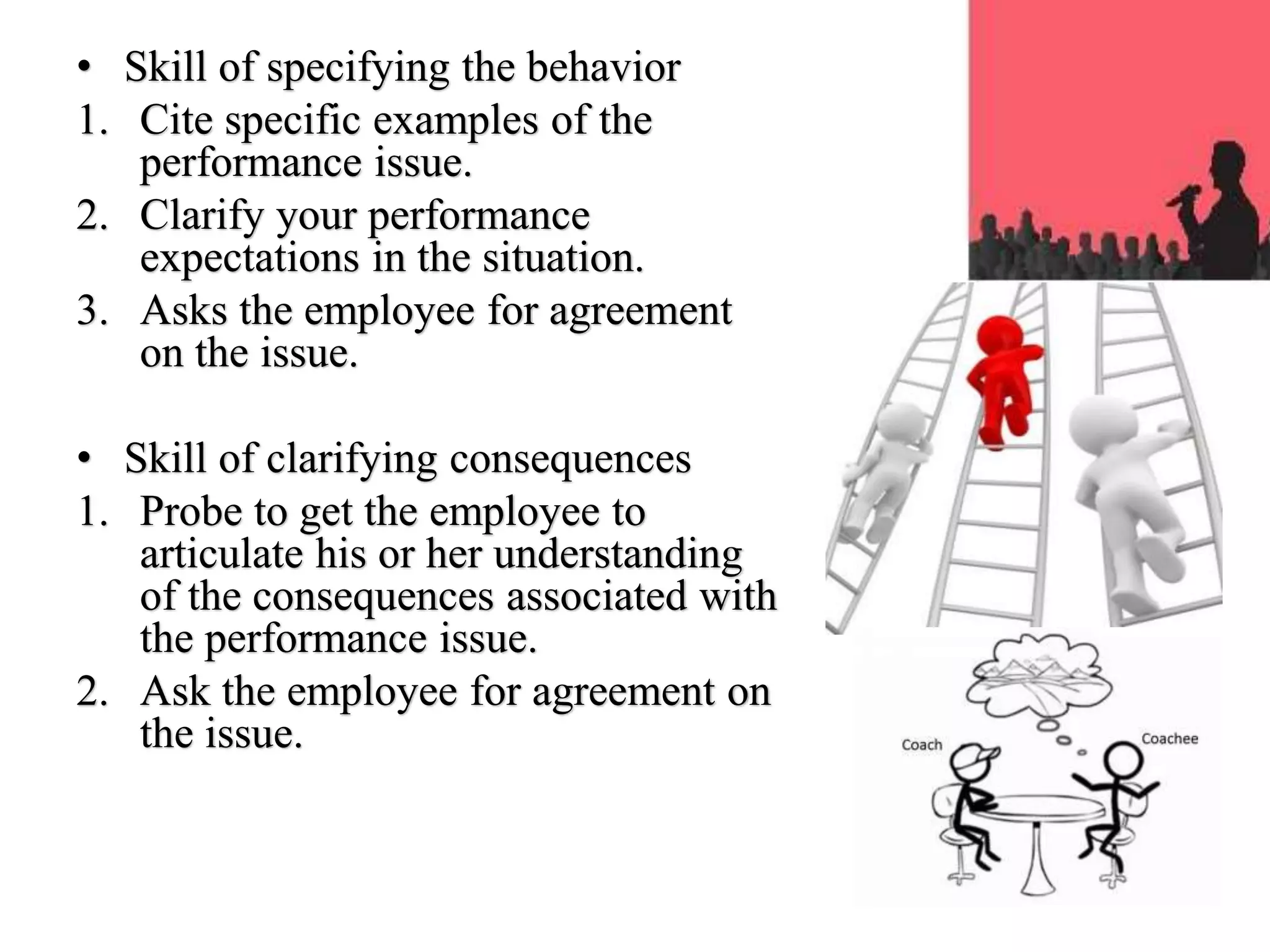
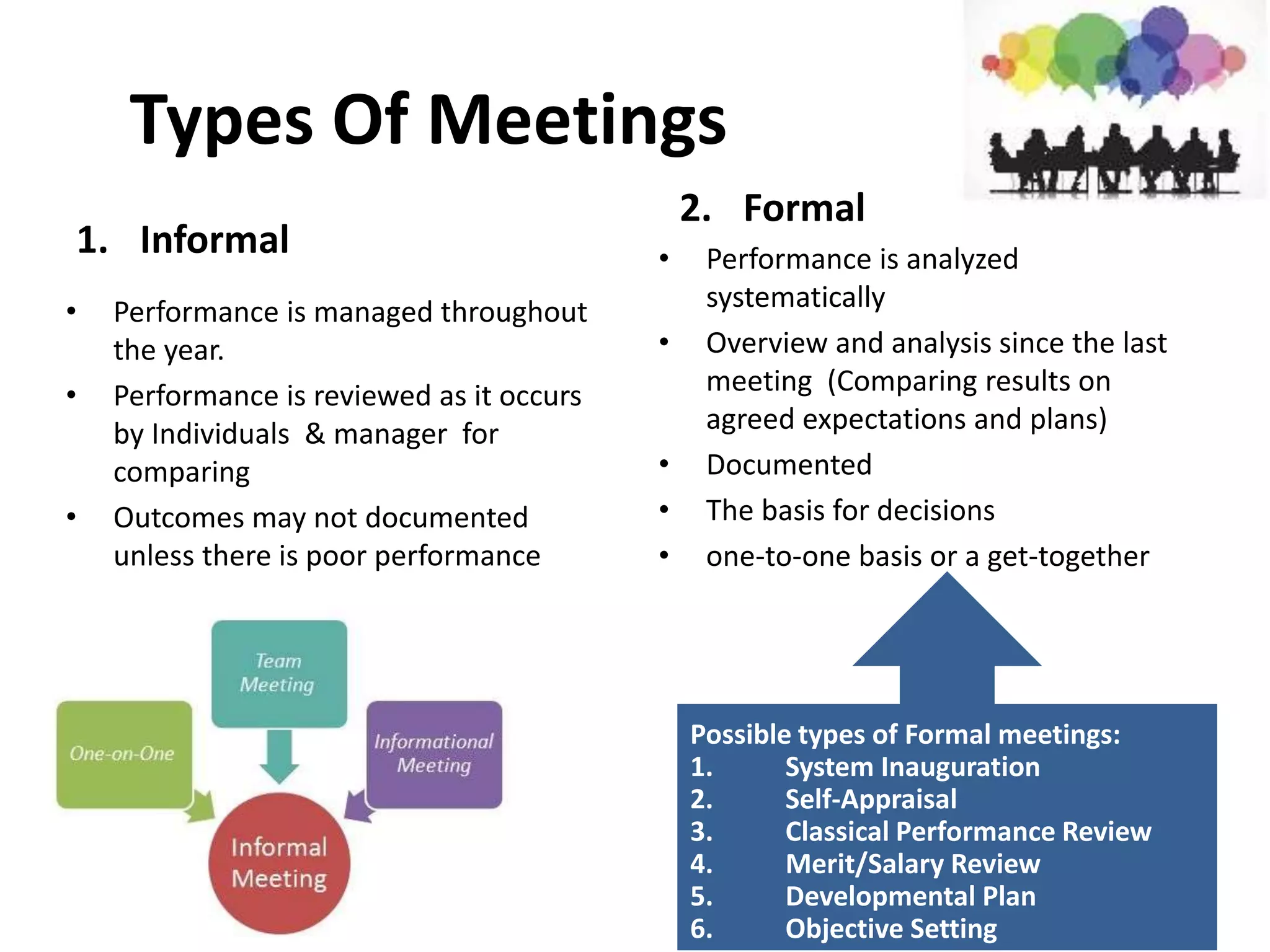
The document discusses important skills for managers, including strategic thinking, time management, communication, problem solving, collaboration, financial skills, and interpersonal skills. It also outlines the coaching process managers should follow, which includes building trust, setting goals, exploring alternatives, getting commitments, and providing feedback. Different types of formal performance review meetings are described, such as for setting objectives, reviewing development plans, and determining merit/salary, and these typically follow sequentially on a quarterly or annual basis.